Asset allocation is a critical aspect of personal finance that often gets overlooked or misunderstood. In simple terms, it refers to the process of distributing your investments among various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash, to achieve your financial goals. Getting it right can significantly impact your long-term financial success. But what exactly is asset allocation in personal finance? It’s the strategic planning and decision-making that allows you to create a well-diversified investment portfolio tailored to your risk tolerance and objectives. So, let’s delve deeper into the world of asset allocation and discover how it can shape your financial future.
What is Asset Allocation in Personal Finance?
Asset allocation is a crucial aspect of personal finance that involves dividing your investments among different asset classes to achieve specific financial goals while managing risk. It is the process of determining how much of your investment portfolio should be allocated to different types of assets such as stocks, bonds, cash, real estate, and more. This strategy aims to strike a balance between potential returns and risk tolerance based on individual circumstances and financial objectives.
The Importance of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation plays a vital role in achieving long-term financial success. Here are some key reasons why asset allocation is important:
- Diversification: By diversifying your investment portfolio across different asset classes, you reduce the risk of losing all your money in case one type of asset performs poorly. Diversification helps smoothen the investment ride and potentially increase returns.
- Risk Management: Asset allocation allows you to allocate investments based on your risk tolerance and investment goals. By spreading investments across various asset classes, you can manage risk levels and potentially minimize losses during market downturns.
- Increased Potential Returns: By allocating your investments strategically, you can potentially enhance your overall returns. Different asset classes tend to perform differently during various market conditions, so spreading your investments across multiple assets can increase the chances of capturing positive market trends.
- Financial Goal Alignment: Asset allocation helps align your investments with your financial goals. Whether you are saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or your child’s education, diversifying your portfolio based on your specific goals and time horizon can optimize your chances of achieving them.
Factors Affecting Asset Allocation
Determining the ideal asset allocation can vary from person to person, depending on several factors. These factors should be carefully considered when creating an asset allocation strategy:
1. Risk Tolerance
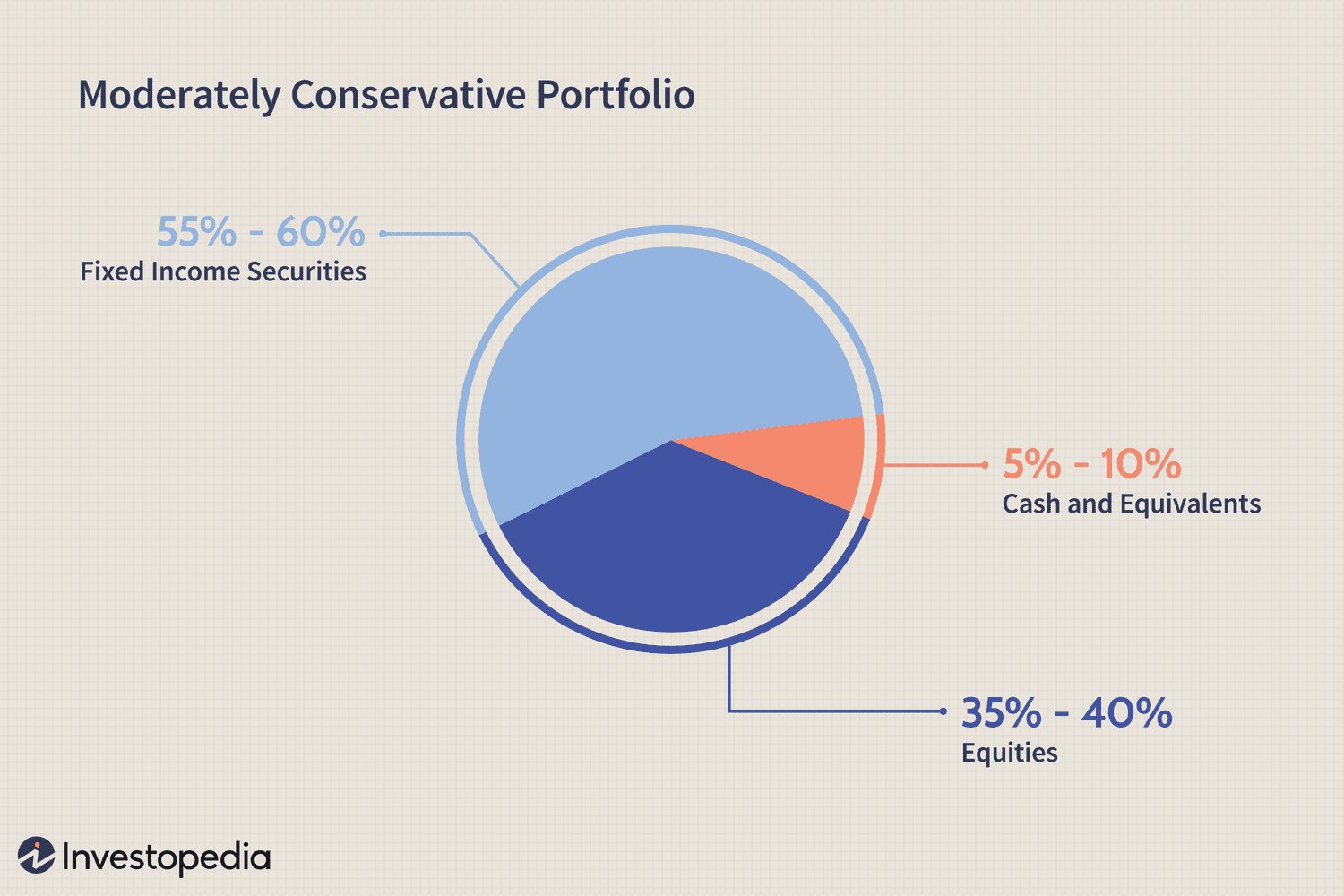
Your risk tolerance refers to your ability and willingness to endure the ups and downs of the market. It depends on various factors, such as your age, financial situation, investment knowledge, and emotional tolerance for potential losses. A higher risk tolerance typically allows for a more aggressive asset allocation with a higher proportion of stocks, while a lower risk tolerance may favor a more conservative approach with a larger allocation to bonds and cash.
