If you’ve ever wondered how interest rates affect your mortgage, you’re not alone. Understanding this relationship is crucial for homeowners and potential buyers alike. So, let’s dive right in and unravel the connection between interest rates and your mortgage payments. Picture this: you’ve found your dream home, but before you can make it yours, you need to secure a mortgage. That’s where interest rates come into play. The interest rate is essentially the cost of borrowing money from the lender. It affects your monthly mortgage payment, the total amount you’ll pay over the loan term, and even your ability to qualify for a mortgage. So, let’s explore the fascinating world of interest rates and discover how they can impact your home ownership journey.
Understanding How Interest Rates Affect Your Mortgage
The interest rate is a key factor that determines the overall cost of your mortgage. It affects how much you pay in monthly payments, the total amount of interest you will pay over the life of the loan, and even your ability to qualify for a mortgage in the first place. In this article, we will delve into the details of how interest rates impact your mortgage, covering topics such as the relationship between interest rates and mortgage rates, the different types of interest rates, how interest rates affect your monthly payments, and strategies for managing interest rates.
Interest Rates vs. Mortgage Rates
When we talk about interest rates in the context of mortgages, we are usually referring to mortgage rates. Mortgage rates are the interest rates that lenders charge on mortgage loans. However, it’s important to know that mortgage rates are influenced by broader interest rates in the financial market.
The benchmark for mortgage rates is often the yield on the 10-year Treasury note. Mortgage rates tend to follow the movement of the 10-year Treasury yield, but they are typically higher due to the added risk associated with mortgage lending. Factors such as inflation, economic indicators, and the supply and demand for mortgage-backed securities can also influence mortgage rates.
Types of Interest Rates
There are two main types of interest rates you need to be familiar with when it comes to mortgages: fixed-rate and adjustable-rate.
1. Fixed-Rate Mortgage: A fixed-rate mortgage has an interest rate that remains constant throughout the life of the loan. This means your monthly payments will stay the same, providing stability and predictability. Fixed-rate mortgages are popular because they offer protection against rising interest rates. However, initially, they may come with higher rates compared to adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs).
2. Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM): An adjustable-rate mortgage has an interest rate that can change periodically, typically after an initial fixed-rate period. ARM loans usually have lower initial rates, making them more affordable in the early years of homeownership. However, after the initial period, the rate can adjust based on changes in a specific index (e.g., the London Interbank Offered Rate – LIBOR). This means your monthly payment can change over time, potentially increasing or decreasing depending on market conditions.
How Interest Rates Affect Your Monthly Payments
Your mortgage payment consists of principal and interest. The principal is the amount borrowed, while the interest is the cost of borrowing money. When interest rates change, your monthly payment can be affected in the following ways:
1. Fixed-Rate Mortgage: Since the interest rate remains the same over the life of a fixed-rate mortgage, your monthly payment will always stay constant. This allows for easier budgeting and planning, as your payment will not change even if interest rates rise.
2. Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM): With an ARM, your monthly payment can change when the interest rate adjusts. If interest rates rise, your payment will increase. Conversely, if rates fall, your payment may decrease. This potential for change can make budgeting more challenging, especially if the interest rates increase significantly.
