Treasury bonds. They may sound complex and intimidating, but fear not! In this article, we will break down what treasury bonds are and how they work in simple, easy-to-understand terms. Whether you’re a novice investor looking to diversify your portfolio or simply curious about government-backed securities, this is the ultimate guide to demystify the world of treasury bonds. So, buckle up and join us as we delve into the fascinating realm of treasury bonds, unraveling their inner workings and shedding light on their role in the financial landscape. Let’s get started!
What Are Treasury Bonds and How Do They Work?
Treasury bonds, also known as T-bonds or government bonds, are long-term debt securities issued by the United States Department of the Treasury. They are a popular investment choice for individuals, institutions, and foreign governments due to their low risk and stable returns. In this article, we will explore what treasury bonds are, how they work, and why they are an important component of the financial market.
1. Understanding Treasury Bonds
Treasury bonds are issued by the U.S. government to finance its operations and fund various projects. They are considered one of the safest investments in the world because they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. These bonds have a maturity period of 30 years, meaning that the government promises to repay the principal amount along with periodic interest payments over this period.
a. Types of Treasury Bonds
There are three main types of treasury bonds:
1. Fixed-Rate Bonds: These bonds pay a fixed interest rate throughout their life, providing a predictable income stream for investors.
2. Inflation-Protected Bonds: Also known as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), these bonds are designed to protect investors from inflation. The principal amount of TIPS is adjusted based on changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), resulting in higher interest payments when inflation is high.
3. Floating-Rate Bonds: These bonds have variable interest rates that are periodically reset based on a reference rate such as the Treasury Bill rate or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). This allows investors to benefit from changes in interest rates over time.
b. Purchasing Treasury Bonds
Individual investors can purchase treasury bonds directly from the U.S. Department of the Treasury through their online portal called TreasuryDirect. Alternatively, investors can buy treasury bonds through a broker or a financial institution. It is important to note that treasury bonds are sold in denominations of $100, with a minimum purchase requirement of $100.
2. How Do Treasury Bonds Work?
When you invest in a treasury bond, you are essentially lending money to the U.S. government. Here’s how it works:
1. Issuance: The U.S. Department of the Treasury conducts regular auctions to sell new treasury bonds to investors. These auctions determine the interest rate, also known as the coupon rate, at which the bonds will be issued. The interest rate is fixed for fixed-rate bonds and adjusted for inflation for TIPS.
2. Interest Payments: Treasury bonds pay interest semi-annually. The interest is calculated based on the face value (also known as the par value) of the bond and the coupon rate. For example, if you own a $10,000 bond with a coupon rate of 3%, you will receive $300 in interest payments each year.
3. Secondary Market Trading: After the initial issuance, treasury bonds can be bought and sold in the secondary market. The market price of the bond may fluctuate based on changes in interest rates, inflation expectations, and general market conditions. When interest rates rise, the market price of existing bonds tends to fall, and vice versa.
4. Maturity and Repayment: At maturity, which is typically after 30 years, the U.S. government repays the full face value of the treasury bond to the bondholder. In the case of TIPS, the adjusted principal amount is paid, accounting for changes in inflation over the bond’s life. Investors can also choose to sell their bonds before maturity in the secondary market if they need to access their funds.
