Understanding financial regulations in banking is crucial for both individuals and businesses. These regulations serve as the framework that ensures stability, fairness, and transparency in the banking industry. Navigating the intricate world of financial regulations can be daunting, but fear not! In this blog article, we will demystify the complexities and provide you with a clear understanding of financial regulations in banking. So, whether you’re a curious individual or a business owner looking to comply with the ever-changing landscape of banking regulations, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Financial Regulations in Banking
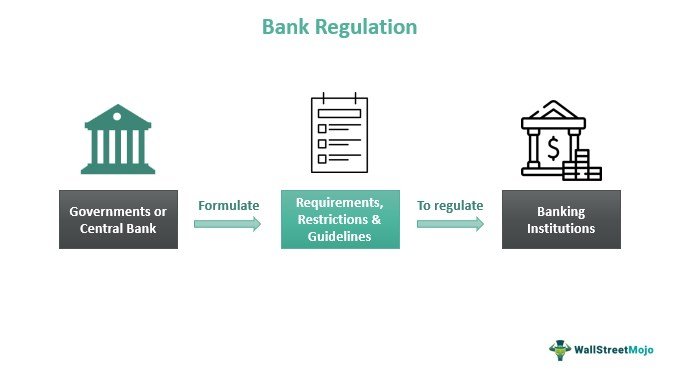
Financial regulations play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the banking industry. They are designed to safeguard depositors, promote fair competition, and prevent financial crises. In this article, we will dive deep into the realm of financial regulations in banking, exploring key concepts, their importance, and the impact they have on both banks and consumers.
Why Do We Need Financial Regulations?
Financial regulations serve various purposes, all of which aim to protect the interests of depositors, investors, and the overall economy. Let’s take a closer look at why these regulations are necessary:
1. Stability: Financial regulations help ensure the stability of the banking system by setting standards and requirements that banks must adhere to. This reduces the likelihood of bank failures and the resulting economic disruptions.
2. Consumer Protection: Regulations are put in place to protect consumers from unfair practices, such as fraud, predatory lending, and deceptive marketing. They establish rules that banks must follow to maintain transparency and treat consumers fairly.
3. Risk Mitigation: Banks engage in activities that carry inherent risks. Regulations help mitigate these risks by imposing capital requirements, liquidity standards, and risk management practices. This ensures that banks have adequate buffers to absorb losses and reduces the probability of systemic risks.
4. Market Confidence: Regulations promote market confidence by providing a framework that fosters trust and transparency. When consumers and investors have confidence in the system, they are more likely to participate in financial activities, which, in turn, boosts economic growth.
Types of Financial Regulations
Financial regulations can be categorized into several types, each addressing specific aspects of banking operations. Here are the main types of financial regulations:
Prudential Regulations
Prudential regulations focus on the soundness and stability of banks. They aim to minimize risks that could threaten the solvency of financial institutions. Key prudential regulations include:
– Capital Adequacy Requirements: Banks are required to maintain a certain amount of capital based on their risk exposure. This ensures that they have sufficient funds to cover losses and protect depositors.
– Liquidity Requirements: Banks must maintain adequate levels of liquid assets to meet short-term obligations and manage liquidity risks effectively.
– Asset Quality Regulations: These regulations ensure that banks maintain a diversified and prudent loan portfolio, reducing the risk of loan defaults and credit concentration.
Consumer Protection Regulations
Consumer protection regulations are designed to safeguard the rights and interests of consumers. They aim to ensure fair and transparent practices in banking and protect consumers from abusive or deceptive behaviors. Key consumer protection regulations include:
– Truth in Lending Act: This regulation requires lenders to disclose the true cost of credit to borrowers, including interest rates, fees, and repayment terms.
– Fair Debt Collection Practices Act: It prohibits unfair, deceptive, or abusive practices by debt collectors and ensures that consumers are treated respectfully during debt collection processes.
– Anti-discrimination Laws: These regulations prohibit discriminatory practices based on race, gender, age, or other protected characteristics, ensuring equal access to financial services for all.
Market Conduct Regulations
Market conduct regulations focus on ensuring fair and efficient market operations. They promote transparency, prevent market manipulation, and protect investors’ interests. Some key market conduct regulations include:
– Insider Trading Regulations: These regulations prohibit individuals from trading securities based on non-public information, ensuring a level playing field for all investors.
– Market Abuse Regulations: They prevent market manipulation, such as spreading false information or engaging in fraudulent trading practices.
– Disclosure Requirements: These regulations mandate that companies disclose accurate and timely information to the public, enabling investors to make informed decisions.
The Role of Regulatory Authorities
Regulatory authorities are responsible for enforcing financial regulations and overseeing the compliance of banks and other financial institutions. They play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and stability of the banking industry. Some prominent regulatory authorities include:
1. Federal Reserve System (Fed): The Fed is the central bank of the United States and is responsible for regulating and supervising banks to ensure the safety and soundness of the banking system.
2. Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC): The OCC is an independent bureau within the U.S. Department of the Treasury, responsible for regulating national banks and federal savings associations.
3. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): The CFPB is tasked with protecting consumers by enforcing consumer protection regulations and promoting fair financial practices.
4. Financial Conduct Authority (FCA): The FCA is the regulatory authority in the United Kingdom, responsible for regulating financial firms to ensure market integrity and consumer protection.
