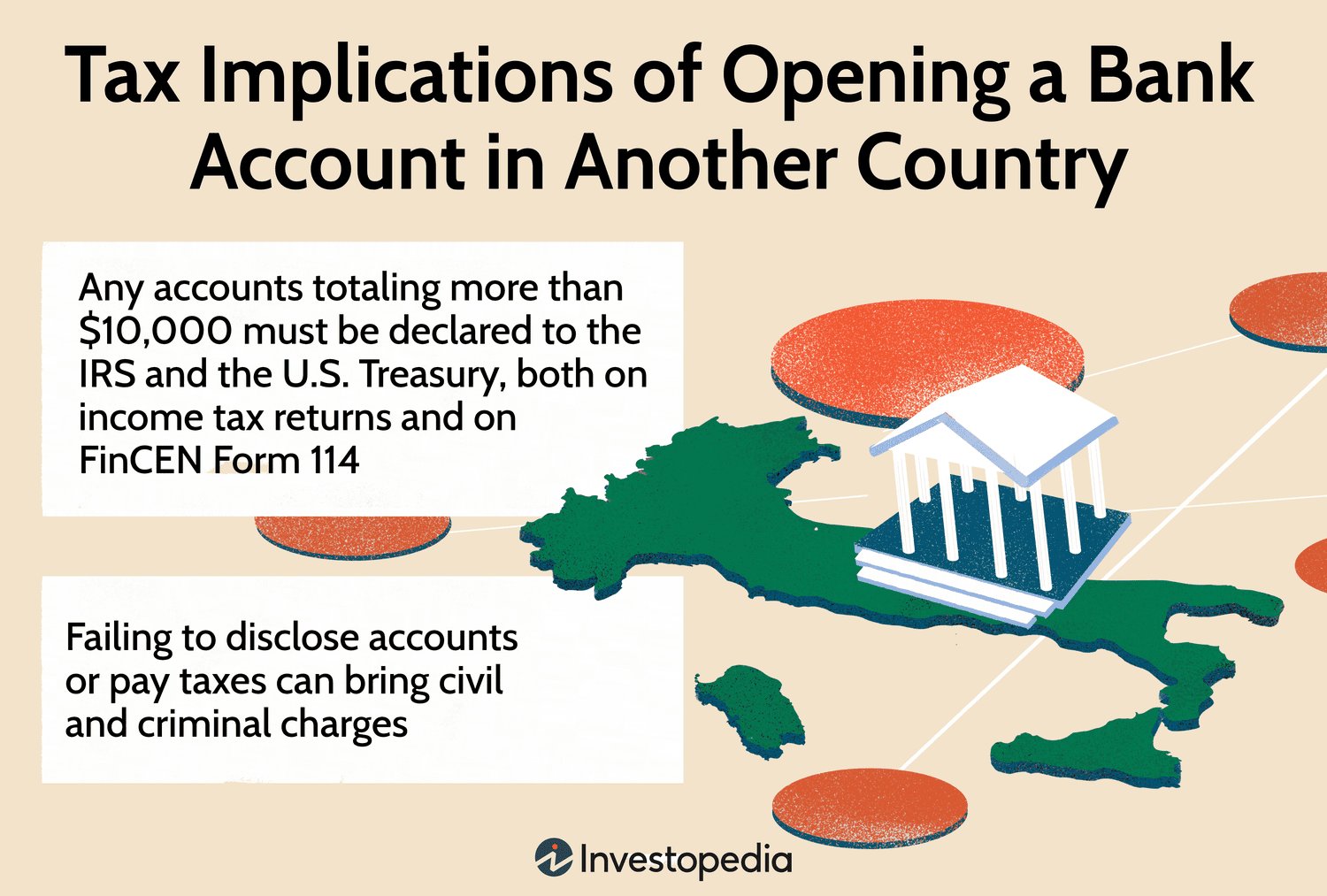
Understanding the tax implications of foreign income can be a complex and overwhelming subject. However, we are here to guide you through it. With so many individuals and businesses now operating globally, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of how foreign income may be taxed and what implications it can have on your financial situation. In this article, we will break down the key concepts, provide practical examples, and offer helpful tips to ensure you navigate this topic with confidence. So, let’s delve into the world of understanding tax implications of foreign income together and unravel its intricacies.
