If you’re new to stock trading or simply looking to deepen your understanding, you may have come across the term “market orders.” Understanding market orders in stock trading is key to navigating the fast-paced world of investments. In this article, we’ll break down the ins and outs of market orders, helping you gain confidence and make informed decisions. So, let’s dive right in and demystify the concept of market orders in the exciting realm of stock trading.
Understanding Market Orders in Stock Trading
When it comes to stock trading, there are different types of orders that investors can use to buy or sell stocks. One of the most commonly used order types is the market order. A market order is an instruction from an investor to a broker to buy or sell a stock at the best available price in the market. In this article, we will delve into the details of market orders in stock trading, their benefits, and considerations to keep in mind when using them.
What is a Market Order?
A market order is a straightforward order that investors use to quickly buy or sell securities at the current market price. When you place a market order, you are essentially telling your broker that you want to execute the order immediately at the best available price in the market. The execution of a market order is typically fast, as the broker will look for the best available price and execute the trade promptly.
Benefits of Market Orders
Market orders offer several advantages that make them popular among investors. Here are some of the key benefits of using market orders in stock trading:
1. Simplicity and Speed
Market orders are incredibly simple to understand and execute. There are no complicated instructions or parameters to set, as you are simply buying or selling at the prevailing market price. This simplicity makes market orders ideal for investors who want to quickly enter or exit a position without delay.
2. Guaranteed Execution
When you place a market order, you can be confident that the trade will be executed. Market orders prioritize execution over the price of the stock, ensuring that you will be able to buy or sell the desired securities. This is particularly crucial for highly liquid stocks, where execution speed is essential.
3. Liquidity
Market orders help provide liquidity to the stock market. When investors place market orders, they are essentially adding to the overall volume of trading activity, making it easier for other market participants to buy or sell stocks. This liquidity can contribute to a more efficient and smoother market.
4. Best Available Price
Market orders aim to execute at the best available price in the market. Since market orders prioritize execution over price, you are likely to get a fill at or near the current market price. This is beneficial when trading highly liquid stocks or in fast-moving markets where prices can change rapidly.
Considerations When Using Market Orders
While market orders offer speed and simplicity, there are a few considerations to keep in mind when using them:
1. Price Volatility
One of the main risks associated with market orders is price volatility. In fast-moving markets, the price of a stock can change significantly between the time you place the market order and when it gets executed. This can result in a higher or lower fill price than expected. If you are trading highly volatile stocks, it is essential to be aware of this risk.
2. Execution Slippage
Execution slippage occurs when the price at which your market order gets executed is different from the expected fill price. This can happen due to market fluctuations, order size, or the depth of the order book. It is crucial to understand that while market orders prioritize execution, the final price may not be exactly what you see at the time of placing the order.
3. Illiquid Stocks
While market orders work well for highly liquid stocks, they may not be suitable for less-traded or illiquid stocks. In these cases, the bid-ask spread can be wider, resulting in a larger difference between the buy and sell prices. It’s important to consider the liquidity of the stock before using a market order.
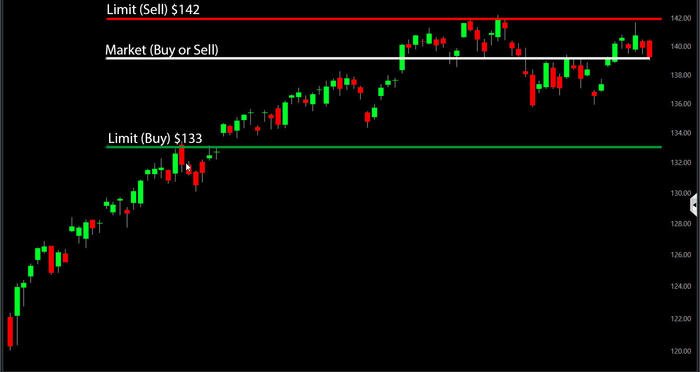
Market Orders vs. Limit Orders
In addition to market orders, another commonly used order type in stock trading is the limit order. Understanding the differences between market orders and limit orders is essential for investors. Here’s a comparison:
Market Orders:
- Execute at the best available price in the market
- Provide guaranteed execution
- Work well for highly liquid stocks
- Can be subject to price volatility and execution slippage
Limit Orders:
- Set a specific price at which you want to buy or sell
- Execution is not guaranteed
- Allow you to control the fill price
- Work well for investors who want more control over the execution price
Depending on your trading strategy, you may choose to use market orders or limit orders in different situations. Market orders are suitable for investors who prioritize speed and execution certainty, while limit orders are preferable for those who want more control over the price at which they buy or sell stocks.
Market orders are a fundamental tool for investors in stock trading. They offer simplicity, speed, and guaranteed execution. While they have advantages, it’s important to keep in mind the considerations associated with market orders, such as price volatility and execution slippage. By understanding the pros and cons of market orders, investors can make informed decisions when executing trades.
Stock Order Types: Market Order, Limit Order, Stop Order, Stop Loss
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a market order in stock trading?
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a stock at the best available price in the market. It ensures that the order is executed quickly, but the actual price may vary from the current price displayed due to market fluctuations.
How does a market order work?
When you place a market order to buy or sell a stock, your broker immediately executes the order at the prevailing market price. The execution is typically swift, ensuring that you enter or exit the position without delay.
Are market orders guaranteed to be executed?
Market orders are designed to be executed quickly, but they are not guaranteed to be filled at a specific price. While the order will be executed, the actual price at which the trade is executed may differ from the displayed price due to market conditions.
What are the advantages of using market orders?
Market orders provide the advantage of immediate execution, allowing you to quickly enter or exit a position. They are useful when you prioritize speed over price precision, especially for highly liquid stocks with minimal bid-ask spreads.
Are there any risks associated with market orders?
Yes, there are risks associated with market orders. Since the execution is at the prevailing market price, you may end up paying a higher price when buying or receiving a lower price when selling than anticipated due to market fluctuations.
Can market orders be placed outside trading hours?
Market orders cannot be executed outside trading hours as there must be active buyers and sellers in the market to facilitate the trade. You can only place market orders during regular trading hours.
Do I have control over the execution price with a market order?
With a market order, you do not have control over the execution price. The order is executed at the best available price in the market at the time of execution, which may differ from the price at the moment the order was placed.
How can I ensure timely execution of market orders?
To ensure timely execution of market orders, it is important to have a reliable internet connection and choose a reputable broker with fast order execution capabilities. Keeping an eye on market liquidity and volatility can also help in making well-timed market orders.
Final Thoughts
Understanding market orders in stock trading is crucial for investors to effectively navigate the financial markets. A market order is a type of order that allows traders to buy or sell securities at the best available price in the market. By placing a market order, investors can quickly execute trades and ensure that they do not miss out on potential opportunities. However, it is important to note that market orders may not always be executed at the exact price expected due to market fluctuations. Therefore, investors should carefully evaluate market conditions and consider using limit orders for more control over the execution price. Overall, comprehending the mechanics of market orders is essential for successful and efficient stock trading.