Non-profit organizations play a vital role in addressing social needs and championing various causes. But what keeps them running efficiently and effectively? The answer lies in their finance structure. Essentially, a non-profit organization’s finance structure refers to the way it manages its financial resources to fulfill its mission and achieve its goals. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of what makes up this financial framework, examining the key components and strategies that ensure the sustainability and success of non-profit organizations. So, whether you’re a budding philanthropist or a passionate advocate, understanding what is a non-profit organization’s finance structure is crucial for making a meaningful impact. Let’s explore!
What is a Non-Profit Organization’s Finance Structure?
Non-profit organizations play a crucial role in society by addressing various social, environmental, and humanitarian issues. To effectively carry out their missions, non-profits need to manage their finances efficiently. In this article, we will delve into the finance structure of non-profit organizations, exploring how they manage their funds, generate revenue, and ensure financial sustainability.
The Importance of Financial Management in Non-Profit Organizations
Effective financial management is essential for the success and sustainability of any non-profit organization. By having a well-defined finance structure in place, non-profits can:
- Ensure transparency and accountability in financial operations
- Make informed decisions based on accurate financial data
- Attract donors by demonstrating sound financial practices
- Allocate resources efficiently to accomplish their mission
- Plan for the long-term financial sustainability of the organization
Types of Non-Profit Organizations
Before diving into the finance structure, it’s important to understand the different types of non-profit organizations, as their financial structures can vary:
1. Public Charities
Public charities are non-profit organizations that receive a significant portion of their funding from the general public or government agencies. They typically have broad missions and serve the community at large. Examples include educational institutions, healthcare organizations, and relief agencies.
2. Private Foundations
Private foundations are non-profit organizations that are usually funded by a single individual, family, or corporation. They distribute funds to other non-profit organizations to carry out specific charitable activities. Private foundations often have a narrower focus and may support causes such as education, research, or arts and culture.
