Looking to buy a home? Understanding different mortgage loan types is key. With so many options available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But fear not, we’ve got you covered. In this article, we’ll break down the various mortgage loan types, helping you make an informed decision that suits your financial needs. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or looking to refinance, having a clear understanding of different mortgage loan types can save you both time and money. So, let’s dive in and explore your options!
Understanding Different Mortgage Loan Types
If you’re in the market to buy a home, chances are you’ll need to take out a mortgage loan to finance your purchase. However, navigating the world of mortgage loans can be overwhelming, with various types of loans available to choose from. Understanding the different types of mortgage loans can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and circumstances. In this article, we’ll explore the most common mortgage loan types and their key features.
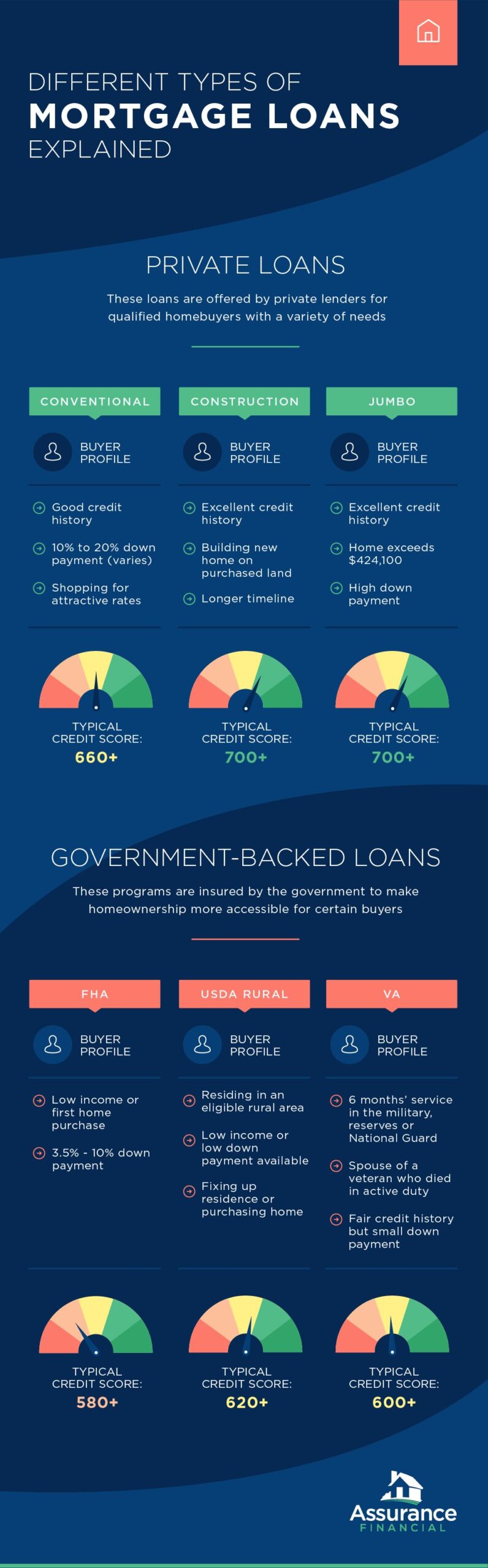
1. Conventional Mortgages
Conventional mortgages are the most traditional and widely used type of mortgage loans. These loans are not insured or guaranteed by any government entity, such as the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) or the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). Instead, conventional mortgages are offered by private lenders, including banks, credit unions, and mortgage companies.
Key Features of Conventional Mortgages:
- Down Payment: Typically, conventional mortgages require a down payment of at least 5% to 20% of the home’s purchase price. However, some lenders may offer specialized loans with lower down payment options, such as 3% down payment programs.
- Credit Score: Lenders typically require a higher credit score for conventional mortgages compared to other loan types. A credit score of 620 or above is generally preferred.
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): If you make a down payment of less than 20%, you may be required to pay for PMI. This insurance protects the lender in case you default on your loan.
- Loan Limits: Conventional mortgages have maximum loan limits set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA). These limits vary based on the location of the property.
2. FHA Loans
FHA loans are mortgage loans insured by the Federal Housing Administration, a government agency under the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). These loans are designed to help individuals and families with lower credit scores or limited down payment savings to become homeowners.
Key Features of FHA Loans:
- Down Payment: FHA loans require a minimum down payment of 3.5% of the home’s purchase price. This lower down payment requirement makes it more accessible for borrowers who may not have substantial savings.
- Credit Score: FHA loans are more lenient when it comes to credit score requirements. Borrowers with a credit score of 580 or higher may qualify for the minimum down payment option. However, those with a credit score between 500 and 579 will need to make a higher down payment of 10%.
- Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP): FHA loans come with an upfront mortgage insurance premium and an annual MIP. The MIP provides lenders with protection in case the borrower defaults on the loan.
- Loan Limits: FHA loan limits vary by county and are set annually by HUD. These limits depend on the median home prices in the area and the maximum loan amount that can be insured by the FHA.
3. VA Loans
VA loans are mortgage loans available to veterans, active-duty service members, and eligible surviving spouses. These loans are guaranteed by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and offer benefits such as no down payment and lower interest rates.
Key Features of VA Loans:
- Down Payment: VA loans typically do not require a down payment, making homeownership more accessible to eligible service members and veterans.
- Credit Score: While the VA does not set a minimum credit score requirement, lenders may have their own credit score criteria. Generally, a credit score of 620 or above is preferred.
- Funding Fee: VA loans require a funding fee, which is a one-time payment to the VA. The fee amount varies based on factors such as the borrower’s military category, down payment percentage, and whether it is the borrower’s first or subsequent VA loan.
