Have you ever wondered how monetary policy works and why it has such a significant impact on the economy? Understanding monetary policy and its impact is crucial in navigating the intricacies of our financial systems. In this article, we will delve into the world of monetary policy and explore its various components, from interest rates to quantitative easing. By the end, you will have a solid grasp of the subject, empowering you to make informed decisions and stay ahead in the ever-changing economic landscape. So, let’s dive right in and unravel the mysteries of understanding monetary policy and its impact.
Understanding Monetary Policy and Its Impact
Monetary policy plays a crucial role in shaping the economy of a country. Implemented by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, the European Central Bank, or the Bank of England, monetary policy involves the management of the money supply and interest rates to control inflation, stabilize the economy, and promote sustainable economic growth. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of understanding monetary policy and explore its profound impact on various aspects of the economy.
The Basics of Monetary Policy
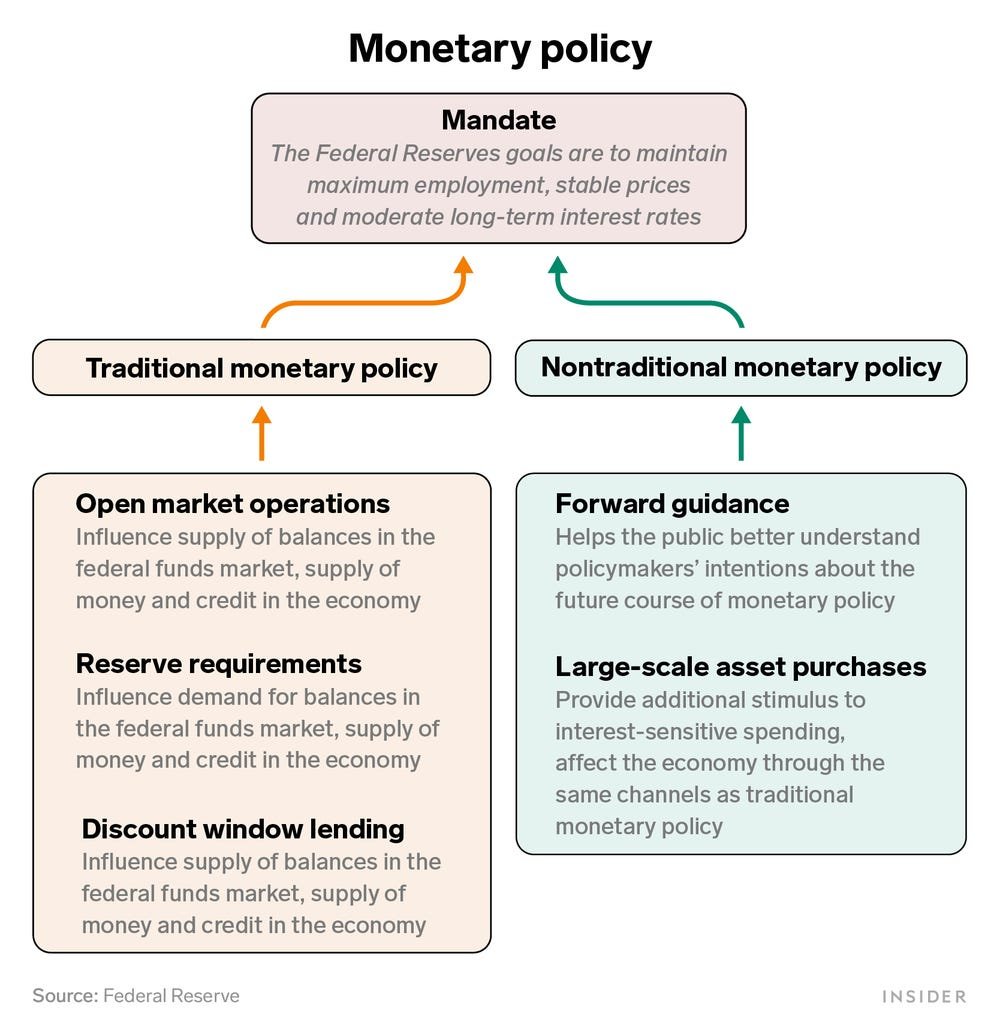
Monetary policy primarily aims to maintain price stability and promote economic growth. It operates by influencing key factors such as interest rates, money supply, and credit availability. Central banks possess several tools to implement monetary policy effectively, including:
- Interest Rates: One of the primary tools utilized by central banks is setting interest rates. By adjusting the base interest rate, central banks can influence borrowing costs, which, in turn, impacts consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity.
