Are you ready to grow your wealth and secure your financial future? Look no further! In this blog article, we will guide you through the process of creating a financial portfolio for long-term growth. Building a portfolio that stands the test of time requires careful planning and strategic decision-making. But fear not, because we are here to simplify this process and provide you with actionable steps to achieve your financial goals. So, let’s dive right in and discover how to create a financial portfolio for long-term growth that will set you on the path to financial success.
How to Create a Financial Portfolio for Long-Term Growth
When it comes to building wealth and securing your financial future, creating a well-diversified portfolio is essential. A financial portfolio is a collection of investments that can help you achieve long-term growth and financial stability. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of creating a financial portfolio that is tailored to your financial goals and risk tolerance.
1. Set Clear Financial Goals
Before diving into the world of investing, it’s important to define your financial goals. Having a clear vision of what you want to achieve will help you make informed investment decisions. Start by asking yourself the following questions:
- What is your desired timeline for achieving your financial goals?
- How much risk are you comfortable taking?
- What is your target return on investment?
- Are you saving for retirement, buying a house, or funding your child’s education?
By answering these questions, you can establish specific and measurable goals that will guide your investment strategy.
2. Determine Your Risk Tolerance
Investing involves risk, and understanding your risk tolerance is crucial in creating a portfolio that aligns with your comfort level. Risk tolerance refers to your ability to handle market fluctuations and the potential loss of your investments. Factors that can influence your risk tolerance include:
- Your age
- Your time horizon
- Your financial obligations
- Your investing experience
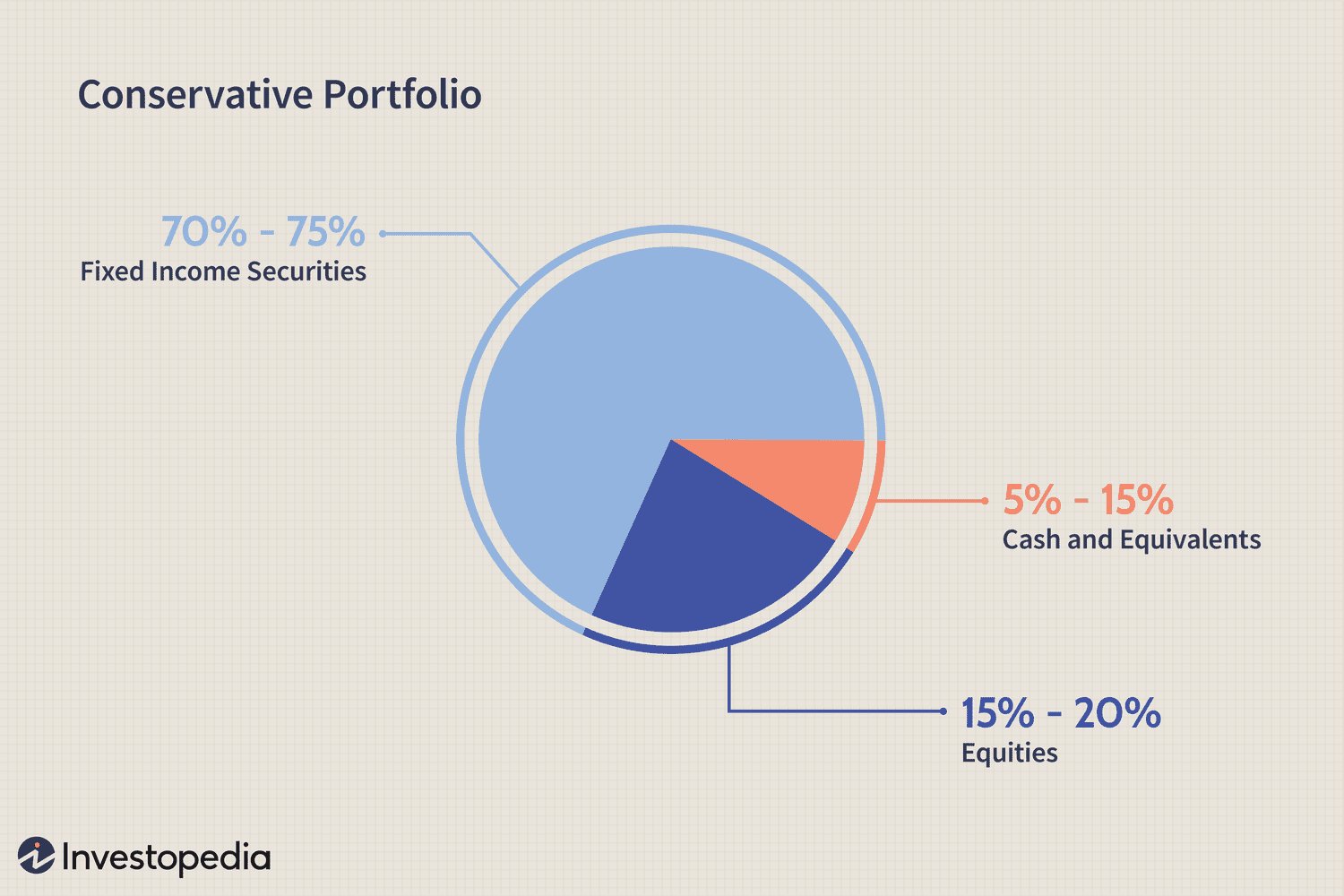
Generally, younger individuals with a longer time horizon can afford to take on more risk, while those approaching retirement may prefer a more conservative approach. By assessing your risk tolerance, you can select investments that match your comfort level and minimize unnecessary stress.
3. Diversify Your Investments
Diversification is a fundamental principle of investing. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, you can reduce the risk associated with any single investment. Diversification can be achieved through the following strategies:
a. Asset Allocation
