Are you a beginner in the world of finance, struggling to make sense of all the complicated jargon? Understanding financial jargon for beginners can be quite a daunting task, but fear not! In this article, we will dive straight into the realm of finance, uncovering the secrets behind those perplexing terms and concepts. No need to worry about deciphering the financial language anymore – we’ve got you covered! So, let’s embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries together.
Understanding Financial Jargon for Beginners
When it comes to finance, there’s a whole new language to learn. From acronyms to complex terminology, understanding financial jargon can often feel like deciphering a code. However, once you learn the basic vocabulary and concepts, navigating the financial world becomes much easier. In this article, we’ll break down the most common financial jargon for beginners, providing you with a solid foundation to build upon. So let’s dive in and demystify the world of finance!
1. Common Financial Terms Explained
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s start by introducing some common financial terms that you’re likely to come across:
- Assets: Anything of value that you own, such as cash, investments, or property.
- Liabilities: Debts or obligations you owe, such as loans, mortgages, or credit card balances.
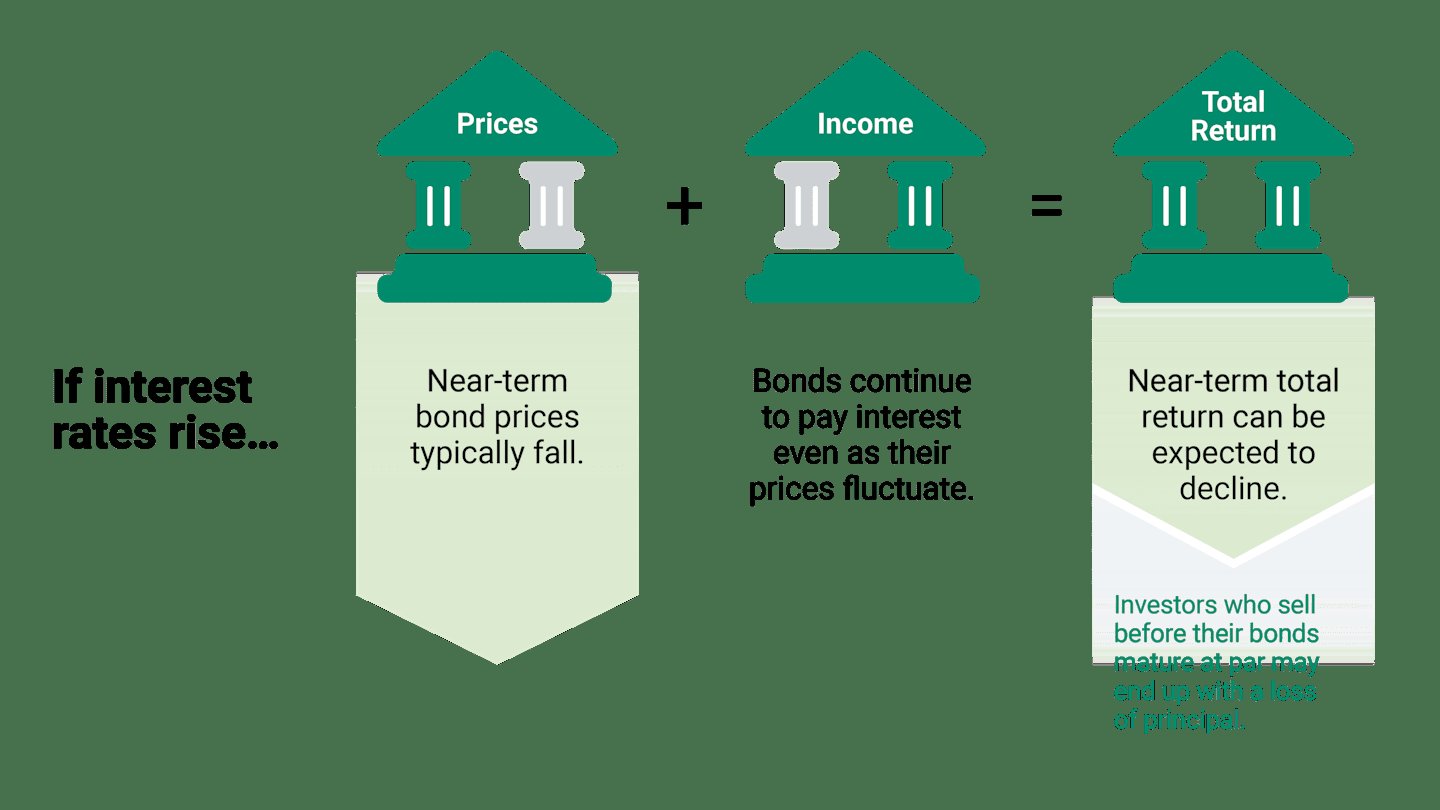
- Interest: The cost of borrowing money or the return on investment.