- Open Market Operations: Central banks can buy or sell government securities to control the money supply. When central banks purchase securities, they inject money into the economy, increasing the money supply. Conversely, selling securities reduces the money supply.
- Reserve Requirements: Central banks may also require commercial banks to maintain a certain amount of reserves. By adjusting these reserve requirements, central banks can regulate the lending capacity of commercial banks and influence credit availability in the economy.
- Forward Guidance: Another tool employed by central banks is forward guidance, whereby they communicate their future monetary policy intentions. This information helps shape market expectations and influences investment decisions.
The Objectives of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy typically aims to achieve the following objectives:
- Price Stability: Controlling inflation is a crucial aspect of monetary policy. Central banks strive to maintain stable prices by targeting a specific inflation rate. By managing the money supply and interest rates, central banks can influence inflationary pressures. Price stability enhances economic certainty and fosters sustainable economic growth.
- Full Employment: Another important objective of monetary policy is to promote maximum employment. By influencing interest rates and credit availability, central banks can stimulate economic activity, leading to increased job creation and reduced unemployment.
- Economic Growth: Monetary policy plays a key role in fostering sustainable economic growth. By influencing interest rates and credit conditions, central banks can encourage investment, stimulate consumer spending, and support overall economic activity.
- Financial Stability: Central banks also aim to maintain a stable and resilient financial system. They monitor and address risks to the stability of the banking sector and financial markets. By implementing appropriate regulations, central banks aim to safeguard the economy from potential financial crises.
The Impact of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy decisions have far-reaching effects on various aspects of the economy. Let’s explore some of the significant impacts of monetary policy.
Interest Rates and Borrowing Costs
Interest rates play a pivotal role in monetary policy, as they influence borrowing costs for businesses and individuals. When central banks decrease interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging businesses to invest in new projects and individuals to obtain loans for various purposes, such as buying homes or cars. Lower interest rates also incentivize consumer spending, which stimulates economic growth.
Conversely, when central banks raise interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive. Higher interest rates can restrain consumer spending and business investments, potentially slowing down economic activity. This approach is typically employed by central banks to curb inflationary pressures in an overheating economy.
Inflation and Deflation
One of the primary aims of monetary policy is to control inflation. By adjusting interest rates and managing the money supply, central banks influence the purchasing power of consumers and the overall level of prices. When the economy experiences excessive growth and inflation starts to rise, central banks may tighten monetary policy by raising interest rates and reducing the money supply. This contractionary policy helps to cool down the economy and prevent excessive inflation.
Conversely, during periods of weak economic activity and low inflation, central banks may implement expansionary monetary policy. By lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply, they aim to stimulate demand, encourage borrowing and spending, and prevent deflationary pressures. Deflation, or sustained price declines, can lead to reduced consumer spending, lower business profits, and economic stagnation.
Exchange Rates and International Trade
Monetary policy also influences exchange rates, which play a vital role in international trade. When central banks adjust interest rates, it affects the relative attractiveness of a country’s currency compared to others. Higher interest rates generally make a country’s currency more appealing, attracting foreign investors seeking higher yields. This increased demand for the currency can lead to an appreciation in its value.
Conversely, lower interest rates can make a country’s currency less attractive, potentially leading to depreciation. A weaker currency can make exports more competitive, benefitting domestic industries. On the other hand, it may increase the cost of imports, leading to higher prices for imported goods. The impact of exchange rates on trade can significantly influence a country’s export and import volumes, affecting economic growth and employment.
Asset Prices and Financial Markets
Monetary policy decisions can also impact asset prices and financial markets. When central banks lower interest rates and inject liquidity into the economy, it can lead to increased demand for assets such as stocks and real estate. This increased demand can drive up asset prices, potentially creating asset price bubbles.