Asset allocation involves dividing your investments among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. The allocation should be based on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon. A general rule of thumb is to allocate a higher percentage to equities when you have a longer time horizon and a greater risk tolerance.
b. Sector Allocation
Within each asset class, it’s important to diversify further by investing in different sectors. For example, if you invest in stocks, consider allocating your funds across technology, healthcare, finance, and other sectors. This way, if one sector experiences a downturn, the impact on your overall portfolio will be minimized.
c. Geographic Allocation
Geographic allocation involves investing in different regions and countries around the world. By spreading your investments globally, you can benefit from the growth potential of different economies and reduce the risk associated with a single country’s economic performance.
4. Choose the Right Investment Vehicles
Once you have determined your asset allocation and diversification strategy, it’s time to select the right investment vehicles for your portfolio. Here are some common investment options to consider:
a. Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for long-term growth. When selecting stocks, consider factors such as the company’s financial health, industry trends, and management team.
b. Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations. They provide fixed interest payments over a specified period of time and are generally considered lower risk than stocks. When investing in bonds, evaluate the issuer’s credit rating, interest rate environment, and bond duration.
c. Mutual Funds
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They are managed by professional fund managers and offer diversification and professional expertise. Before investing in mutual funds, assess the fund’s performance, fees, and investment strategy.
d. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
ETFs are similar to mutual funds, but they trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They offer diversification, flexibility, and low expense ratios. Research the ETF’s underlying assets, expense ratio, and trading volume before making an investment.
e. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs allow individuals to invest in real estate properties without directly buying and managing properties. They generate income through rent and property appreciation. Consider factors such as property type, geographical location, and historical returns when investing in REITs.
f. Index Funds
Index funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. They offer broad market exposure, low fees, and low portfolio turnover. Look for index funds with low expense ratios and a strong track record.
