As a freelancer, finding ways to reduce taxable income is essential for maximizing your earnings. So, how can you minimize your tax burden and keep more money in your pocket? In this blog article, we will explore practical strategies that freelancers can employ to lower their taxable income. By implementing these methods, you can potentially save a significant amount of money and achieve greater financial stability. So, let’s dive in and discover the ways to reduce taxable income for freelancers.
Ways to Reduce Taxable Income for Freelancers
As a freelancer, managing your finances can be a daunting task. One crucial aspect of financial management is understanding how to reduce your taxable income. By implementing certain strategies and taking advantage of available deductions, you can significantly minimize your tax burden. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various ways to reduce taxable income for freelancers, ensuring you make informed decisions to optimize your financial situation.
Understanding Taxable Income for Freelancers
Before diving into the strategies, let’s first understand what taxable income means for freelancers. Taxable income is the portion of your income that is subject to taxation after taking into account allowable deductions. For freelancers, taxable income includes your self-employment income minus any deductible business expenses. It’s important to keep detailed records of your income and expenses throughout the year to accurately determine your taxable income.
1. Take Advantage of Deductible Business Expenses
One of the most effective ways to reduce taxable income as a freelancer is by claiming deductible business expenses. The following are common business expenses that freelancers can deduct:
- Office supplies and equipment
- Home office expenses
- Professional services (accounting, legal, etc.)
- Software and hardware expenses
- Travel and transportation costs
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Insurance premiums
By keeping proper documentation and understanding the IRS guidelines, you can ensure that you claim all eligible deductions, effectively reducing your taxable income.
Home Office Deduction
If you have a dedicated space in your home used exclusively for your freelance work, you may be eligible for the home office deduction. This deduction allows you to write off a portion of your rent or mortgage, utilities, and other home-related expenses. To claim this deduction, you must meet specific criteria set by the IRS, such as using your home office regularly and exclusively for your business.
Health Insurance Premiums
Freelancers often have to manage their own health insurance, which can be costly. However, you can deduct your health insurance premiums as a business expense, reducing your taxable income. This deduction is especially valuable for freelancers who do not qualify for employer-sponsored health insurance.
2. Maximize Retirement Contributions
Contributing to a retirement account not only helps secure your financial future but also offers tax advantages. Freelancers can reduce their taxable income by maximizing contributions to retirement accounts such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRAs.
- Traditional IRA: Contributions to a Traditional IRA are tax-deductible, meaning they reduce your taxable income. The earnings on these contributions grow tax-deferred until you withdraw them in retirement.
- SEP IRA: If you have a higher income, a SEP IRA allows you to contribute a higher percentage of your income, up to a certain limit. Contributions to a SEP IRA are also tax-deductible.
By taking advantage of these retirement account options, you not only save for the future but also lower your taxable income in the present.
3. Utilize Self-Employment Tax Deductions
Freelancers are responsible for paying self-employment tax, which includes both the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. However, freelancers can deduct the employer portion of these taxes, effectively reducing their taxable income.
Qualified Business Income Deduction
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act introduced the Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction, also known as the Section 199A deduction. This deduction allows certain self-employed individuals, including freelancers, to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income. The QBI deduction is subject to various limitations and thresholds, so it’s essential to consult with a tax professional to determine if you qualify.
4. Consider Incorporating Your Freelance Business
Incorporating your freelance business may offer additional tax benefits. By establishing a separate legal entity, such as a Limited Liability Company (LLC) or S Corporation, you may have access to deductions and tax advantages not available to individuals.
Employer-Employee Tax Split
As an incorporated freelancer, you can structure your income to split it between salary and dividends. By paying yourself a reasonable salary, you can reduce the amount subject to self-employment taxes. Dividends, which are typically taxed at a lower rate, make up the remainder of your income. This strategy can result in significant tax savings.
