Curious about the world of peer-to-peer lending and its risks? You’ve come to the right place. Peer-to-peer lending, also known as P2P lending, is a form of borrowing and lending that takes place between individuals online, cutting out traditional financial institutions like banks. It offers an alternative way to secure funds or invest money, but it’s not without its potential pitfalls. In this blog article, we’ll dive into what peer-to-peer lending entails and explore the risks associated with this increasingly popular financial practice. So, let’s delve into the world of peer-to-peer lending and its risks together.
What is Peer-to-Peer Lending and Its Risks
Peer-to-peer lending, also known as P2P lending or crowdfunding, is a financial innovation that has gained significant popularity in recent years. It allows individuals or businesses to lend and borrow money directly from each other through online platforms, bypassing traditional financial institutions like banks. While P2P lending offers several advantages, such as lower interest rates and more accessible borrowing options, it also comes with its fair share of risks. In this article, we will delve into the concept of peer-to-peer lending and explore the potential risks involved.
How Does Peer-to-Peer Lending Work?
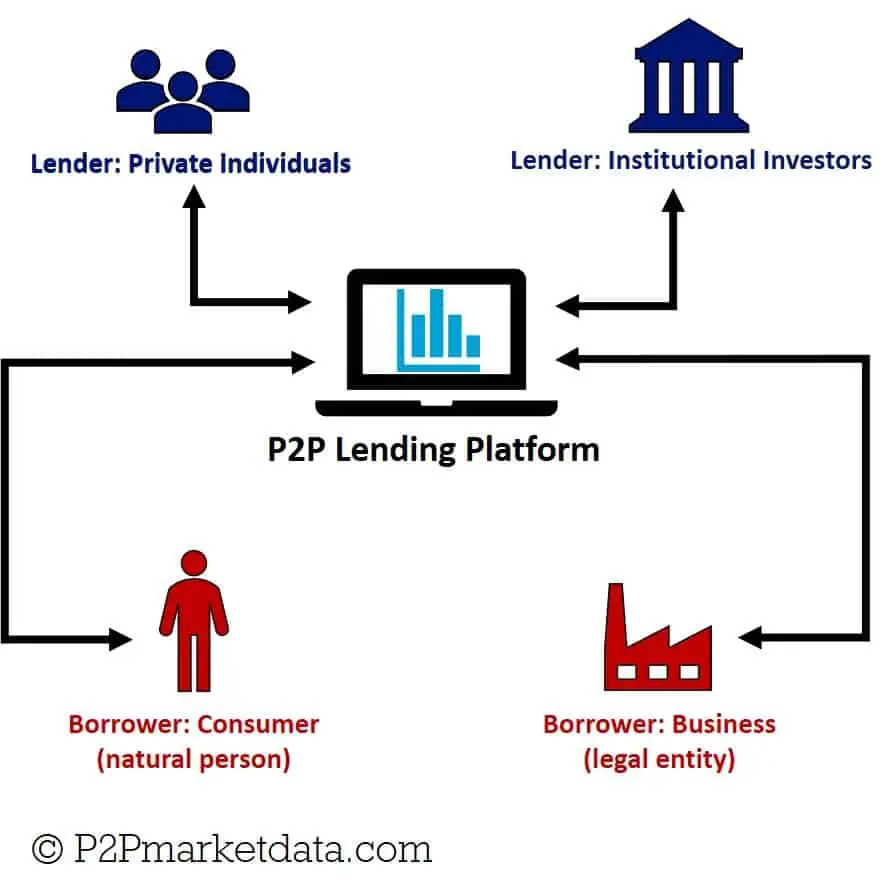
Peer-to-peer lending platforms act as intermediaries that connect lenders with borrowers. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the process typically works:
1. Application: Borrowers apply for a loan by submitting their personal and financial information on the P2P lending platform. They provide details such as the loan amount, purpose, and repayment term.
2. Lender Evaluation: The platform assesses the borrower’s creditworthiness through various means, such as credit checks, income verification, and risk assessment models. This evaluation helps determine the borrower’s risk profile and the interest rate they may be eligible for.
3. Loan Listings: Once approved, the borrower’s loan request is listed on the platform, along with relevant details like interest rate, loan term, and risk category. Potential lenders can browse through these listings to choose the loans they want to fund.
4. Lender Selection: Lenders review the loan listings and select the ones they wish to fund based on their risk appetite and investment objectives. They can either fund the entire loan or a portion of it, which is known as fractional lending.
5. Funding: Once lenders commit to funding a loan, the platform aggregates the funds from multiple lenders to fulfill the borrower’s loan request. This pooling of funds enables the platform to offer loans of various sizes.
6. Loan Repayment: Borrowers make periodic payments, typically monthly, to repay the loan. The platform ensures the distribution of these payments to the respective lenders, including interest earned.
7. Default and Collections: In case of borrower default, the P2P lending platform takes appropriate measures to recover the outstanding debt. This may involve employing collection agencies, legal actions, or other debt recovery strategies.
The Risks of Peer-to-Peer Lending
While peer-to-peer lending presents an alternative and often more convenient borrowing and lending option, it is not without its risks. As with any investment or lending activity, understanding and managing these risks is crucial. Let’s explore some of the potential risks involved in peer-to-peer lending:
- Default Risk: One of the primary risks in P2P lending is the possibility of borrowers defaulting on their loan payments. If a borrower fails to repay the loan, lenders may lose a portion or all of their invested funds. Default rates can vary significantly depending on the borrower’s creditworthiness and the platform’s risk assessment practices.