3. Religious Organizations
Religious organizations are non-profit entities that engage in religious activities and provide spiritual guidance to their members. They rely on donations and contributions from their congregations to fund their operations and carry out charitable initiatives.
4. Professional or Trade Associations
Professional or trade associations are non-profit organizations that represent a specific profession, trade, or industry. They serve their members by providing networking opportunities, professional development resources, and advocacy. Funding for these organizations often comes from membership dues, event fees, and sponsorships.
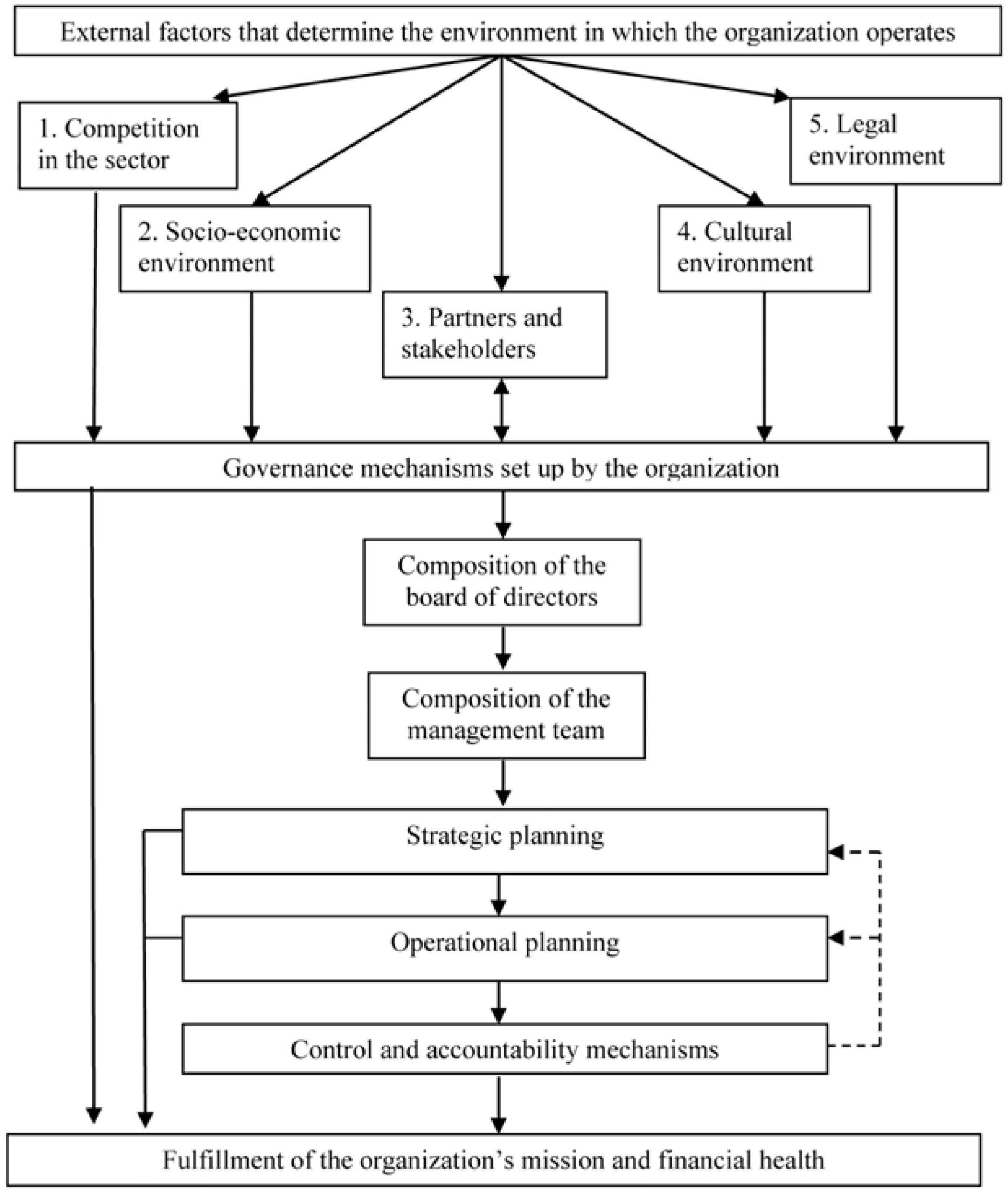
The Financial Structure of Non-Profit Organizations
To understand the finance structure of non-profit organizations, we will explore the key components that make up their financial management system:
1. Budgeting and Financial Planning
Budgeting and financial planning are crucial for non-profit organizations to allocate resources effectively. It involves estimating the organization’s income and expenses for a specific period (typically one year) and creating a detailed budget to guide financial decisions. The budget should align with the organization’s mission and strategic goals.
2. Revenue Sources
Unlike for-profit businesses, non-profit organizations do not aim to generate profits for shareholders. Instead, they rely on various revenue sources to fund their operations and initiatives. Some common revenue sources for non-profits include:
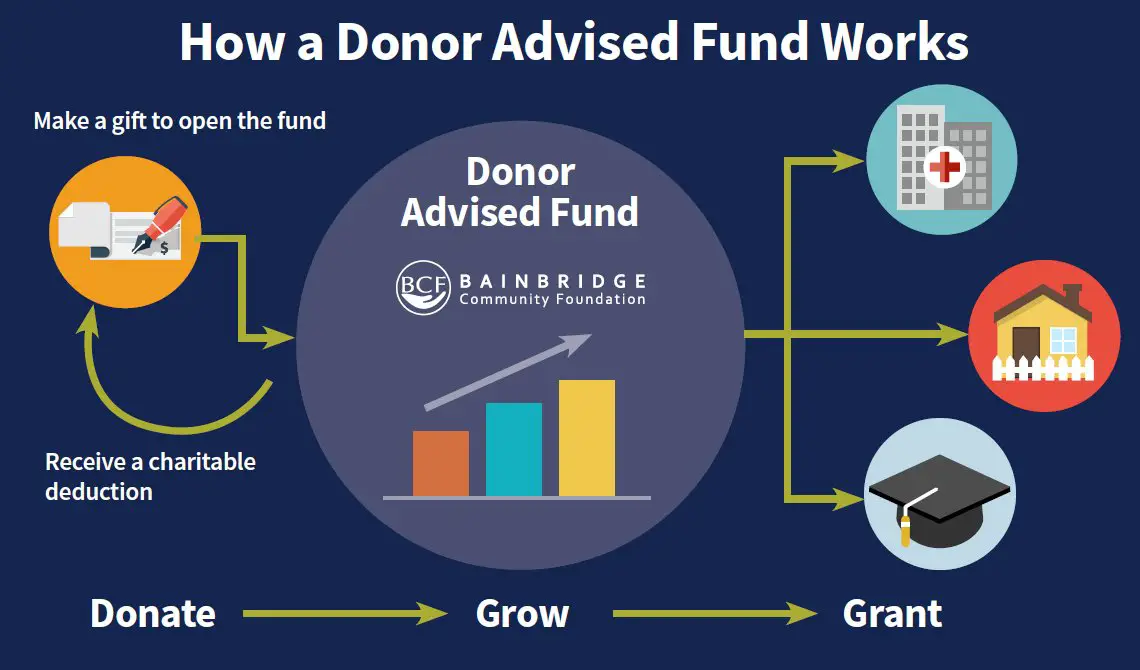
- Donations and Contributions: Non-profits often rely heavily on individual and corporate donations to support their activities. These donations can be one-time or recurring.
- Grants: Non-profit organizations may receive grants from government agencies, foundations, or other organizations that provide funding for specific projects or initiatives.
- Program Fees: Some non-profits charge fees for the services or programs they offer. For example, a non-profit educational institution may charge tuition fees, while a healthcare organization may charge for medical services.
- Membership Dues: Non-profit associations often collect membership dues from their members to fund their operations and member services.
- Fundraising Events: Non-profits may organize fundraising events such as galas, auctions, or charity runs to generate funds for their organizations.
- Investment Income: Non-profits may invest their funds in stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments to generate income.
