A defined benefit pension plan is one of the key components of a comprehensive retirement package. It offers employees a specific monthly benefit during their retirement years, based on a set formula that typically considers their years of service and salary history. So, what exactly is a defined benefit pension plan? It is a retirement plan that provides a guaranteed income stream, ensuring that employees can maintain their standard of living once they retire. In this blog article, we will delve deeper into the details of this type of pension plan, its benefits, and how it differs from other retirement options. So, let’s get started!
What is a Defined Benefit Pension Plan?
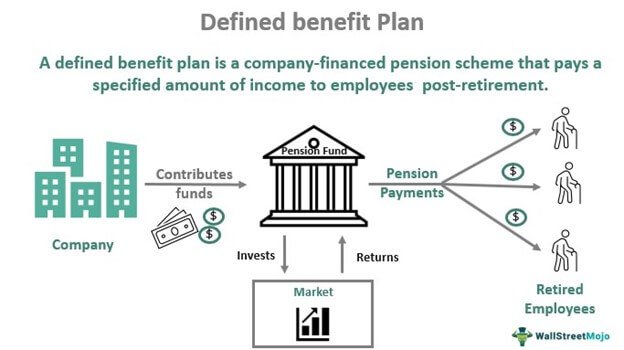
A defined benefit pension plan is a type of retirement plan that provides a specified monthly benefit to retirees based on a formula that takes into account factors such as salary history, years of service, and age. Unlike defined contribution plans, where the retirement benefit is dependent on the contributions made and investment returns, defined benefit plans offer a guaranteed retirement income, often for life.
Defined benefit pension plans are typically offered by employers as a form of employee benefit. These plans aim to provide employees with a secure and stable source of income during their retirement years. The employer, in collaboration with pension administrators and actuaries, establishes the plan’s structure, funding requirements, and benefit calculations.
How Does a Defined Benefit Pension Plan Work?
Let’s delve deeper into how a defined benefit pension plan operates:
1.
Eligibility and Participation
– Employees become eligible to participate in a defined benefit pension plan after completing a certain period of service, such as one year of employment.
– The plan may have specific requirements regarding age and years of service needed to qualify for full benefits or early retirement.
– Once eligible, employees typically become participants in the plan and begin accruing benefits based on their earnings and service.
2.
Benefit Calculation
– The formula used to calculate the retirement benefit varies from plan to plan.
– Common elements considered in the calculation include the employee’s years of service, average salary, and a benefit accrual rate (often expressed as a percentage of salary).
– For example, a defined benefit plan might offer a benefit equal to 1.5% of the average of the employee’s highest five years of salary for each year of service.
– The benefit accrual rate may increase with additional years of service, incentivizing long-term employment.
– Some plans use a career average salary rather than the highest years to determine the benefit.
3.
Funding
– Employers are responsible for funding defined benefit pension plans.
– They contribute to a pension fund, which is invested to generate returns and ensure sufficient assets are available to meet future benefit obligations.
– The employer’s contributions are determined based on actuarial calculations that consider factors such as the plan’s funding target, expected investment returns, and participant demographics.
– Employers bear the investment risk and are obligated to make up any funding shortfalls if the plan’s assets underperform.
4.
Vesting and Retirement
– Vesting refers to an employee’s right to receive the accrued benefits from a pension plan.
– Plans can have different vesting schedules, such as a cliff vesting where employees become fully vested after a specific number of years.
– Once vested, employees are eligible to receive their pension benefits upon retirement, subject to the plan’s rules.
– Retirement age and options may vary, but many plans offer early retirement options with reduced benefits for those who want to retire before reaching normal retirement age.
– Retirees receive regular payments, which can be monthly or annually, based on the predetermined formula.
5.
Protection and Regulation
– Defined benefit pension plans are subject to various legal and regulatory requirements to protect employees’ retirement benefits.
– Government oversight and regulations aim to ensure the plans are adequately funded and that employers meet their obligations.
– Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC) in the United States is a government agency that provides limited protection by guaranteeing benefits within certain limits if a plan terminates without sufficient funds.