- Platform Risk: Peer-to-peer lending platforms are responsible for vetting borrowers, managing loan transactions, and facilitating repayments. However, there is a risk of platform failure or fraudulent activities. If a platform shuts down or engages in unethical practices, lenders may face difficulties in recovering their investments.
- Liquidity Risk: Unlike traditional bank deposits or other fixed-income investments, P2P loans often have a fixed term. Lenders may face challenges in accessing their invested funds before the loan term expires. In some cases, platforms offer secondary markets where lenders can sell their loan investments to other investors, but liquidity is not guaranteed.
- Interest Rate Risk: P2P loans typically come with fixed interest rates. However, lenders are exposed to interest rate risk if prevailing market rates rise significantly. This can result in lower returns compared to alternative investment options with higher interest rates.
- Lack of Regulation: While peer-to-peer lending is regulated in many countries, the level of regulation may vary. Some jurisdictions have strict regulations in place to protect investors and borrowers, while others have limited oversight. Limited regulation can expose lenders and borrowers to potential risks related to unfair practices, inadequate dispute resolution mechanisms, or insufficient disclosure of information.
Managing Risks in Peer-to-Peer Lending
While the risks associated with peer-to-peer lending cannot be completely eliminated, there are steps borrowers and lenders can take to mitigate them. Consider the following risk management strategies:
- Diversify Your Investments: Lenders can reduce the impact of default risk by spreading their investments across multiple loans or borrowers. This diversification strategy helps minimize the potential loss from a single default.
- Thoroughly Evaluate Borrowers: Lenders should carefully review the borrower’s profile, credit history, and financial stability before committing to fund a loan. P2P platforms provide information such as credit scores, employment details, and loan purpose to assist lenders in making informed decisions.
- Research and Choose Reliable Platforms: Before participating in P2P lending, conduct thorough research on different platforms. Look for well-established platforms with a track record of successfully facilitating loans and providing reliable investor protection mechanisms.
- Understand the Platform’s Risk Assessment: Each platform may adopt different risk assessment models. Understand how the platform evaluates borrowers’ creditworthiness and assigns risk ratings. This knowledge will help lenders gauge the risk-reward profile of potential loans.
- Monitor and Reinvest: Regularly review the performance of your P2P lending portfolio. Monitor payments, defaults, and the overall health of the loans. Reinvest repaid funds into new loans to maintain a balanced and diversified portfolio.
- Stay Informed about Regulations: Keep yourself updated about the regulatory environment governing P2P lending in your jurisdiction. Understand the rights and protections available to both borrowers and lenders. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions and mitigate regulatory risks.
Peer-to-peer lending can be an attractive alternative for both borrowers and lenders, providing opportunities for financial inclusion and potentially higher returns. However, it is essential to approach P2P lending with caution and awareness of the associated risks. By understanding and managing these risks effectively, participants in peer-to-peer lending can make informed decisions and navigate the lending landscape more confidently. Remember to diversify your investments, thoroughly evaluate borrowers, choose reliable platforms, and stay informed about regulations to enhance your P2P lending experience.
Peer-to-Peer Lending (AKA P2P Loans or Crowdlending) Explained in One Minute
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is peer-to-peer lending and how does it work?
Peer-to-peer lending, also known as P2P lending, is a method of borrowing and lending money directly through an online platform, cutting out traditional financial institutions like banks. Individuals or businesses looking for loans are matched with investors who are willing to provide the funds. The lending process is facilitated by the platform, which verifies borrowers and lenders, sets loan terms, and handles repayments.
What are the risks associated with peer-to-peer lending?
While peer-to-peer lending can be an attractive investment opportunity, it also carries certain risks. These risks include:
1.
Default Risk:
There is a chance that borrowers may default or be unable to repay the loan, resulting in potential losses for lenders.
2.
Lack of Regulation:
Peer-to-peer lending platforms have less regulatory oversight compared to traditional financial institutions, meaning there may be fewer protections for investors.
3.
Liquidation Risk:
Unlike in traditional lending, it can be challenging to sell or transfer the loan to another party in case of financial difficulties.
4.
Platform Risk:
The success and reliability of a peer-to-peer lending platform can impact the overall experience and returns of investors. Operational issues or platform failures may lead to delays or loss of funds.
5.
Marketplace Risk:
Peer-to-peer lending is influenced by market conditions. Economic downturns, changes in interest rates, or shifts in investor sentiment can impact the performance of loans.
6.
Information Asymmetry:
Lenders may face challenges in assessing the creditworthiness of borrowers accurately. Limited access to complete financial information increases the risk of making uninformed lending decisions.
7.
Diversification Risk:
Investing in a single loan or a limited number of loans exposes lenders to higher risk compared to a well-diversified portfolio of loans.
8.
Regulatory Changes:
Changes in regulations can affect peer-to-peer lending platforms and may impact the availability, profitability, or overall viability of this form of lending.
Please note that these risks can vary depending on the specific platform and loan characteristics. It is important for investors to carefully evaluate the risks and consider diversification strategies when engaging in peer-to-peer lending.
Final Thoughts
Peer-to-peer lending is a financing alternative that connects individual lenders with borrowers through online platforms. While it offers potential benefits such as higher returns for lenders and easier access to credit for borrowers, it also carries certain risks. One of the main risks is the potential for default or late repayment by borrowers, which can result in financial losses for lenders. Additionally, the lack of regulation and oversight in some peer-to-peer lending platforms increases the risk of fraud and scams. It is crucial for both lenders and borrowers to carefully assess the risks involved and diversify their portfolios to minimize potential losses in this form of lending.