5. Regularly Monitor and Rebalance Your Portfolio
Creating a financial portfolio is not a one-time task. It requires regular monitoring and rebalancing to ensure it stays aligned with your goals and risk tolerance. Here’s what you need to do:
a. Review Your Portfolio
Regularly review your portfolio’s performance to assess if it’s meeting your expectations. Monitor the individual investments within your portfolio and evaluate their performance relative to their benchmarks.
b. Rebalance Your Portfolio
Rebalancing involves adjusting your portfolio’s asset allocation to bring it back in line with your desired targets. If one asset class outperforms others, its weightage in your portfolio may become unbalanced. Rebalancing helps to manage risk and maintain your desired level of diversification.
c. Take Advantage of Tax-Efficient Strategies
Consider tax-efficient investment strategies, such as investing in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s. These accounts offer tax benefits that can help maximize your returns.
d. Stay Informed
Keep up-to-date with market trends, economic news, and changes in investment regulations. Staying informed will help you make informed decisions and adapt your portfolio strategy as needed.
Creating a financial portfolio for long-term growth is a journey that requires careful planning, diversification, and regular monitoring. By setting clear goals, determining your risk tolerance, diversifying your investments, choosing the right investment vehicles, and regularly rebalancing your portfolio, you can position yourself for long-term financial success. Remember, investing involves risks, and it’s important to seek professional advice and educate yourself before making any investment decisions. Start building your financial portfolio today and take control of your financial future.
How to Build a Rock-Solid Investment Portfolio
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a financial portfolio?
A financial portfolio refers to a collection of investments held by an individual or organization. It typically includes various assets such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other securities.
Why is creating a financial portfolio important for long-term growth?
Creating a financial portfolio is crucial for long-term growth as it helps individuals or organizations diversify their investments and potentially maximize returns. A well-diversified portfolio allows for spreading the risk across different asset classes, which can help protect against market volatility.
How do I start creating a financial portfolio for long-term growth?
To begin creating a financial portfolio for long-term growth, follow these steps:
1. Set clear financial goals and determine your risk tolerance.
2. Conduct thorough research on various investment options.
3. Decide on an asset allocation strategy that suits your goals and risk tolerance.
4. Diversify your investments across different asset classes.
5. Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation.
What factors should I consider when selecting investments for my portfolio?
When selecting investments for your portfolio, consider the following factors:
1. Risk: Assess the risk associated with each investment and determine if it aligns with your risk tolerance.
2. Return potential: Evaluate the historical performance and growth prospects of the investment.
3. Liquidity: Consider the ease of buying or selling the investment.
4. Cost: Analyze the fees, commissions, and expenses associated with the investment.
5. Time horizon: Determine how long you intend to hold the investment.
Should I seek professional help to create a financial portfolio?
While creating a financial portfolio can be done independently, seeking professional help can provide valuable expertise and guidance. Financial advisors can help assess your financial goals, risk tolerance, and recommend suitable investments tailored to your needs.
How often should I review my financial portfolio?
Regularly reviewing your financial portfolio is essential. It is recommended to review at least once a year or when significant life events occur, such as a change in income, marital status, or investment goals. Additionally, consider reviewing your portfolio when the market conditions change significantly.
What is portfolio rebalancing, and why is it important?
Portfolio rebalancing involves adjusting the allocations of assets within a portfolio to maintain the desired mix of investments. It is important because over time, certain assets may outperform or underperform, causing the portfolio’s asset allocation to deviate from the initially set goals. Rebalancing helps bring the portfolio back in line with the desired asset allocation and ensures that the risk and return objectives are met.
Can I make changes to my financial portfolio as my goals change?
Yes, you can and should make changes to your financial portfolio as your goals change. Life circumstances, such as a change in income, age, or risk tolerance, may require adjustments to your investment strategy. Regularly revisit your financial goals and consult with a financial advisor to make informed decisions about modifying your portfolio.
Final Thoughts
Creating a financial portfolio for long-term growth requires careful planning and consideration. Start by setting clear financial goals and determining your risk tolerance. Next, diversify your investments across different asset classes to minimize risk and maximize potential returns. Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it remains aligned with your objectives. Consider seeking professional advice to ensure you make informed decisions. Finally, be patient and stay committed to your long-term goals, making adjustments as needed. By following these steps, you can effectively create a financial portfolio for long-term growth.