3. Financial Controls and Governance
Non-profit organizations must have robust financial controls in place to ensure transparency, accountability, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Key financial controls include:
- Separation of Duties: Roles and responsibilities related to financial management should be clearly defined and segregated to prevent any potential conflicts of interest or fraudulent activities.
- Financial Policies and Procedures: Non-profits should establish and document clear financial policies and procedures that govern areas such as budgeting, purchasing, accounting, and reporting.
- Internal and External Audits: Regular internal audits and periodic external audits help verify the accuracy of financial records, identify any irregularities, and maintain the trust of donors and stakeholders.
- Board Oversight: Non-profit organizations are typically governed by a board of directors who have fiduciary responsibility for overseeing the financial affairs of the organization. The board ensures compliance with financial regulations and makes strategic financial decisions.
4. Financial Reporting
Non-profit organizations are required to provide transparent and comprehensive financial reporting to stakeholders, including donors, board members, and government agencies. Financial reports typically include:
- Income Statement: This statement summarizes the organization’s revenue, expenses, and net income or loss over a specific period.
- Balance Sheet: The balance sheet provides an overview of the organization’s assets, liabilities, and net assets (the difference between assets and liabilities).
- Cash Flow Statement: This statement tracks the organization’s cash inflows and outflows, highlighting its ability to generate and manage cash.
- Statement of Functional Expenses: Non-profits often prepare a statement of functional expenses, which categorizes expenses by their function (e.g., program services, administration, fundraising).
- Annual Report: Non-profits may also produce an annual report, which provides a comprehensive overview of the organization’s accomplishments, financial performance, and future plans.
5. Financial Sustainability and Fundraising Strategies
To ensure long-term financial sustainability, non-profit organizations need to develop effective fundraising strategies. These strategies may include:
- Diversifying Revenue Sources: Relying on a single source of funding can pose risks to the financial stability of a non-profit. By diversifying revenue sources, organizations can mitigate these risks.
