Are you curious about how mortgage rates fluctuate? Understanding the factors that cause these rates to change is essential for anyone considering a home loan. In this blog article, we will delve into the world of mortgage rates, exploring the key influences that make them rise and fall. By gaining insights into this subject, you will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of the housing market and make informed decisions. So, let’s dive right in and uncover the fascinating dynamics behind understanding how mortgage rates fluctuate.
Understanding How Mortgage Rates Fluctuate
The world of mortgages can sometimes feel like a complex labyrinth, filled with intricate calculations and fluctuating rates. For potential homebuyers, it’s crucial to grasp the basics of how mortgage rates fluctuate. By understanding these fluctuations, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
Mortgage rates are not set in stone; they are influenced by various factors, both economic and individual. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the mechanisms behind mortgage rate fluctuations, providing you with the knowledge needed to navigate the ever-changing landscape. Let’s embark on this journey of understanding together.
The Role of Economic Factors
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping mortgage rates. Lenders take into account various indicators of economic health to evaluate the risk associated with lending money for a mortgage. Some key economic factors that influence mortgage rates include:
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product): The strength of the overall economy, as measured by the GDP, can impact mortgage rates. A robust economy usually leads to higher mortgage rates.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. Lenders consider inflation rates when determining mortgage rates. Higher inflation often leads to higher mortgage rates.
- Employment: The state of the job market has an impact on mortgage rates. When employment rates are high, lenders perceive less risk, resulting in lower mortgage rates.
- Central Bank Policies: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, influence mortgage rates through their monetary policies. Changes in interest rates set by central banks can directly affect mortgage rates.
- Housing Market Conditions: The demand and supply dynamics of the housing market also influence mortgage rates. When the demand for housing is high, lenders may increase rates to balance the risk.
Individual Factors
In addition to economic factors, individual factors unique to each borrower also come into play when determining mortgage rates. Lenders consider these factors to assess the risk associated with an individual borrower. Some key individual factors include:
- Credit Score: Your credit score is a numeric representation of your creditworthiness. Lenders use credit scores to gauge the likelihood of timely mortgage payments. Higher credit scores often result in lower mortgage rates.
- Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV): LTV ratio is the percentage of the loan amount compared to the appraised value of the property. A lower LTV ratio indicates less risk for lenders, potentially leading to lower mortgage rates.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): DTI ratio measures your monthly debt payments compared to your monthly income. A lower DTI ratio demonstrates lower financial risk, which can positively influence mortgage rates.
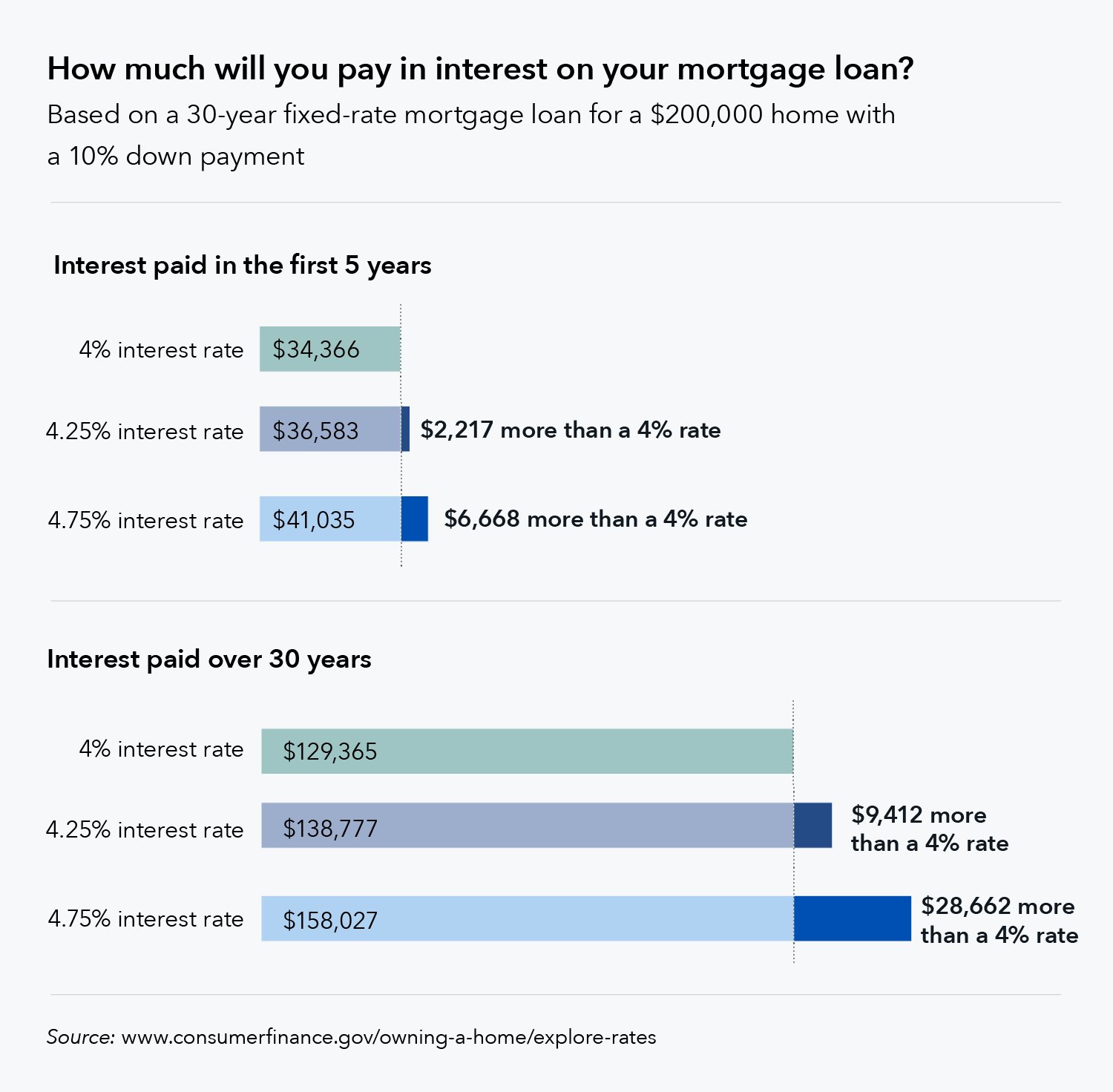
- Loan Term: The length of your mortgage also affects the interest rate. Generally, longer-term loans may have slightly higher interest rates compared to shorter-term loans.