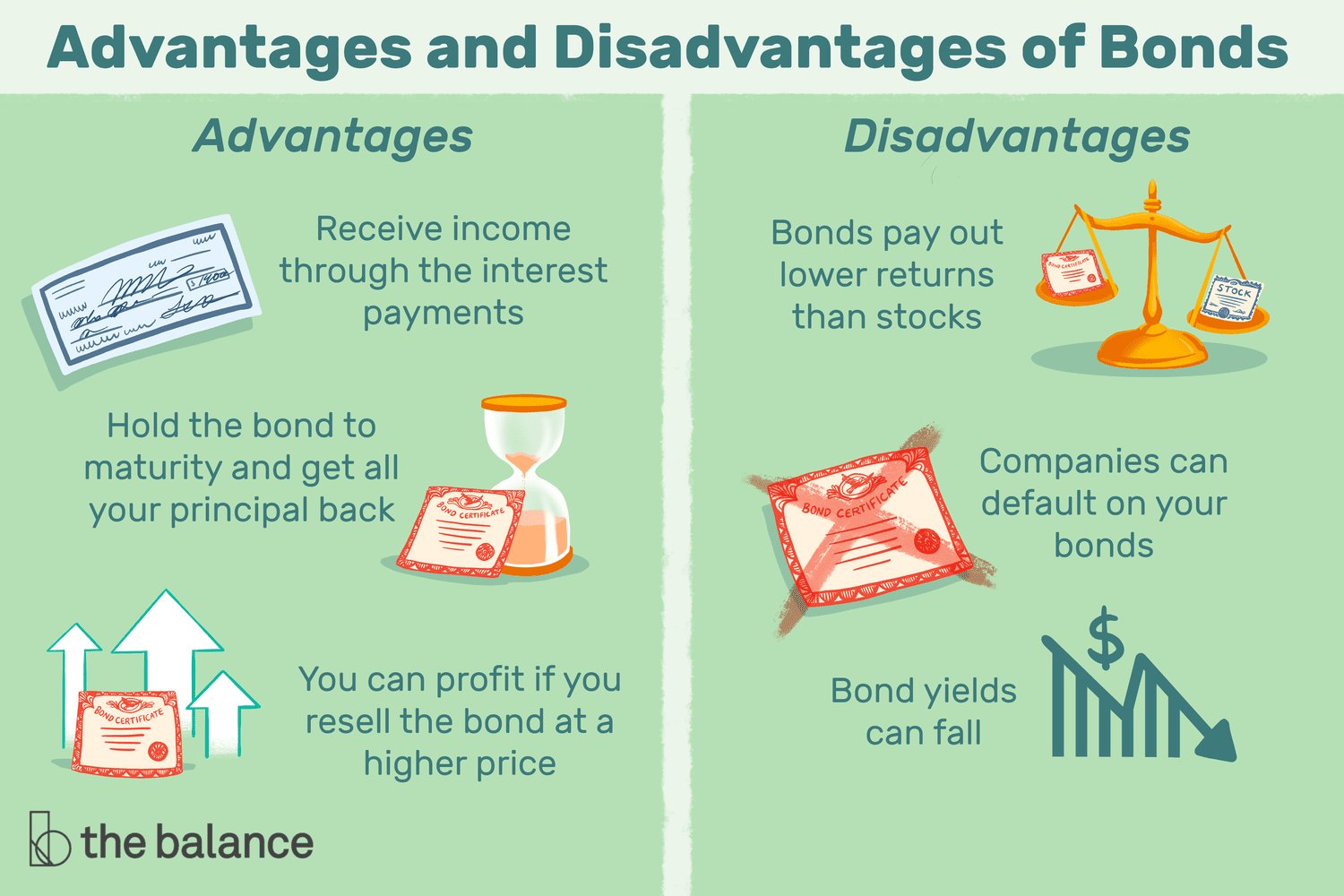
3. Benefits of Investing in Treasury Bonds
Investing in treasury bonds offers several benefits that make them attractive to a wide range of investors:
a. Safety and Stability
Treasury bonds are considered one of the safest investments because they are backed by the U.S. government. The risk of default is extremely low, making them an ideal choice for conservative investors looking for stable returns.
b. Diversification
Treasury bonds provide a diversification opportunity for investors as they typically have a low correlation with other asset classes, such as stocks and corporate bonds. This means that adding treasury bonds to your investment portfolio can help reduce overall risk.
c. Income Generation
Treasury bonds pay regular interest payments, providing a steady stream of income for investors. This can be particularly beneficial for retirees or individuals seeking a reliable source of income.
d. Inflation Protection
TIPS offer investors protection against inflation by adjusting the principal amount based on changes in the CPI. This ensures that investors maintain their purchasing power even when inflation is high.
e. Liquidity
Treasury bonds are highly liquid, meaning they can be easily bought and sold in the secondary market. This provides investors with the flexibility to access their funds if needed before the bond’s maturity.
f. Tax Benefits
Interest income earned from treasury bonds is exempt from state and local taxes, while it is subject to federal income tax. This tax advantage can make treasury bonds more attractive for investors in higher tax brackets.
