Are you feeling overwhelmed by the thought of preparing for a financial audit? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. In this article, we will guide you through the process of how to prepare for a financial audit, step by step. Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a large organization, ensuring that your financial records are accurate and organized is crucial. So, let’s dive right in and learn how to prepare for a financial audit effectively. You’ll find that it’s not as daunting as it may seem! Let’s get started.
How to Prepare for a Financial Audit
Preparing for a financial audit can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, it can be a smooth and efficient process. A financial audit is an examination of an organization’s financial records, systems, and controls performed by either an internal team or an external auditor. It helps ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial information, as well as compliance with applicable laws and regulations. In this article, we will guide you through the steps to prepare for a financial audit and provide useful tips and best practices along the way.
1. Understand the Purpose and Scope of the Audit
Before diving into the preparation process, it’s crucial to understand the purpose and scope of the audit. Take the time to review the engagement letter or agreement with the auditor, which outlines the objectives, timelines, and specific areas to be examined. This will give you a clear understanding of what to expect and allow you to focus your efforts on the relevant areas.
1.1 Identify Key Stakeholders
Identify the key stakeholders involved in the audit process within your organization. These may include the finance team, senior management, board of directors, or external consultants. Establish clear lines of communication and assign responsibilities to ensure a coordinated and efficient audit preparation.
1.2 Determine the Audit Period
Determine the audit period, which usually corresponds to the organization’s fiscal year. Ensure that all financial records, transactions, and supporting documentation for the specified period are organized and readily accessible.
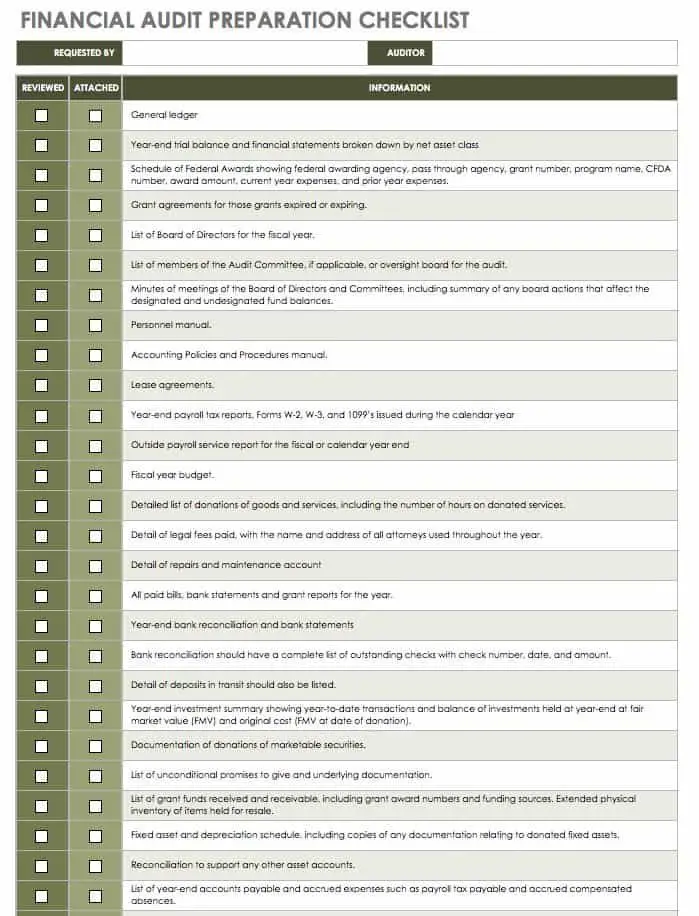
2. Organize and Review Financial Records
One of the most crucial aspects of preparing for a financial audit is organizing and reviewing your financial records. By having well-organized records, you not only streamline the audit process but also demonstrate your commitment to financial transparency and accountability.