- Type of Interest Rate: The type of interest rate you choose, whether fixed or adjustable, can impact mortgage rates. Fixed-rate mortgages provide stability and predictable payments, while adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) offer lower rates initially but can fluctuate over time.
Market Forces and Mortgage Rates
Mortgage rates are also subject to market forces and investor sentiment. The mortgage market is interconnected with the broader financial markets, and changes in market conditions can influence mortgage rates. Here are some key market factors that can impact mortgage rates:
- Bond Yields: Mortgage rates often move in tandem with bond yields. When bond yields rise, mortgage rates tend to follow suit.
- Competition Among Lenders: Lenders compete to attract borrowers, and this competition can lead to lower rates. Keep an eye on different lenders and compare their offerings to secure the best possible mortgage rate.
- Investor Demand for Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS): Mortgage loans are often packaged together as mortgage-backed securities and sold in the secondary market to investors. The demand for these securities affects mortgage rates. When demand is high, rates may decrease.
- Market Sentiment and Global Events: Financial markets are influenced by both domestic and global events. Economic uncertainties or geopolitical tensions may lead investors to seek safer investments, causing mortgage rates to decrease.
Impact of Interest Rate Trends
Interest rate trends, determined by the factors discussed above, impact both existing mortgage holders and potential homebuyers. Understanding these trends can help you make informed decisions:
- Refinancing Opportunities: When interest rates drop significantly, it may be an opportune time to refinance your mortgage. Refinancing allows you to replace your existing mortgage with a new one at a lower interest rate, potentially reducing your monthly payments.
- Mortgage Affordability: Rising interest rates may decrease your purchasing power, as higher rates lead to higher monthly mortgage payments. It’s essential to consider interest rate trends when determining your budget for homeownership.
- Housing Market Dynamics: Fluctuating mortgage rates can impact the housing market overall. When rates are low, it may spur more homebuying activity, potentially driving up house prices. Conversely, higher rates may slow down the market.
- Timing Your Mortgage: Taking advantage of favorable interest rate trends can result in significant savings over the life of your mortgage. Careful monitoring of interest rate trends allows you to time your mortgage application for optimal rates.
Understanding how mortgage rates fluctuate empowers you to make informed decisions as a homeowner or homebuyer. By staying informed about economic factors, individual factors, and market forces, you can navigate the mortgage landscape with confidence.
Remember, mortgage rates can change daily, so it’s crucial to stay updated and consult with mortgage professionals to ensure you find the most suitable mortgage product for your needs. Armed with knowledge, you can embark on your homeownership journey with confidence and financial prudence.
Interest Rate Secrets: How Mortgage Rates Are Determined
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What factors cause mortgage rates to fluctuate?
Mortgage rates can fluctuate due to various factors such as changes in the economy, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, inflation rates, and the overall demand and supply for mortgages in the market.
How often do mortgage rates change?
Mortgage rates can change daily or even multiple times within a day, depending on the market conditions and other factors affecting interest rates.
What is the role of the Federal Reserve in mortgage rate fluctuations?
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in mortgage rate fluctuations as it sets the target for the federal funds rate. When the Federal Reserve raises or lowers this rate, it can influence mortgage rates indirectly, impacting borrowing costs for consumers.
Are mortgage rates affected by inflation rates?
Yes, mortgage rates can be influenced by inflation rates. When inflation is high, lenders may increase mortgage rates to compensate for the eroding purchasing power of the money they lend out.
How can I monitor mortgage rate fluctuations?
To monitor mortgage rate fluctuations, you can follow financial news sources, check with local lenders or mortgage brokers, and utilize online resources that provide real-time updates on mortgage rates.
Do mortgage rates fluctuate regionally?
Yes, mortgage rates can vary from one region to another due to factors such as local housing market conditions, economic indicators specific to certain areas, and even lender competition within a particular region.
Can my credit score impact mortgage rate fluctuations?
Absolutely. Credit scores play a significant role in determining the interest rate you may qualify for when applying for a mortgage. Higher credit scores often result in lower interest rates, while lower credit scores can lead to higher rates.
What can I do to take advantage of lower mortgage rates?
To take advantage of lower mortgage rates, you can consider refinancing your existing mortgage, shopping around for the best rates and terms, improving your credit score, and paying attention to market trends and economic indicators that may signal a favorable time to buy or refinance a home.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how mortgage rates fluctuate is crucial for anyone considering buying or refinancing a home. Various factors contribute to these fluctuations, such as economic conditions, inflation, and market demand. By monitoring these indicators, borrowers can gain insight into potential changes in mortgage rates. Additionally, staying informed about the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions and regularly reviewing credit scores can help borrowers secure more favorable rates. While predicting exact rate changes is impossible, understanding the factors that influence mortgage rates empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their home loans.