- Equity: The difference between the value of your assets and liabilities.
- Inflation: The gradual increase in prices over time, reducing the purchasing power of money.
- Dividends: Payments made to shareholders from a company’s profits.
- Capital: Money used to invest or start a business.
While this list is by no means exhaustive, it provides a starting point to familiarize yourself with some essential financial terms. Don’t worry if it seems overwhelming at first. As you continue your journey, these terms will become second nature.
2. Understanding Acronyms and Abbreviations
The finance industry loves acronyms and abbreviations, and it’s important to understand what they mean. Here are a few common ones:
- APR: Annual Percentage Rate, which represents the yearly cost of borrowing or the return on investment.
- ROA: Return on Assets, a measure of how efficiently a company is using its assets to generate profits.
- IRA: Individual Retirement Account, a tax-advantaged account for retirement savings.
- ETF: Exchange-Traded Fund, a type of investment fund that trades on stock exchanges.
- NAV: Net Asset Value, the value of a mutual fund or investment company’s assets minus its liabilities.
- ROI: Return on Investment, a measure of the gain or loss generated on an investment relative to its cost.
- P/E Ratio: Price-to-Earnings Ratio, a valuation metric used to assess a company’s stock price.
Learning these acronyms will help you decipher financial reports, investment advice, and other financial information more effectively.
3. The Importance of Financial Statements
Financial statements provide a snapshot of a company’s financial health, and they often contain various terms and metrics that may be unfamiliar to beginners. Let’s explore the three primary financial statements:
Income Statement
Also known as the profit and loss statement, the income statement shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period. Key terms to understand include:
- Revenue: The total amount of money generated from business activities.
- Expenses: The costs incurred to operate the business.
- Net Income: The company’s profit after deducting all expenses from revenue.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a particular point in time. It comprises three main components:
- Assets: The company’s resources, including cash, inventory, property, and investments.
- Liabilities: The company’s debts or obligations, such as loans and accounts payable.
- Equity: The residual interest in the company’s assets after deducting liabilities.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the flow of cash in and out of a company over a specific period. It consists of three sections:
- Cash from Operating Activities: The cash generated from day-to-day business operations.
- Cash from Investing Activities: The cash used for investing in assets or received from selling assets.
- Cash from Financing Activities: The cash obtained from or used for financing, such as borrowing or repaying debt.
Understanding these financial statements and the associated terms will help you assess a company’s financial performance and make more informed investment decisions.
4. Key Investment Concepts
Whether you’re investing in stocks, bonds, or other assets, it’s crucial to understand some key investment concepts. Here are a few important ones:
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. It helps manage risk and maximize returns.
Risk Tolerance
Your risk tolerance refers to your ability and willingness to bear the uncertainty of investment returns. It influences your investment decisions and asset allocation strategy.
Diversification
Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across various assets or sectors to reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your portfolio.
Market Order
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a security at the current market price. It guarantees execution but doesn’t guarantee the exact price.
Limit Order
A limit order is an instruction to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. It ensures price certainty but may not guarantee execution.
By familiarizing yourself with these investment concepts, you’ll be better equipped to make strategic investment decisions and manage your portfolio effectively.