Conversely, when central banks tighten monetary policy by raising interest rates, it can reduce the attractiveness of assets relative to other investment options. This can cause asset prices to decline, potentially leading to market corrections or even financial crises. Central banks closely monitor financial market conditions to ensure stability and mitigate risks associated with rapid asset price movements.
Consumer and Business Confidence
Monetary policy decisions and communication from central banks can significantly impact consumer and business confidence. When central banks provide forward guidance about their future policy actions, it helps individuals and businesses anticipate and plan for potential interest rate changes. Clear communication fosters certainty and stability, which can positively influence consumer and business decision-making.
Moreover, successful monetary policy implementation that ensures price stability and sustainable economic growth enhances overall confidence in the economy. When individuals and businesses have trust in the economic outlook, they are more likely to invest, spend, and contribute to economic expansion.
Understanding monetary policy and its impact is crucial for comprehending how central banks manage the economy. By employing various tools such as interest rate adjustments, open market operations, and forward guidance, central banks aim to maintain price stability, promote full employment, stimulate economic growth, and safeguard financial stability. The impact of monetary policy can be observed through its influence on interest rates, inflation, exchange rates, asset prices, consumer confidence, and business investment. Keeping a close eye on monetary policy decisions is paramount for individuals, businesses, and policymakers to navigate and make informed decisions in an ever-changing economic landscape.
Monetary Policy explained
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is monetary policy?
Monetary policy refers to the actions and decisions taken by a central bank or monetary authority to manage the supply of money and interest rates in an economy. It is aimed at achieving specific economic objectives such as controlling inflation, stabilizing prices, and promoting economic growth.
How does monetary policy impact the economy?
Monetary policy influences the economy through various channels. By adjusting interest rates, the central bank can encourage or discourage borrowing and spending, affecting consumption and investment. Changes in the money supply also impact inflation, exchange rates, employment levels, and overall economic activity.
What are the key tools of monetary policy?
The primary tools used in monetary policy include open market operations, reserve requirements, and the discount rate. Open market operations involve buying or selling government securities to influence the money supply. Reserve requirements determine the portion of deposits that banks must hold as reserves. The discount rate is the interest rate at which banks can borrow directly from the central bank.
How does expansionary monetary policy work?
Expansionary monetary policy, also known as loose or accommodative monetary policy, aims to stimulate economic growth. It involves decreasing interest rates, which encourages borrowing and spending. By increasing the money supply, central banks aim to boost consumption and investment, ultimately leading to greater economic activity.
What is contractionary monetary policy?
Contractionary monetary policy, also referred to as tight or restrictive monetary policy, is employed to slow down economic growth and control inflation. This policy involves increasing interest rates, which reduces borrowing and spending. By decreasing the money supply, central banks aim to dampen inflationary pressures and stabilize the economy.
How does monetary policy affect inflation?
Monetary policy has a significant impact on inflation. When central banks implement expansionary policies, such as lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply, it can lead to rising inflationary pressures. Conversely, contractionary monetary policies that involve raising interest rates or reducing the money supply are aimed at controlling inflation.
Does monetary policy influence exchange rates?
Yes, monetary policy can influence exchange rates. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can affect the attractiveness of a currency to foreign investors. Higher interest rates can lead to an appreciation of the currency, while lower interest rates can result in a depreciation. Exchange rate movements, in turn, affect international trade, investment, and competitiveness.
What are the limitations of monetary policy?
Monetary policy has certain limitations. One limitation is the existence of other factors that influence the economy, such as fiscal policy or external shocks. Additionally, the effectiveness of monetary policy may vary based on the economic situation, including the level of interest rates and the willingness of businesses and households to borrow and spend. Monetary policy may also have unintended consequences, such as asset price bubbles or increased income inequality.
Final Thoughts
Understanding monetary policy and its impact is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. It can directly influence interest rates, inflation, employment, and overall economic stability. By comprehending how central banks regulate the money supply and adjust interest rates, we can anticipate how these changes will affect borrowing costs, investment decisions, and consumer spending. An understanding of monetary policy empowers us to make informed financial choices, navigate economic uncertainties, and adapt our strategies accordingly. By staying informed and aware of monetary policy decisions, we can position ourselves to thrive in a dynamic and ever-changing economic landscape.