2.1 Establish a Document Management System
Implement a document management system that allows you to easily store, retrieve, and track financial records. This could be a physical filing system or an electronic system such as cloud storage or accounting software. Whichever system you choose, ensure it meets your organization’s needs and provides adequate security for sensitive financial information.
2.2 Gather Financial Statements and Reports
Compile all the necessary financial statements and reports for the audit. These typically include the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in equity. Review these documents for accuracy and completeness, and ensure they adhere to the applicable accounting standards.
2.3 Reconcile Accounts and Transactions
Perform a thorough reconciliation of all accounts and transactions. This involves comparing your financial records with external sources such as bank statements, invoices, receipts, and payroll records. Identify and resolve any discrepancies or irregularities before the audit to maintain the integrity of your financial data.
2.4 Review Internal Controls
Evaluate your organization’s internal controls, including financial policies, procedures, and systems. Ensure they are designed effectively to mitigate the risk of errors, fraud, and non-compliance. Document any weaknesses or areas for improvement and develop action plans to address them.
3. Prepare Supporting Documentation
In addition to financial statements, auditors often request supporting documentation to substantiate the recorded transactions. Properly preparing and organizing these documents will facilitate the audit process and demonstrate your commitment to compliance.
3.1 Gather Invoices and Receipts
Collect all invoices, receipts, and other supporting documentation for the recorded transactions. Make sure they are properly labeled, dated, and filed according to the corresponding ledger entries. This will enable auditors to verify the accuracy and legitimacy of the transactions.
3.2 Compile Contracts and Agreements
If your organization has entered into contracts or agreements relevant to the audit, gather copies of these documents. These could include lease agreements, loan agreements, partnership agreements, and any other legally binding contracts. Auditors may review these documents to ensure compliance and assess any associated financial implications.
3.3 Document Insurance Policies and Legal Matters
Compile documentation related to your organization’s insurance policies and any ongoing legal matters. This could include insurance certificates, claims history, pending litigations, or regulatory compliance matters. Providing this information to the auditors will help them assess any potential financial risks and liabilities.
3.4 Maintain Personnel Records
Keep comprehensive personnel records, including employment contracts, salary information, and employee benefits documentation. Auditors may review these records to ensure proper financial reporting and compliance with labor laws and regulations.
4. Conduct Internal Pre-Audit Reviews
Before the external audit begins, it’s beneficial to conduct internal pre-audit reviews to identify and address potential issues or areas of concern. These reviews simulate the audit process and allow you to rectify any deficiencies internally, resulting in a more efficient and effective audit.
4.1 Perform a Mock Audit
Simulate the audit process by conducting a mock audit internally or engaging the services of an external consultant. This exercise helps identify any weaknesses in your processes, internal controls, or financial reporting. Address any findings and implement corrective actions as necessary.
4.2 Review Compliance with Regulations
Assess your organization’s compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and accounting standards. This includes tax compliance, financial reporting requirements, and industry-specific regulations. Identify any potential compliance gaps and develop strategies to rectify them before the audit.
4.3 Address Previous Audit Findings
If your organization has undergone previous audits, review any findings or recommendations from those audits. Ensure that the necessary corrective actions have been implemented and that any recurring issues have been resolved. This demonstrates your commitment to continuous improvement and strengthens your audit readiness.
In conclusion, preparing for a financial audit requires careful planning, organization, and review of your financial records. By understanding the purpose and scope of the audit, organizing your documents, preparing supporting documentation, and conducting internal pre-audit reviews, you can streamline the audit process and ensure a successful outcome. Remember to maintain open communication with the auditors and address any concerns or questions promptly. A well-prepared financial audit not only ensures compliance and accuracy but also instills confidence in stakeholders and strengthens the overall financial management of your organization.
How to audit financial statements | FloQast
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I prepare for a financial audit?