The Global Impact of Financial Regulations
Financial regulations have a significant impact beyond national boundaries. In a globalized economy, actions taken by one country can reverberate worldwide. Here are some key aspects of the global impact of financial regulations:
1. Cross-Border Transactions: Financial regulations affect cross-border transactions, as banks and financial institutions must comply with regulations in both the host country and the country where they operate.
2. Capital Flows: Regulations influence the flow of capital between countries. Stringent regulations may discourage foreign investment, while lenient regulations can attract investment but increase the risk of financial instability.
3. Global Financial Stability: Coordinated efforts among regulatory authorities worldwide are crucial for maintaining global financial stability. Collaboration and information sharing help identify and address potential risks in the global financial system.
4. Regulatory Arbitrage: Differences in regulations across countries can create opportunities for regulatory arbitrage, where financial institutions exploit gaps or inconsistencies in regulation to gain a competitive advantage. This can undermine the effectiveness of regulations and pose risks to the global financial system.
The Future of Financial Regulations
The banking industry is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing consumer needs, and emerging risks. As a result, financial regulations must adapt to stay relevant and effective. Here are some key trends that may shape the future of financial regulations:
1. Technology and Innovation: The rise of fintech and digital banking has prompted regulators to develop new frameworks to address the unique risks and challenges associated with technology-driven financial services.
2. Cybersecurity: With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, regulators are placing more emphasis on cybersecurity regulations to protect financial institutions and consumer data.
3. Sustainability and Climate Risk: As environmental concerns grow, regulators are incorporating sustainability and climate risk considerations into financial regulations to address the potential impact of climate change on financial stability.
4. Enhanced Data Protection: With the proliferation of personal data collection, regulators are focusing on strengthening data protection regulations to safeguard consumer privacy and prevent data breaches.
In conclusion, understanding financial regulations in banking is essential for both banks and consumers. These regulations promote stability, protect consumers, ensure fair market operations, and contribute to the overall integrity of the global financial system. By complying with these regulations, banks can safeguard their operations, build trust, and maintain a healthy and sustainable banking industry. Similarly, consumers benefit from increased transparency, fair treatment, and enhanced confidence in the financial services they rely on. As the banking landscape continues to evolve, regulators must continuously adapt and develop new regulations to address emerging risks and challenges, ensuring a safe and efficient banking ecosystem for all.
Understanding Financial Regulation – The Origins of the Basel Accords
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are financial regulations in banking?
Financial regulations in banking refer to the rules and guidelines set by regulatory authorities to govern the conduct and operations of banks and financial institutions. These regulations aim to ensure the stability and integrity of the banking system, protect consumers, and prevent financial crimes.
Why are financial regulations important in banking?
Financial regulations are important in banking to safeguard the interests of the public, maintain stability in the financial system, and prevent unethical practices. They help regulate the activities of banks, ensure fair competition, and promote transparency and accountability within the banking industry.
How do financial regulations impact banks and customers?
Financial regulations have a direct impact on both banks and customers. For banks, compliance with the regulations requires them to adhere to certain standards of operation, risk management, and reporting. Customers benefit from the regulations as they can have more confidence in the safety of their deposits, fair treatment, and protection from fraudulent practices.
Who sets financial regulations in banking?
Financial regulations in banking are established by regulatory bodies and government agencies tasked with overseeing the financial sector. These may include central banks, financial regulatory authorities, and government ministries responsible for finance or banking.
What are some common financial regulations in banking?
Some common financial regulations in banking include capital adequacy requirements, liquidity regulations, anti-money laundering laws, consumer protection regulations, privacy and data security requirements, and restrictions on risky financial activities. These regulations vary across countries but aim to ensure the stability and integrity of the banking system.
How are financial regulations enforced?
Financial regulations in banking are enforced through various mechanisms. Regulatory bodies conduct regular inspections and audits of banks to assess their compliance. Non-compliance can result in penalties, fines, or other disciplinary actions. Banks are also required to submit regular reports to regulatory authorities to demonstrate their adherence to the regulations.
What is the role of central banks in financial regulations?
Central banks play a crucial role in financial regulations. They are responsible for overseeing the stability and soundness of the banking system. Central banks set monetary policy, supervise banks, and ensure compliance with regulations. They also act as lenders of last resort during financial crises and play a key role in maintaining financial stability.
How do financial regulations adapt to changing market conditions?
Financial regulations need to adapt to changing market conditions to remain effective. Regulatory authorities continuously monitor the industry and assess emerging risks. They review and update regulations as necessary to address new challenges, technological advancements, and evolving market practices. Regular consultations with industry stakeholders are conducted to ensure regulations remain relevant and beneficial for all parties involved.
Final Thoughts
Understanding financial regulations in banking is crucial for both financial institutions and individuals. These regulations serve to protect the stability of the banking system, prevent fraudulent activities, and ensure fair practices. By comprehending these regulations, banks can operate within the legal framework, minimize risks, and maintain customer trust. Moreover, individuals can make informed decisions about their finances, knowing that their money is being handled according to the established rules. Staying up-to-date with financial regulations is an ongoing process as they evolve to adapt to changing economic conditions and emerging technologies. By continually educating ourselves on these regulations, we can contribute to a safer and more transparent banking environment. So, let us strive to deepen our understanding of financial regulations in banking for the benefit of all stakeholders involved.