Additional Deductions for Incorporated Freelancers
Incorporating your freelance business may open the door to additional deductions, such as:
- Business-related meals and entertainment expenses
- Employee benefit programs
- Business-related travel expenses
- Medical expense reimbursement plans
Consider consulting with a tax professional to understand the implications and potential benefits of incorporating your freelance business.
5. Stay Organized and Keep Accurate Records
Maintaining organized and accurate financial records is crucial for maximizing deductions and minimizing taxable income. As a freelancer, you have the responsibility of tracking income, expenses, and receipts consistently. Consider utilizing accounting software or hiring a professional to help you manage your finances efficiently.
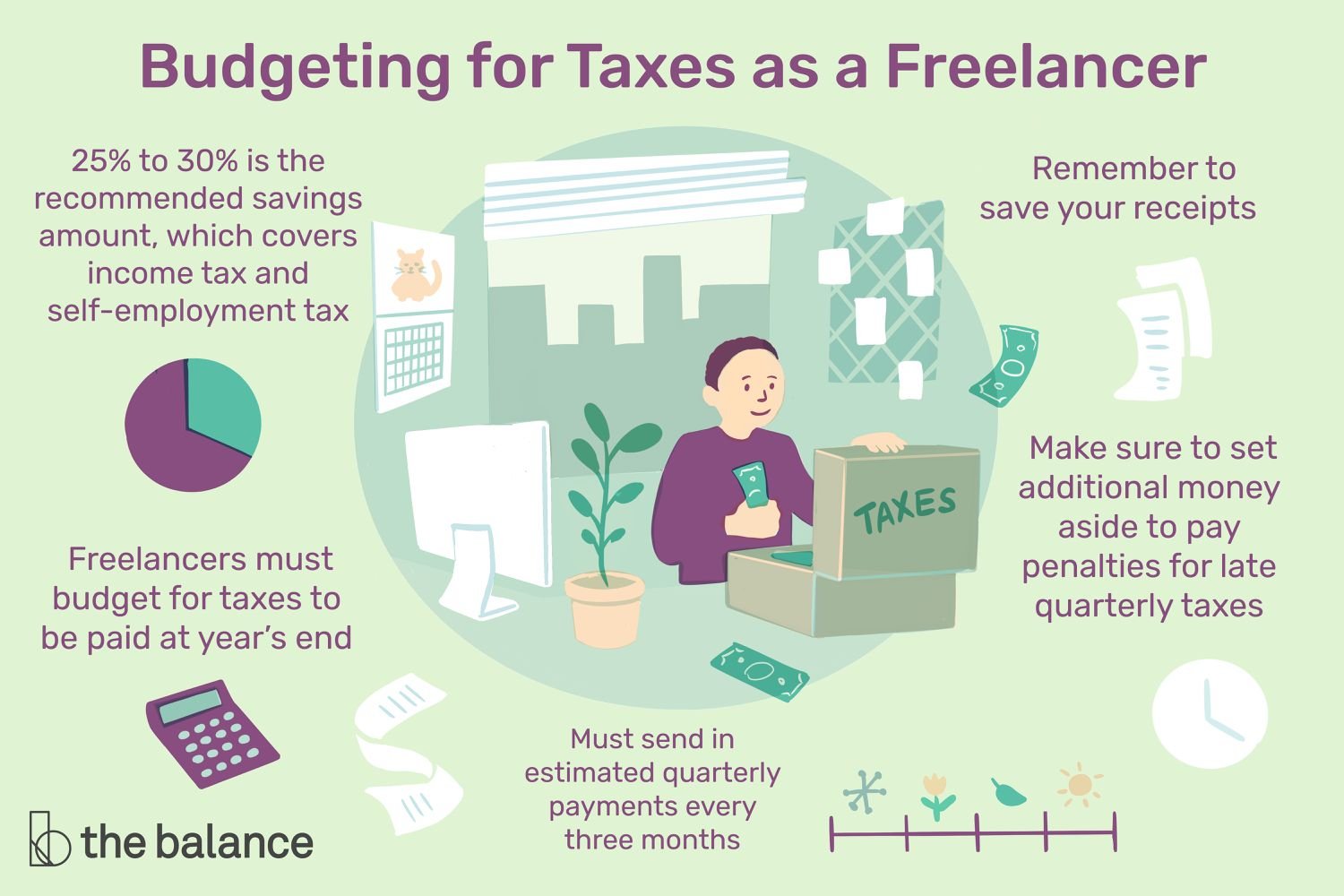
6. Pay Estimated Taxes
As a freelancer, you are likely not subject to employer withholding taxes. Instead, you are responsible for paying estimated taxes throughout the year. By making quarterly tax payments based on your estimated income, you can avoid underpayment penalties. It’s essential to accurately estimate your tax liability to ensure you are paying the appropriate amount.