4. Risks Associated with Treasury Bonds
While treasury bonds are generally considered safe investments, there are a few risks to be aware of:
a. Interest Rate Risk
Treasury bond prices are negatively affected by rising interest rates. If interest rates increase after you have purchased a bond, the market value of your bond may decrease. However, if you hold the bond until maturity, you will still receive the full face value.
b. Inflation Risk
Although TIPS provide inflation protection, there is still a risk that inflation could be higher than expected, resulting in lower real returns. It’s important to consider your inflation expectations when investing in TIPS.
c. Opportunity Cost
Investing in treasury bonds may result in lower potential returns compared to riskier investments such as stocks or corporate bonds. Depending on your investment goals and risk tolerance, it may be necessary to diversify your portfolio with other asset classes.
5. Conclusion
In summary, treasury bonds are a secure and reliable investment option issued by the U.S. government. They offer a predictable income stream, inflation protection, and diversification benefits. While they may not offer the highest potential returns, treasury bonds are an essential component of a well-rounded investment portfolio due to their low risk and stability.
By understanding how treasury bonds work and weighing the associated risks, investors can make informed decisions about adding them to their investment strategy. Whether you are a conservative investor seeking stability or someone looking to diversify their portfolio, treasury bonds can be a valuable addition to your financial plan.
Government Bond Basics: Treasury and Agency Bonds
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are treasury bonds?
Treasury bonds are fixed-income securities issued by the government to finance its spending and manage national debt. They are considered one of the safest investments, as they are backed by the full faith and credit of the government.
How do treasury bonds work?
When you purchase a treasury bond, you are essentially lending money to the government. In return, the government promises to pay you interest over a specific period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. At maturity, the government returns the initial investment amount.
What is the purpose of treasury bonds?
The government issues treasury bonds as a way to raise funds to cover budget deficits or finance various projects. It allows the government to borrow money from individuals, corporations, and other entities to meet its financial obligations.
Who can invest in treasury bonds?
Anyone can invest in treasury bonds, including individual investors, financial institutions, and foreign entities. They are widely regarded as a low-risk investment option and are often included in diverse investment portfolios.
How are treasury bond interest rates determined?
Treasury bond interest rates are influenced by various factors, such as the demand for government debt, prevailing market interest rates, inflation expectations, and overall economic conditions. The rates are set through regular auctions conducted by the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
Can treasury bond prices fluctuate?
Yes, treasury bond prices can fluctuate in response to changes in interest rates. When rates rise, bond prices often fall, and vice versa. However, since treasury bonds are backed by the government, their prices tend to be more stable compared to other types of bonds.
Can I sell treasury bonds before they mature?
Yes, treasury bonds can be sold before they reach their maturity date. Their value in the secondary market may be higher or lower than the initial purchase price, depending on changes in interest rates and market conditions. Selling before maturity allows investors to access the funds before the bond’s term ends.
Are treasury bonds taxable?
Interest earned from treasury bonds is subject to federal income tax but exempt from state and local taxes. While you don’t receive the interest until maturity, you need to report it annually for tax purposes. Some investors may be eligible for tax benefits depending on the purpose of investing in treasury bonds.
How can I buy treasury bonds?
You can buy treasury bonds directly from the U.S. Department of the Treasury through their online platform, TreasuryDirect. Additionally, they are also available for purchase through brokerage firms and banks. It’s important to consider transaction costs and fees associated with buying treasury bonds from third-party sources.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, treasury bonds are a type of government-issued investment that allows individuals and institutions to lend money to the government in exchange for regular interest payments. These bonds are considered low-risk investments due to the backing of the government, making them attractive to risk-averse investors. Treasury bonds work by investors purchasing bonds and holding them for a specified period of time until maturity. During this time, they receive interest payments, and at maturity, the principal amount is returned. Overall, understanding what treasury bonds are and how they work can provide individuals with a secure investment option for their financial goals.