To prepare for a financial audit, follow these steps:
1. Gather all relevant financial documents, such as bank statements, invoices, receipts, and financial reports.
2. Organize your financial records in a systematic and easily accessible manner.
3. Review and reconcile your accounts to ensure accuracy.
4. Perform internal audits to identify and address any potential issues beforehand.
5. Familiarize yourself with auditing standards and regulations applicable to your industry.
6. Maintain clear and transparent communication with your auditors.
7. Address any deficiencies identified in previous audits.
8. Review and update your internal controls to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
9. Conduct a mock audit to identify areas for improvement.
10. Stay up to date with the latest accounting standards and changes in regulations.
What documents should I have prepared for a financial audit?
For a financial audit, you should have the following documents prepared:
1. Income statements and balance sheets
2. Bank statements and reconciliations
3. Sales and purchase invoices
4. General ledger and chart of accounts
5. Tax returns and supporting documents
6. Account receivable and account payable records
7. Payroll records and employee expense reports
8. Internal control documentation
9. Auditor’s work papers from previous audits
10. Any other supporting financial documents relevant to your business.
What are the key benefits of preparing for a financial audit?
Preparing for a financial audit offers several benefits:
1. Ensures accuracy and reliability of financial statements
2. Identifies and rectifies any errors or irregularities in financial records
3. Increases trust and credibility among stakeholders, such as investors and lenders
4. Helps in detecting and preventing fraud
5. Improves financial management and decision-making
6. Provides an opportunity to review and enhance internal controls
7. Helps in understanding the financial health and stability of the business
8. Facilitates compliance with legal and regulatory requirements
How long does it take to prepare for a financial audit?
The time required to prepare for a financial audit varies depending on various factors, including the size and complexity of the organization, the completeness and accuracy of financial records, and the resources available for audit preparation. Generally, the preparation process can take several weeks to a few months.
Do I need to hire an external auditor for a financial audit?
While hiring an external auditor is not always mandatory, it is highly recommended to ensure an independent and unbiased assessment of your financial statements. External auditors bring expertise and credibility to the audit process, providing assurance to stakeholders that the financial statements are reliable and accurate.
What can I do if my business fails the financial audit?
If your business fails a financial audit, it indicates that there are significant issues or deficiencies in your financial records. To address this situation:
1. Analyze the audit findings to understand the specific areas of concern.
2. Take immediate action to rectify any identified errors or irregularities.
3. Consult with professionals, such as accountants or auditors, to seek guidance in resolving the issues.
4. Implement stronger internal controls and improve financial management practices.
5. Communicate transparently with stakeholders about the audit results and the steps taken to address the deficiencies.
Can I prepare for a financial audit without prior audit experience?
While prior audit experience can be beneficial, it is not a prerequisite for preparing for a financial audit. You can still prepare for the audit by:
1. Familiarizing yourself with auditing standards and regulations applicable to your industry.
2. Seeking guidance from professionals, such as accountants or auditors, for specific audit preparation tasks.
3. Reviewing audit documentation and guidelines provided by regulatory bodies.
4. Collaborating closely with your auditors and maintaining clear communication throughout the process.
Should I inform my employees about the financial audit?
It is generally recommended to inform your employees about an upcoming financial audit. Transparency about the audit process helps in fostering a cooperative and supportive environment. Employees can provide necessary documentation and assist with audit inquiries, which can streamline the audit process and help ensure its success.
Final Thoughts
Preparing for a financial audit is a crucial aspect of maintaining a healthy and transparent financial system within an organization. By following a few essential steps, you can ensure a smooth and successful audit process. First, gather and organize all relevant financial documents, such as bank statements, invoices, and receipts. Next, review and reconcile your accounts to identify any discrepancies. It is important to maintain accurate and up-to-date records throughout the year. Additionally, establish internal controls and procedures to safeguard your financial information. Finally, communicate and collaborate with your auditors, providing them with all necessary documentation and addressing any questions or concerns promptly. By proactively preparing for a financial audit, you can demonstrate your commitment to financial integrity and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.