2. Time Horizon
Your time horizon is the length of time you have until you need to access your investment funds. It plays a significant role in determining your asset allocation because the longer your time horizon, the more risk you can afford to take. For goals that are far in the future, such as retirement, you may allocate a larger portion of your portfolio to growth-oriented assets like stocks. Conversely, if you have a short-term goal, like purchasing a house in a few years, a more conservative asset allocation may be appropriate.
3. Financial Goals
Your financial goals shape your asset allocation strategy. For instance, if you have a goal to save for your child’s education, your asset allocation may be different than someone who is saving for retirement. Each goal has a unique time horizon and risk tolerance level, which will influence the allocation of assets in your portfolio.
4. Investment Knowledge
Your understanding of different asset classes and investment vehicles can impact your asset allocation decisions. If you lack knowledge in a particular area, it may be wise to seek professional advice or conduct thorough research before making investment choices. Educating yourself about different investments can help you allocate your assets more effectively.
Common Asset Classes for Asset Allocation
1. Stocks
Stocks, also known as equities, represent ownership shares in a company. Investing in stocks gives you the opportunity to participate in the growth and profitability of businesses. While stocks can be volatile, they tend to generate higher returns over the long term. Including stocks in your asset allocation can help capitalize on potential market growth.
2. Bonds
Bonds, also referred to as fixed-income securities, are debt instruments issued by governments or corporations to raise capital. When you buy a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity. Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks and provide a fixed income stream. Including bonds in your asset allocation can provide stability and income generation.
3. Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include savings accounts, money market funds, and short-term government bonds. These assets are highly liquid and provide stability to your portfolio. Cash and cash equivalents are crucial for emergency funds and short-term financial goals. While they typically generate lower returns compared to stocks and bonds, their presence can balance the risk of other investments.
4. Real Estate
Real estate investments involve purchasing properties or investing in real estate investment trusts (REITs) that own and manage income-generating property portfolios. Real estate can provide both rental income and potential capital appreciation. Allocating a portion of your portfolio to real estate can diversify your investments beyond traditional stocks and bonds.
5. Alternative Investments
Alternative investments include assets such as commodities, hedge funds, private equity, and precious metals like gold. These investments often have low correlation with traditional asset classes, offering potential diversification benefits. However, alternative investments are typically more complex and may require a higher level of expertise or professional guidance.