7. Seek Professional Tax Advice
Navigating the complex world of freelance taxation can be overwhelming. It’s always beneficial to seek advice from a qualified tax professional who specializes in working with freelancers. They can provide personalized guidance, help you identify potential deductions, and ensure compliance with tax laws.
In conclusion, reducing taxable income is an integral part of freelance financial management. By implementing the strategies discussed in this guide, including claiming deductible business expenses, maximizing retirement contributions, utilizing self-employment tax deductions, considering incorporation, staying organized, paying estimated taxes, and seeking professional tax advice, freelancers can effectively lower their tax burden and optimize their financial situation. Remember to consult with a tax professional to ensure you make informed decisions based on your specific circumstances.
ACCOUNTANT EXPLAINS: How to Pay Less Tax
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can freelancers reduce their taxable income?
Freelancers can reduce their taxable income through various strategies such as deducting business expenses, contributing to retirement plans, taking advantage of tax credits, and utilizing tax deductions specifically available for freelancers.
2. What business expenses can freelancers deduct to reduce taxable income?
Freelancers can deduct a wide range of business expenses, including office rent, equipment costs, professional services fees, marketing expenses, travel costs related to business, and even a portion of their home office expenses if they meet certain criteria.
3. Are there retirement plans specifically designed for freelancers?
Yes, freelancers can contribute to retirement plans like the Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA, Solo 401(k), or a Simple IRA. These plans offer tax advantages and allow freelancers to save for retirement while reducing their taxable income.
4. Can freelancers claim tax deductions for health insurance premiums?
Yes, self-employed freelancers can deduct their health insurance premiums, including medical, dental, and long-term care insurance, as well as premiums for their dependents. However, there are certain criteria and limitations to be considered.
5. Are there any tax credits available for freelancers?
Freelancers may be eligible for tax credits such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), the Child and Dependent Care Credit, and the Retirement Savings Contributions Credit. These credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed, hence reducing taxable income.
6. How can freelancers minimize their tax liability through quarterly estimated tax payments?
Freelancers can avoid underpayment penalties and minimize their tax liability by making quarterly estimated tax payments. By accurately estimating their income and paying taxes throughout the year, freelancers can spread the tax burden evenly and reduce the likelihood of facing a large tax bill at the end of the year.
7. Can freelancers deduct their business-related education expenses?
Yes, freelancers can deduct qualifying business-related education expenses, such as workshops, conferences, online courses, and certifications that enhance their skills and directly relate to their freelance business.
8. How can freelancers keep track of their expenses to reduce taxable income?
Freelancers can maintain organized records by utilizing accounting software or apps, keeping receipts and invoices, categorizing expenses, and regularly reconciling their financial transactions. By doing so, they can easily identify deductible business expenses and effectively reduce their taxable income.
Final Thoughts
Freelancers have several effective strategies to reduce their taxable income. Carefully tracking and deducting business expenses is crucial, ensuring that only legitimate expenses are claimed. Maximizing deductible retirement contributions, such as setting up a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k), can help lower taxable income. Additionally, strategic income timing, such as deferring payments to the next tax year, can be advantageous. Investing in education or professional development can provide valuable deductions. Implementing these ways to reduce taxable income for freelancers allows for greater financial flexibility and minimizes the burden of taxes.