- Loan Limits: VA does not set a specific loan limit. However, they do limit the amount they will guarantee, which in turn affects the loan limit that lenders are willing to offer without requiring a down payment.
4. USDA Loans
USDA loans, also known as Rural Development loans, are offered by the United States Department of Agriculture. These loans are specifically designed to help moderate- to low-income borrowers in rural areas achieve homeownership.
Key Features of USDA Loans:
- Location Eligibility: USDA loans are only available in designated rural areas. These areas are determined by the USDA based on population density.
- Income Eligibility: Borrowers must meet income eligibility requirements to qualify for a USDA loan. The program aims to assist borrowers with modest incomes.
- Down Payment: USDA loans do not require a down payment, making it an attractive option for borrowers with limited savings.
- Mortgage Insurance: USDA loans require mortgage insurance, both an upfront guarantee fee and an annual fee. The guarantee fee acts similarly to mortgage insurance, protecting the lender in case of default.
- Loan Limits: USDA loans do not have set loan limits. However, the borrower’s income and debt-to-income ratio may determine the maximum loan amount they qualify for.
5. Jumbo Loans
Jumbo loans, also known as non-conforming loans, are mortgage loans that exceed the loan limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, the two government-sponsored enterprises that buy and sell mortgages. These loans are typically used for high-priced properties.
Key Features of Jumbo Loans:
- Loan Amount: Jumbo loans have higher loan limits than conventional mortgages. The specific loan limit varies by location but is generally above $548,250.
- Down Payment: Jumbo loans usually require a larger down payment compared to conventional loans. Lenders may require a down payment of 20% or more of the home’s purchase price.
- Credit Score: Lenders typically have stricter credit score requirements for jumbo loans. A higher credit score is often necessary to qualify for these loans.
- Interest Rates: Jumbo loans often have higher interest rates compared to conventional loans. This is because they carry more risk for lenders due to their larger loan amounts.
6. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs)
Adjustable-rate mortgages, or ARMs, are mortgage loans with an interest rate that adjusts periodically based on an index. These loans typically offer a fixed interest rate for an initial period, often 5, 7, or 10 years, before the rate adjusts annually.
Key Features of Adjustable-Rate Mortgages:
- Initial Fixed-Rate Period: ARMs have an initial fixed-rate period during which the interest rate remains constant. This initial period often provides borrowers with lower interest rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages.
- Adjustment Periods: After the initial fixed-rate period ends, the interest rate adjusts based on a specific index, such as the U.S. Treasury Bill rate or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). The adjustment period determines how often the rate can change.
- Rate Caps: ARMs often come with rate caps to limit how much the interest rate can change during each adjustment period. Rate caps provide borrowers with some protection against significant rate increases.
- Interest Rate Risk: One of the drawbacks of ARMs is the uncertainty surrounding future interest rate fluctuations. If interest rates increase significantly, borrowers may face higher monthly mortgage payments.
Understanding the different types of mortgage loans is crucial when choosing the right loan for your home purchase. Whether you’re considering a conventional mortgage, FHA loan, VA loan, USDA loan, jumbo loan, or adjustable-rate mortgage, each loan type has its own unique features, benefits, and eligibility requirements. By evaluating your financial situation, credit score, down payment savings, and long-term goals, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your needs and helps you achieve your homeownership dreams. Remember to consult with a mortgage professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Types of Mortgage Loans Explained | Chase
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the different types of mortgage loans available?
There are several types of mortgage loans available, including conventional loans, FHA loans, VA loans, USDA loans, and jumbo loans. Each loan type has its own eligibility criteria and benefits.
How does a conventional mortgage loan work?
A conventional mortgage loan is not insured or guaranteed by the government. It typically requires a higher credit score and a down payment of at least 3%. The interest rates may vary based on market conditions and the borrower’s creditworthiness.
What is an FHA loan?
An FHA loan is a mortgage loan insured by the Federal Housing Administration. It is designed to help borrowers with lower credit scores and smaller down payments. FHA loans often have more flexible eligibility requirements and may offer lower interest rates.
What is a VA loan?
A VA loan is a mortgage loan available to eligible veterans, active-duty service members, and surviving spouses. It is guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs and offers several benefits, including no down payment requirement and lower interest rates.
What is a USDA loan?
A USDA loan is a mortgage loan offered by the United States Department of Agriculture for properties located in eligible rural areas. It is designed to help low-to-moderate-income borrowers with no down payment requirement and low-interest rates.
What is a jumbo loan?
A jumbo loan is a mortgage loan that exceeds the conforming loan limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. These loans are typically used to finance high-value properties and may have stricter eligibility criteria and higher interest rates.
What is the difference between fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgage loans?
A fixed-rate mortgage loan has a set interest rate for the entire loan term, providing consistent monthly payments. On the other hand, an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) loan has an interest rate that can change periodically, resulting in varying monthly payments.
Which mortgage loan type is best for me?
The best mortgage loan type for you depends on your financial situation, credit score, down payment amount, and specific needs. It is recommended to consult with a mortgage lender or advisor who can assess your circumstances and guide you towards the most suitable option.
Final Thoughts
Understanding different mortgage loan types is crucial when making one of the most significant financial decisions in life. With a variety of options available, it is important to have a clear understanding of each type. Fixed-rate mortgages offer stability and predictability, while adjustable-rate mortgages provide flexibility. FHA loans are ideal for first-time homebuyers with low down payment requirements, while VA loans cater to veterans and military personnel. Jumbo loans are designed for high-priced properties, and USDA loans offer financing for rural areas. By understanding the nuances of these mortgage loan types, borrowers can make informed decisions to suit their needs and financial goals.