– Employers must comply with reporting and disclosure requirements, including providing participants with periodic benefit statements and plan summaries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Defined Benefit Pension Plans
As with any retirement plan, defined benefit pension plans have their advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore them:
1.
Advantages
– Guaranteed Income: Defined benefit plans provide a predictable and stable income stream during retirement, often for life.
– Employer Responsibility: Employers bear the investment risk and are responsible for funding the plan adequately, alleviating some financial burdens for employees.
– Long-Term Security: Participants can rely on the plan’s longevity and the employer’s commitment to provide income, reducing uncertainty in retirement planning.
– Pension Protections: Governments may provide regulatory oversight and limited protection through agencies like the PBGC.
2.
Disadvantages
– Reduced Flexibility: Participants have limited control over their pension funds and the timing of payments.
– Lack of Portability: If employees leave the company before becoming vested, they may forfeit the right to receive pension benefits.
– Employer Dependency: The ultimate security of the pension benefit relies on the financial health and continued existence of the employer.
– Limited Inflation Protection: Some plans may not offer full protection against inflation, resulting in decreasing purchasing power over time.
In summary, a defined benefit pension plan is a retirement plan that provides employees with a specified monthly benefit based on factors like salary history, years of service, and age. These plans offer the advantage of a guaranteed income stream during retirement, but they come with reduced flexibility and employer dependency. Understanding how defined benefit pension plans work can help individuals make informed decisions about their retirement savings and income strategies.
What Are Defined Contribution and Defined Benefit Pension Plans?
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a defined benefit pension plan?
A defined benefit pension plan is a retirement plan that guarantees a specific payout amount to employees based on a formula that considers factors like years of service, age, and salary history. This type of plan is also known as a traditional or final salary pension plan.
How does a defined benefit pension plan work?
In a defined benefit pension plan, the employer is responsible for funding the plan and assumes the investment risk. The plan calculates the eventual pension payout based on predetermined factors and guarantees a specific amount for the employee after retirement, usually on a monthly basis.
What are the advantages of a defined benefit pension plan?
One of the key advantages of a defined benefit pension plan is the guaranteed income stream it provides during retirement. The payout is usually based on the employee’s salary history and is not impacted by investment performance or fluctuations in the financial markets.
Who contributes to a defined benefit pension plan?
In most cases, the employer is primarily responsible for contributing to a defined benefit pension plan. However, employees may also be required to make contributions, although the employer’s contributions typically outweigh those of the employees.
Can I withdraw my money from a defined benefit pension plan?
Unlike other retirement plans, such as defined contribution plans like 401(k)s, employees usually cannot withdraw their funds from a defined benefit pension plan as a lump sum. The plan is designed to provide a regular stream of income during retirement rather than a one-time payout.
What happens to my defined benefit pension plan if I change jobs?
If you change jobs before reaching retirement age, your defined benefit pension plan may allow you to receive a portion of the accrued benefits based on the time you spent with the employer. However, the specific rules and options may vary depending on the plan and your employment terms.
Is my defined benefit pension plan protected if my employer goes bankrupt?
In many countries, there are provisions or government programs in place to protect employees’ defined benefit pension plans in the event of their employer’s bankruptcy. These protections help ensure that the pension benefits are not entirely lost, although the details may vary based on jurisdiction and specific circumstances.
How is the payout amount determined in a defined benefit pension plan?
The payout amount in a defined benefit pension plan is typically calculated using a formula that considers various factors such as the employee’s years of service, final average salary, and a predetermined accrual rate. These factors are used to determine the monthly pension amount the employee will receive after retirement.
Final Thoughts
A defined benefit pension plan is a retirement plan where the employer guarantees a specific benefit payout to employees upon retirement. This payout is typically based on factors such as salary history and years of service. With a defined benefit pension plan, the responsibility of investment performance and risk lies with the employer, allowing employees to have a predictable income stream during retirement. This type of plan offers financial security and stability for retirees, as they can rely on a predetermined amount of income throughout their retirement years. Overall, a defined benefit pension plan provides a valuable retirement benefit to employees, ensuring their financial well-being in their later years.