Hedge funds. You may have heard the term before, but what exactly are they and what risks do they entail? In a nutshell, hedge funds are investment vehicles managed by professional managers who aim to generate high returns for their clients. These funds employ various strategies, such as leverage, derivatives, and short-selling, to capitalize on market opportunities. But along with potential rewards, hedge funds come with their fair share of risks. From market volatility and liquidity concerns to regulatory changes and operational risks, navigating the hedge fund landscape requires a keen understanding of the potential pitfalls. So, let’s delve deeper into the world of hedge funds and explore the inherent risks that investors should be aware of.
What is a Hedge Fund and Its Risks
Introduction
Hedge funds are investment vehicles that pool capital from high net worth individuals and institutional investors to invest in a wide range of assets. While they can offer potential high returns, hedge funds also come with inherent risks that investors should be aware of. In this article, we will explore the concept of hedge funds, their strategies, and the risks associated with investing in them.
Understanding Hedge Funds
A hedge fund is an alternative investment vehicle managed by professional fund managers who employ various investment strategies to generate returns. Unlike traditional investment funds, hedge funds have fewer regulatory restrictions, allowing them to employ more complex and aggressive investment techniques to potentially achieve higher returns.
Hedge Fund Strategies
Hedge funds employ a variety of investment strategies, including:
- Long/short equity: This strategy involves taking long positions in undervalued stocks expected to rise and short positions in overvalued stocks expected to decline.
- Event-driven: Event-driven hedge funds aim to profit from specific events like mergers, acquisitions, bankruptcies, or other corporate actions.
- Global macro: Global macro funds focus on major macroeconomic trends and invest in various asset classes like currencies, commodities, and global equities.
- Quantitative: Quantitative hedge funds utilize mathematical models and algorithms to make investment decisions based on large sets of data.
- Arbitrage: Arbitrage funds seek to profit from price discrepancies between related securities in different markets or instances.
- Distressed securities: Distressed securities hedge funds invest in the debt or equity of companies facing financial distress, aiming to profit from a successful turnaround.
- Multi-strategy: Multi-strategy hedge funds employ a combination of different strategies to diversify their investments and potentially generate more consistent returns.
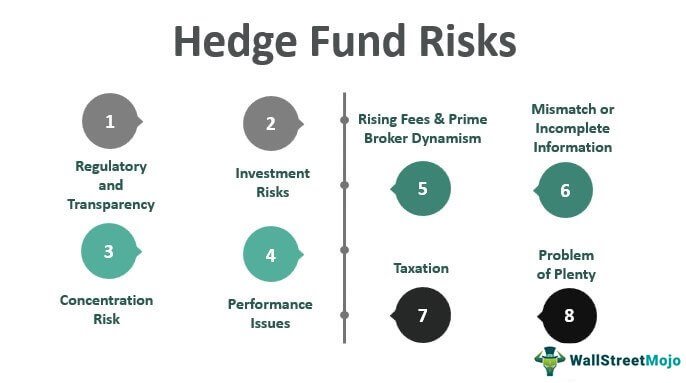
Risks Associated with Hedge Funds
While hedge funds offer the potential for high returns, they also come with significant risks. Investors should carefully consider these risks before investing:
- Loss of principal: Investments in hedge funds are subject to market fluctuations and the possibility of losing the entire invested capital.
- Lack of liquidity: Hedge funds often have lock-up periods, during which investors cannot withdraw their funds. Additionally, secondary markets for hedge fund shares may be limited, further reducing liquidity.
- Leverage: Hedge funds commonly use leverage to amplify their returns. While leverage can magnify gains, it also increases the potential for losses.
- Complex strategies: Hedge funds may employ complex investment strategies that can be difficult for investors to fully understand. This complexity introduces additional risks and the potential for unexpected outcomes.
- Regulatory risks: Due to their less regulated nature, hedge funds may face regulatory scrutiny, which can impact their operations and investment strategies.
- Counterparty risks: Hedge funds may enter into derivative contracts or engage in borrowing from other institutions, exposing investors to counterparty risks if those institutions fail to meet their obligations.
- Performance fees: Hedge funds often charge performance fees, typically a percentage of the profits generated. These fees can erode overall returns, especially during periods of underperformance.
Due Diligence and Risk Management
To mitigate the risks associated with hedge funds, investors should conduct thorough due diligence and implement risk management strategies. Some important considerations include:
- Evaluating the fund manager’s track record and experience in managing similar strategies.
- Understanding the fund’s investment strategy and assessing its suitability to the investor’s risk appetite and investment objectives.
- Examining the fund’s historical performance, including both return and risk metrics, such as volatility and drawdowns.
- Assessing the fund’s risk management procedures, including measures to control and monitor leverage and potential downside risks.
- Reviewing the fund’s terms and conditions, including fees, lock-up periods, and redemption policies.
In conclusion, hedge funds offer unique investment opportunities with the potential for high returns. However, it is important for investors to understand the risks associated with hedge fund investments. Conducting thorough due diligence and implementing risk management strategies can help investors make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of hedge fund investing. By understanding the risks and rewards, investors can make more informed choices and potentially maximize their investment returns. Always consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
What is a hedge fund
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a hedge fund and what are its risks?
A hedge fund is an investment vehicle that pools together funds from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets. Hedge funds aim to generate high returns by using various investment strategies, such as leverage, derivatives, and short selling. However, hedge funds also come with certain risks that investors should be aware of:
What are the risks associated with hedge fund investments?
Investing in hedge funds involves the following risks:
1. Market Risk
Hedge funds are exposed to market risk, which is the potential for losses due to adverse market movements. Factors such as economic conditions, interest rates, and geopolitical events can impact the performance of hedge funds.
2. Liquidity Risk
Hedge funds may impose restrictions on the withdrawal of funds, known as lock-up periods or redemption gates. This can limit investors’ ability to access their money when they need it, potentially creating liquidity risk.
3. Leverage Risk
Hedge funds often use leverage, which involves borrowing money to amplify investment returns. While leverage can enhance profits, it also increases the potential for losses if investments perform poorly.
4. Counterparty Risk
Hedge funds engage in transactions with various counterparties, such as prime brokers and derivative dealers. There is a risk that these counterparties may default on their obligations, leading to losses for the fund.
5. Manager Risk
Hedge funds are highly dependent on the skills and expertise of their fund managers. Poor investment decisions or unexpected events impacting the manager’s ability to execute the investment strategy can result in losses for the fund.
6. Operational Risk
Operational risk refers to the risk of losses due to inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or human error within the hedge fund organization. This can include risks such as fraud, compliance failures, or technology disruptions.
7. Regulatory Risk
Hedge funds operate in a complex regulatory environment and are subject to various rules and regulations. Changes in regulatory requirements can impact the fund’s operations and may result in additional compliance costs.
8. Performance Fee Risk
Hedge funds typically charge a performance fee based on a percentage of the fund’s profits. While this fee structure aligns the interests of the fund manager with investors, it can also create an incentive for the manager to take excessive risks to generate higher fees.
Final Thoughts
Hedge funds are investment vehicles that pool funds from multiple investors and employ various strategies to generate high returns. However, they also come with significant risks. One of the primary risks associated with hedge funds is their use of leverage, which amplifies potential gains but also increases the potential for substantial losses. Additionally, hedge funds operate with less regulatory oversight than traditional investment vehicles, making them prone to more speculative and aggressive investment strategies. Furthermore, hedge funds often charge high fees and have complex structures, limiting accessibility to the average investor. Understanding what a hedge fund is and its risks is essential for investors to make informed decisions about their investment choices.