Creating an Asset Allocation Strategy
Creating an effective asset allocation strategy involves a careful consideration of your financial situation, goals, risk tolerance, and investment knowledge. Here are some steps to help you get started:
1. Determine Your Financial Goals
Identify your short-term and long-term financial goals, such as retirement planning, buying a house, or funding your child’s education. Knowing your goals will help you allocate your assets based on different time horizons and risk levels.
2. Assess Your Risk Tolerance
Evaluate your risk tolerance by considering your age, financial stability, investment knowledge, and emotional capacity to withstand market fluctuations. This assessment will guide you in determining the appropriate balance between growth-oriented assets and more conservative investments.
3. Understand Asset Classes
Educate yourself about different asset classes and their characteristics. Understand how stocks, bonds, cash equivalents, real estate, and alternative investments behave in various market conditions. This knowledge will enable you to make informed decisions when allocating your assets.
4. Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification is key to managing risk in your investment portfolio. Allocate your assets across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to spread risk. Diversification can help mitigate the impact of poor performance in one area by potentially benefiting from better performance in another.
5. Regularly Monitor and Rebalance
Review your asset allocation periodically and make adjustments as needed. Market fluctuations can cause imbalances in your portfolio, deviating from your intended allocation. Rebalancing involves buying or selling assets to restore your desired allocation. Regular monitoring and rebalancing ensure that your asset allocation remains aligned with your goals and risk tolerance.
In conclusion, asset allocation is a fundamental strategy in personal finance that involves dividing investments across different asset classes. It helps manage risk, optimize returns, and align investments with specific financial goals. By understanding the factors influencing asset allocation and following a systematic approach, individuals can create an effective asset allocation strategy tailored to their unique circumstances and aspirations. Remember, seeking professional advice from a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and guidance throughout this process.
Asset Allocation | What You Need To Know
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is asset allocation in personal finance?
Asset allocation in personal finance refers to the strategy of distributing your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash. It involves determining the ideal mix of these assets based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Why is asset allocation important?
Asset allocation is important because it helps to diversify your investment portfolio and spread out the risk. By investing in different asset classes, you reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio. It allows you to balance the potential for growth with the need for stability and income.
How does asset allocation work?
Asset allocation works by dividing your investment portfolio into different asset classes based on their characteristics, such as risk and return. The aim is to create a diversified portfolio that aligns with your financial objectives. Different asset classes have varying levels of risk and potential for returns, so by allocating your investments accordingly, you can manage risk while aiming for growth.
What factors should I consider when determining asset allocation?
Several factors should be considered when determining asset allocation, including your financial goals, time horizon, risk tolerance, and current market conditions. It is important to assess your investment objectives, understand how long you can stay invested, evaluate your comfort level with risk, and consider the current economic climate and market trends.
Should I adjust my asset allocation over time?
Yes, it is generally recommended to periodically review and adjust your asset allocation. As your financial situation and goals change, you may need to rebalance your portfolio to ensure it remains aligned with your objectives. Additionally, market conditions and economic trends can also impact the performance of different asset classes, making adjustments necessary.
What are the different asset classes used in asset allocation?
The main asset classes used in asset allocation include stocks (equities), bonds (fixed income), cash equivalents, and alternative investments. Stocks offer the potential for high returns but also come with higher volatility. Bonds provide income and stability. Cash equivalents are low-risk investments like money market funds. Alternative investments include real estate, commodities, and hedge funds.
How do I determine the right asset allocation for me?
The right asset allocation depends on various factors, including your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. It is recommended to consult with a financial advisor who can assess your personal circumstances and help create an asset allocation strategy that aligns with your specific needs and objectives.
What are the potential risks of improper asset allocation?
Improper asset allocation can expose you to potential risks such as overexposure to a single asset class, lack of diversification, and failure to achieve your financial goals. If your investments are not properly allocated, you may miss out on potential returns or be overly vulnerable to market downturns. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your asset allocation can help mitigate these risks.
Final Thoughts
Asset allocation is a crucial aspect of personal finance that involves diversifying investments across different asset classes. By allocating funds to a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash, individuals reduce their exposure to any single investment. This strategy helps to maximize returns while minimizing risk. Through proper asset allocation, investors can balance their portfolio based on their financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. It is important to periodically review and adjust asset allocation to ensure alignment with changing circumstances. In personal finance, understanding and implementing asset allocation is essential for building a well-rounded and resilient investment portfolio.