understanding tax implications of foreign income
Foreign income refers to any income that is earned from sources outside of an individual’s home country. With global mobility on the rise, more and more people are earning income from foreign sources such as investments, business ventures, or employment opportunities abroad. However, it is important to understand the tax implications that come with earning foreign income, as failing to comply with the tax laws of both the home country and the foreign country can lead to penalties, fines, or even legal consequences. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of understanding tax implications of foreign income, covering various subtopics such as tax residency, double taxation, tax treaties, and reporting requirements. So let’s dive right in!
Tax Residency
Before delving into the tax implications of foreign income, it is crucial to determine one’s tax residency status in both the home country and the foreign country. Tax residency is generally determined by the length of time an individual spends in a particular country and other factors such as the purpose of stay, ties to the country, and the individual’s permanent home.
Home Country Tax Residency
In most countries, individuals are considered tax residents if they spend a significant amount of time within the country or have a permanent home there. The specific criteria for tax residency can vary from one country to another, so it is important to consult the tax laws and regulations of the home country to determine one’s tax residency status.
If an individual is considered a tax resident in their home country, they are generally subject to taxation on their worldwide income, including income earned from foreign sources. This means that even if you earn income abroad, you may still be required to report and pay taxes on that income in your home country.
Foreign Country Tax Residency
Similarly, the foreign country where an individual earns income may also consider them as tax residents if they meet certain criteria. This can vary depending on the laws and regulations of the foreign country. Being considered a tax resident in a foreign country can have significant implications on the individual’s tax obligations, as they may be subject to taxation on their income earned within that country.
Double Taxation
One of the major concerns for individuals earning foreign income is the possibility of double taxation. Double taxation occurs when an individual is required to pay taxes on the same income in both their home country and the foreign country where the income was earned. This can significantly reduce the income available to the taxpayer and create an unfair burden.
To avoid or minimize double taxation, many countries have entered into bilateral or multilateral tax treaties with each other. These tax treaties aim to provide relief to taxpayers by specifying rules that allocate taxing rights between the two countries and provide mechanisms for the avoidance of double taxation.
Bilateral and Multilateral Tax Treaties
Bilateral tax treaties are agreements between two countries, while multilateral tax treaties involve more than two countries. These treaties generally address issues like the definition of permanent establishment, taxation of business profits, dividends, interest, royalties, and capital gains. They also establish procedures for resolving any disputes that may arise between the two countries.
The presence of a tax treaty between the home country and the foreign country can help determine which country has the primary right to tax specific types of income. This can prevent the occurrence of double taxation or provide mechanisms for claiming tax credits or exemptions to offset any tax paid in the foreign country.
Reporting Requirements
When earning foreign income, it is important to comply with the reporting requirements of both the home country and the foreign country. Failure to report foreign income can result in penalties, fines, or even criminal charges.
Home Country Reporting
Most countries require their tax residents to report their worldwide income, regardless of where it was earned. This means that if you earn income from foreign sources, you must report it on your tax return in your home country. The specific forms and reporting requirements vary from country to country, so it is essential to familiarize yourself with the rules and regulations of your home country.
In some cases, your home country may also require you to disclose information about your foreign bank accounts or foreign assets. This is typically done through Foreign Bank Account Reports (FBAR) or similar reporting mechanisms. Failing to disclose foreign assets or accounts can result in significant penalties.
Foreign Country Reporting
Additionally, the foreign country where you earn income may also require you to report and pay taxes on that income. It is essential to understand the specific reporting requirements of the foreign country to ensure compliance. This may involve filing tax returns, disclosing foreign assets, or adhering to any other reporting obligations set forth by the foreign country’s tax authorities.
Tax Planning and Professional Assistance
Given the complexity of understanding tax implications of foreign income, it is wise to seek professional assistance to navigate through the process. Tax planning becomes crucial in ensuring that you optimize your tax obligations and comply with the laws of both your home country and the foreign country.