5. Financial Ratio Analysis
Financial ratios provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and position. Here are a few commonly used financial ratios:
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate profits relative to its revenue, assets, or equity. Examples include the gross profit margin, return on equity (ROE), and return on assets (ROA).
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios assess a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations. The current ratio and quick ratio are common liquidity ratios.
Debt Ratios
Debt ratios indicate a company’s leverage and ability to repay its debts. The debt-to-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio fall into this category.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios measure how well a company utilizes its assets and resources. The inventory turnover ratio and asset turnover ratio are examples of efficiency ratios.
While these ratios provide a starting point for assessing a company’s financial health, it’s important to consider them in conjunction with industry benchmarks and other factors.
6. The Role of a Financial Advisor
When it comes to managing your finances and making investment decisions, seeking the guidance of a financial advisor can be invaluable, especially for beginners. A financial advisor can help:
- Assess your financial situation and goals
- Create a personalized financial plan
- Recommend suitable investment strategies
- Provide ongoing portfolio management
- Offer guidance on tax planning and retirement savings
Working with a financial advisor can give you peace of mind, knowing that you have a professional guiding you through the complexities of the financial world.
Remember, mastering financial jargon takes time and practice. As you continue your financial education journey, you’ll become more comfortable with the terminology and concepts. Don’t hesitate to ask questions, seek advice, and stay curious. The more you understand, the more empowered you’ll be to make informed financial decisions that align with your goals.
Financial Terms Explained as Simply as Possible
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is financial jargon?
Financial jargon refers to the specialized language and terminology used in the field of finance. It includes terms and phrases that may not be commonly understood by beginners or those unfamiliar with financial concepts.
2. Why is it important to understand financial jargon?
Understanding financial jargon is crucial for beginners as it allows them to navigate the complex world of finance with confidence. It helps in making informed decisions, communicating effectively with financial professionals, and comprehending financial documents.
3. How can I start learning financial jargon?
To start learning financial jargon, you can begin by reading books or articles that introduce basic financial concepts. Online resources, such as financial glossaries or educational websites, can also provide valuable assistance. Additionally, engaging with financial professionals or taking courses can further enhance your understanding.
4. What are some common financial terms that beginners should know?
Some common financial terms that beginners should be familiar with include assets, liabilities, equity, interest, dividends, inflation, credit score, stocks, bonds, and budgeting. These are foundational concepts that form the basis of financial knowledge.
5. Can you provide examples of financial jargon in everyday life?
Certainly! Examples of financial jargon in everyday life include terms such as APR (Annual Percentage Rate), ROI (Return on Investment), 401(k), FICO score, mortgage, mutual fund, and net worth. Understanding these terms can help individuals make better financial decisions.
6. Are there any resources available to help in understanding financial jargon?
Yes, there are several resources available to help beginners understand financial jargon. Online platforms, such as Investopedia and NerdWallet, offer comprehensive dictionaries and guides on financial terms. Additionally, financial literacy courses and workshops provided by educational institutions or community organizations can be beneficial.
7. How long does it usually take to grasp financial jargon?
The time it takes to grasp financial jargon can vary depending on individual learning abilities and dedication. With consistent effort and practice, beginners can acquire a solid understanding of financial jargon within a few months. However, it’s important to continue learning and staying updated as financial language evolves.
8. Can understanding financial jargon improve my personal finances?
Absolutely! Understanding financial jargon can significantly improve your personal finances. When you can decipher financial terms and documents, you can make informed decisions about investments, loans, and savings. It allows you to better assess risks and opportunities, ultimately helping you manage and grow your wealth more effectively.
Final Thoughts
Understanding financial jargon can be overwhelming for beginners. However, it is a crucial step towards financial literacy and making informed decisions. By familiarizing yourself with terms such as stocks, bonds, dividends, and interest rates, you can gain confidence in managing your personal finances. Take the time to research and learn about these concepts, and consider seeking guidance from financial experts or educational resources. With patience and persistence, you can gradually develop a solid understanding of financial jargon and navigate the complexities of the financial world with ease.