To understand the impact of interest rate changes on your monthly payment, consider this example:
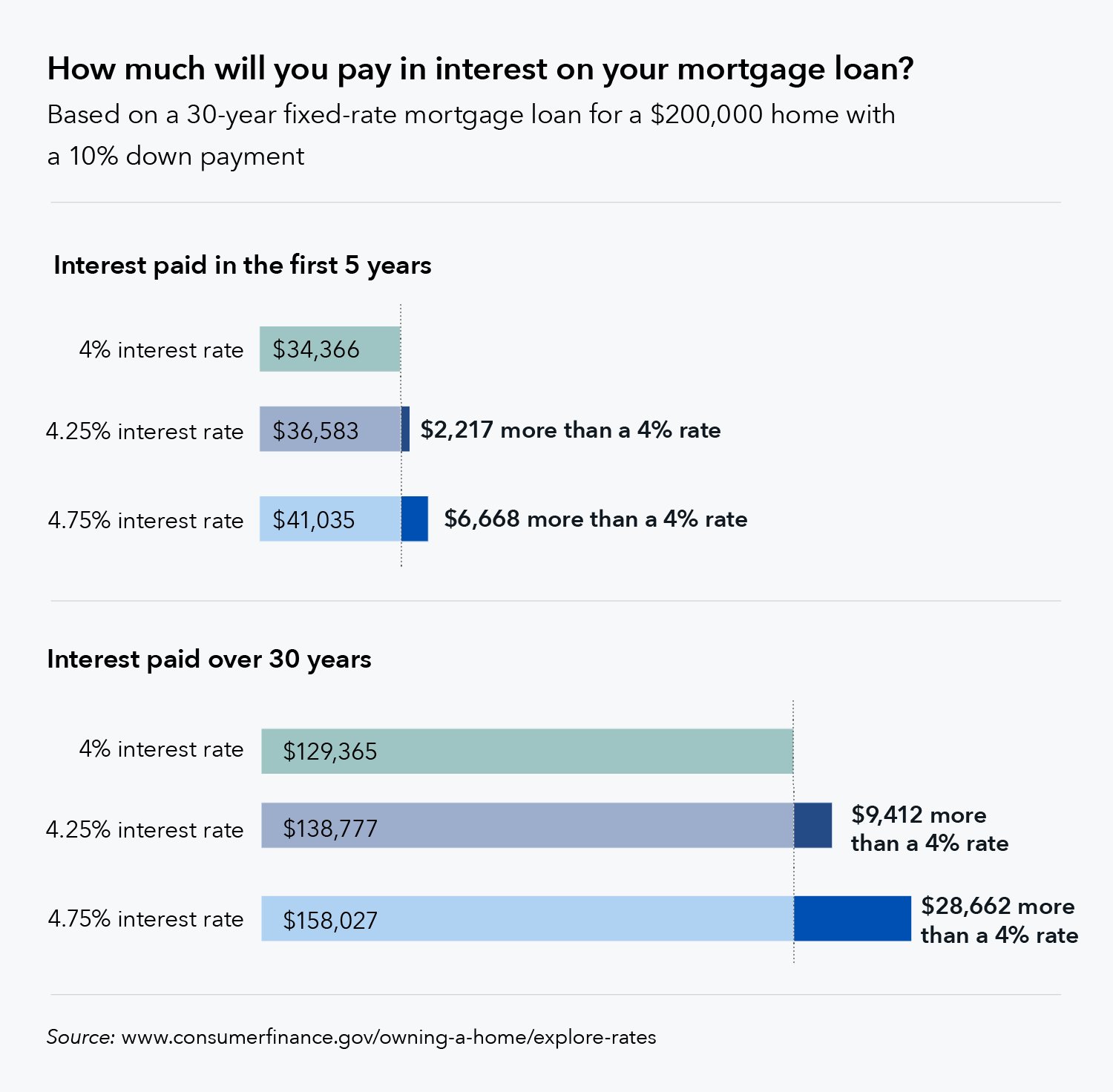
Let’s say you have a fixed-rate mortgage of $200,000 with a 4% interest rate and a 30-year term. Your monthly payment would be approximately $955. If the interest rate increased to 5%, your monthly payment would rise to around $1,073. Conversely, if the rate decreased to 3%, your payment would decrease to about $843.
Strategies for Managing Interest Rates
Managing interest rates is crucial to ensure you get the best possible terms for your mortgage. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Monitor Market Conditions: Keep an eye on interest rate trends and economic indicators that influence mortgage rates. This will help you determine the right time to lock in a rate or consider refinancing.