Engaging a Tax Professional
A tax professional who is knowledgeable in international tax matters can provide valuable guidance specific to your situation. They can help you determine your tax residency, understand the tax treaties between the countries involved, assist with the completion of tax forms, and ensure compliance with reporting requirements. Engaging a tax professional can help alleviate the stress of navigating the complexities of international taxation and ensure that you make the most informed decisions.
Tax Planning Strategies
Tax planning strategies can also be employed to minimize your tax liabilities. These strategies may include:
- Utilizing tax-efficient investment vehicles
- Structuring your business operations in a tax-advantageous manner
- Maximizing available deductions and credits
- Optimizing the timing of repatriation of income
However, it is important to note that tax planning should always be conducted within the bounds of the law and should not involve any illegal or unethical activities. Engaging in tax evasion can have severe consequences, both financially and legally.
In conclusion, understanding the tax implications of foreign income is essential for anyone earning income from foreign sources. Tax residency, double taxation, tax treaties, and reporting requirements are key aspects to consider when navigating the complexities of international taxation. Seeking professional assistance and engaging in tax planning can help you optimize your tax obligations and ensure compliance with the tax laws of both your home country and the foreign country. By understanding and fulfilling your tax obligations, you can ensure a smooth and hassle-free experience when earning income from foreign sources.
Important IRS Tax Tips for Reporting Foreign Income and Activities
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the tax implications of foreign income?
Foreign income is subject to taxation in most countries, including the United States. As a taxpayer, you need to understand the tax implications of earning income abroad to ensure compliance with relevant tax laws and avoid penalties.
How is foreign income taxed?
The taxation of foreign income depends on several factors, such as your residency status, the country where the income was earned, and any applicable tax treaties between countries. Generally, you may be required to report and pay taxes on your foreign income, either in your home country or the country where the income was earned.
Do I need to report all my foreign income?
Yes, as a general rule, you are required to report all your worldwide income, including foreign income, on your tax return. Failure to do so can result in penalties and potential legal consequences. Make sure to consult with a tax advisor or refer to official tax guidelines for accurate reporting.
Are there any exceptions or exclusions for foreign income?
Yes, some taxpayers may qualify for certain exclusions or deductions for their foreign income. For example, the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) allows qualifying individuals to exclude a certain amount of their foreign earned income from U.S. federal taxes. Similarly, tax treaties between countries can provide specific exemptions or reduced tax rates.
How do I determine my residency status for tax purposes?
Your residency status for tax purposes is determined by different criteria, including the number of days you spend in a particular country, your immigration status, and your intentions regarding the length and purpose of your stay. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional or refer to the tax laws of the specific country to determine your residency status accurately.
What are the potential penalties for not reporting foreign income?
Failing to report your foreign income can result in various penalties, such as monetary fines, interest charges on unpaid taxes, and even criminal charges in severe cases. It is crucial to understand and comply with the tax reporting requirements to avoid such penalties.
Are there any tax planning strategies to minimize the tax burden on foreign income?
Yes, there are several tax planning strategies you can employ to legally minimize your tax burden on foreign income. These may include taking advantage of tax treaties, structuring your investments or business operations tax-efficiently, utilizing applicable exclusions and deductions, and consulting with a tax professional to optimize your tax position.
Can I claim a tax credit for foreign taxes paid?
In many cases, you may be eligible to claim a tax credit or deduction for foreign taxes paid on your foreign income. The purpose of this credit is to avoid double taxation, allowing you to offset the taxes paid to the foreign country against your home country’s tax liability. The eligibility criteria and procedures for claiming the foreign tax credit vary by jurisdiction, so it is recommended to consult with a tax advisor.
Final Thoughts
Understanding tax implications of foreign income is crucial for individuals and businesses engaging in global transactions. It is essential to ensure compliance with tax regulations and maximize financial benefits. By comprehending the tax requirements related to foreign income, one can avoid potential penalties and legal issues. Consulting with tax professionals or experts in international tax law can provide valuable guidance in navigating the complexities of cross-border taxation. Stay informed about the latest updates and changes in tax laws to make informed decisions and optimize your financial strategies. Understanding tax implications of foreign income is a key aspect of successful global financial management.