- Cultivating Donor Relationships: Building strong relationships with individual donors, corporate sponsors, and foundations increases the likelihood of recurring donations and ongoing support.
- Grant Writing: Non-profits often invest time and resources in developing grant proposals to secure funding from government agencies and foundations.
- Major Gift Programs: Implementing major gift programs allows non-profits to target high-net-worth individuals and solicit large donations.
- Planned Giving: Encouraging donors to include the non-profit organization in their estate plans or make long-term financial commitments can provide a reliable source of funding.
By implementing these strategies and maintaining financial sustainability, non-profit organizations can continue to make a meaningful impact in their communities and the world at large.
Remember, effective financial management is crucial for the success of any non-profit organization. By understanding the finance structure and implementing sound financial practices, non-profits can maximize their impact and ensure their long-term viability.
What's the Profit in Nonprofits? | Areva Martin | TEDxCrenshaw
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the financial structure of a non-profit organization?
Non-profit organizations typically have a diverse financial structure that includes various sources of revenue and expenses. These organizations rely on donations, grants, fundraising events, membership fees, and program service fees to generate income. Their expenses may include staff salaries, program costs, administrative expenses, and fundraising expenses.
How are non-profit organizations funded?
Non-profit organizations are typically funded through a combination of sources such as individual and corporate donations, government grants, foundation grants, sponsorships, and fundraising events. These funding sources enable non-profits to support their programs, services, and operational costs.
What is the role of donations in a non-profit organization’s finance structure?
Donations play a crucial role in the finance structure of non-profit organizations. Individuals, corporations, and philanthropic foundations provide financial support through cash donations, in-kind contributions, and planned giving. These donations help fund various programs and projects undertaken by non-profits.
How do non-profit organizations manage their expenses?
Non-profit organizations manage their expenses by creating budgets that allocate funds to different areas of operation. They prioritize their spending based on the organization’s mission and objectives. Monitoring expenses, implementing cost-saving measures, and ensuring transparency in financial transactions are other ways non-profits manage their expenses.
Do non-profit organizations pay taxes?
Non-profit organizations, if recognized as tax-exempt by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) under section 501(c)(3) of the tax code, are exempt from federal income taxes. However, they may still be subject to certain state and local taxes, such as sales tax or property tax, depending on the jurisdiction.
Why is financial transparency important for non-profit organizations?
Financial transparency is crucial for non-profit organizations as it helps build trust with donors, stakeholders, and the public. By being transparent about their financial activities, non-profits demonstrate accountability, credibility, and responsible stewardship of funds. This transparency also assists potential donors in making informed decisions about supporting the organization.
What is the role of financial reporting in non-profit organizations?
Financial reporting in non-profit organizations involves the preparation and presentation of financial statements, such as the statement of financial position, statement of activities, and cash flow statement. These reports provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health, activities, and use of funds. Financial reporting helps stakeholders evaluate the organization’s performance and make informed decisions.
How can non-profit organizations ensure financial sustainability?
Non-profit organizations can ensure financial sustainability by diversifying their funding sources, building long-term relationships with donors, implementing effective fundraising strategies, and developing sustainable revenue-generating programs. They should also adopt sound financial management practices, regularly review and adjust budgets, and invest in building strong financial reserves for future stability.
Final Thoughts
Non-profit organizations have unique finance structures that are designed to support their mission-driven objectives. These structures typically include multiple sources of funding, such as donations, grants, and fundraising events. Monetary resources are allocated to various areas, such as program development, administrative costs, and marketing efforts. Additionally, financial statements and reports play a crucial role in providing transparency to stakeholders and ensuring accountability. By effectively managing their finances, non-profit organizations can sustain their operations and make a positive impact in their respective communities. Understanding the intricacies of what is a non-profit organization’s finance structure is essential for successful and sustainable operations.