2. Locking in Your Rate: When you find an interest rate that you are comfortable with, you can lock it in with your lender. This protects you from potential rate increases during the loan processing period.
3. Consider Refinancing: If interest rates have dropped significantly since you obtained your mortgage, refinancing may be an option. Refinancing allows you to replace your existing loan with a new one, potentially at a lower interest rate, which can result in lower monthly payments.
4. Improve Your Credit Score: Lenders use credit scores to determine mortgage rates. By improving your credit score, you can increase your chances of qualifying for a lower interest rate. Paying bills on time, reducing your debt-to-income ratio, and fixing errors on your credit report are some ways to boost your credit score.
5. Shorten Your Loan Term: Choosing a shorter loan term, such as a 15-year mortgage instead of a 30-year one, can result in a lower interest rate. While your monthly payments may be higher, you will pay less interest over the life of the loan.
Conclusion
Understanding how interest rates affect your mortgage is essential for making informed decisions about homeownership. Whether you opt for a fixed-rate mortgage or an adjustable-rate mortgage, interest rates play a significant role in determining your monthly payments and the total cost of your loan. By staying informed about market conditions, considering different loan options, and managing your credit score, you can navigate the complexities of interest rates and secure the best possible mortgage terms for your financial situation.
How Do Interest Rates Affect Your Mortgage and Monthly Payment? Interest Rates Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding How Interest Rates Affect Your Mortgage
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do interest rates impact mortgage payments?
Higher interest rates result in higher mortgage payments, as the interest is calculated as a percentage of the loan amount. When interest rates are lower, borrowers typically have lower monthly mortgage payments.
What factors determine the interest rate on a mortgage?
Several factors influence the interest rate on a mortgage, including the borrower’s credit score, loan term, loan amount, and the current economic conditions. Lenders also consider the borrower’s income, employment history, and the type of property being financed.
What is the difference between fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages?
With a fixed-rate mortgage, the interest rate remains the same throughout the loan term. On the other hand, an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) has an interest rate that may change periodically, usually after an initial fixed-rate period.
How can I lock in a favorable interest rate?
To lock in a favorable interest rate, you can consider getting pre-approved for a mortgage. Pre-approval allows you to secure a specific interest rate for a certain period, typically ranging from 60 to 90 days.
Should I consider refinancing my mortgage if interest rates drop?
If interest rates have significantly dropped since you obtained your mortgage, refinancing might be a viable option. By refinancing, you can secure a lower interest rate, potentially reducing your monthly mortgage payments and overall interest costs.
Can I negotiate the interest rate on my mortgage?
While you cannot directly negotiate the interest rate itself, you can shop around and compare offers from different lenders. By comparing rates and fees, you may be able to find a mortgage with a more favorable interest rate.
How do interest rate changes impact mortgage affordability?
When interest rates increase, mortgage affordability decreases as borrowers will have higher monthly mortgage payments. Conversely, when interest rates decrease, mortgage affordability improves, giving borrowers more purchasing power.
What are the long-term effects of interest rate fluctuations on my mortgage?
Interest rate fluctuations can have long-term effects on your mortgage. If interest rates rise, your monthly payments could increase, potentially causing financial strain. Conversely, if interest rates decrease, you may have the opportunity to save money by refinancing or paying off your mortgage faster.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how interest rates affect your mortgage is crucial for any homeowner or prospective buyer. When interest rates are low, it becomes more affordable to borrow, as the cost of borrowing decreases. This can lead to lower monthly mortgage payments and potential savings over the life of the loan. On the other hand, when interest rates increase, borrowing becomes more expensive, resulting in higher monthly payments and potentially impacting your budget. By staying informed about interest rate trends and working with a trusted mortgage advisor, you can make informed decisions, secure the best rates, and navigate the mortgage market with confidence. Understanding how interest rates affect your mortgage empowers you to make sound financial choices and achieve your homeownership goals.