Understanding mortgage-backed securities can be a complex topic, but fear not! In this article, we’ll break it down in a conversational and easy-to-understand manner. So, what exactly are mortgage-backed securities? Well, they are financial instruments that involve pooling together a large number of individual mortgage loans and creating securities that can be bought and sold in the market. These securities provide investors with the opportunity to earn a return based on the interest and principal payments made by homeowners on their mortgages. Now, let’s dive into the details and unravel the world of mortgage-backed securities together.
Understanding Mortgage-Backed Securities
Introduction
Investing in the financial markets can be a complex and intimidating endeavor, especially when it comes to understanding the various types of securities available. One such type is mortgage-backed securities (MBS), which play a crucial role in the housing market and the broader economy. In this article, we will explore what mortgage-backed securities are, how they work, and the risks and benefits associated with them.
What are Mortgage-Backed Securities?
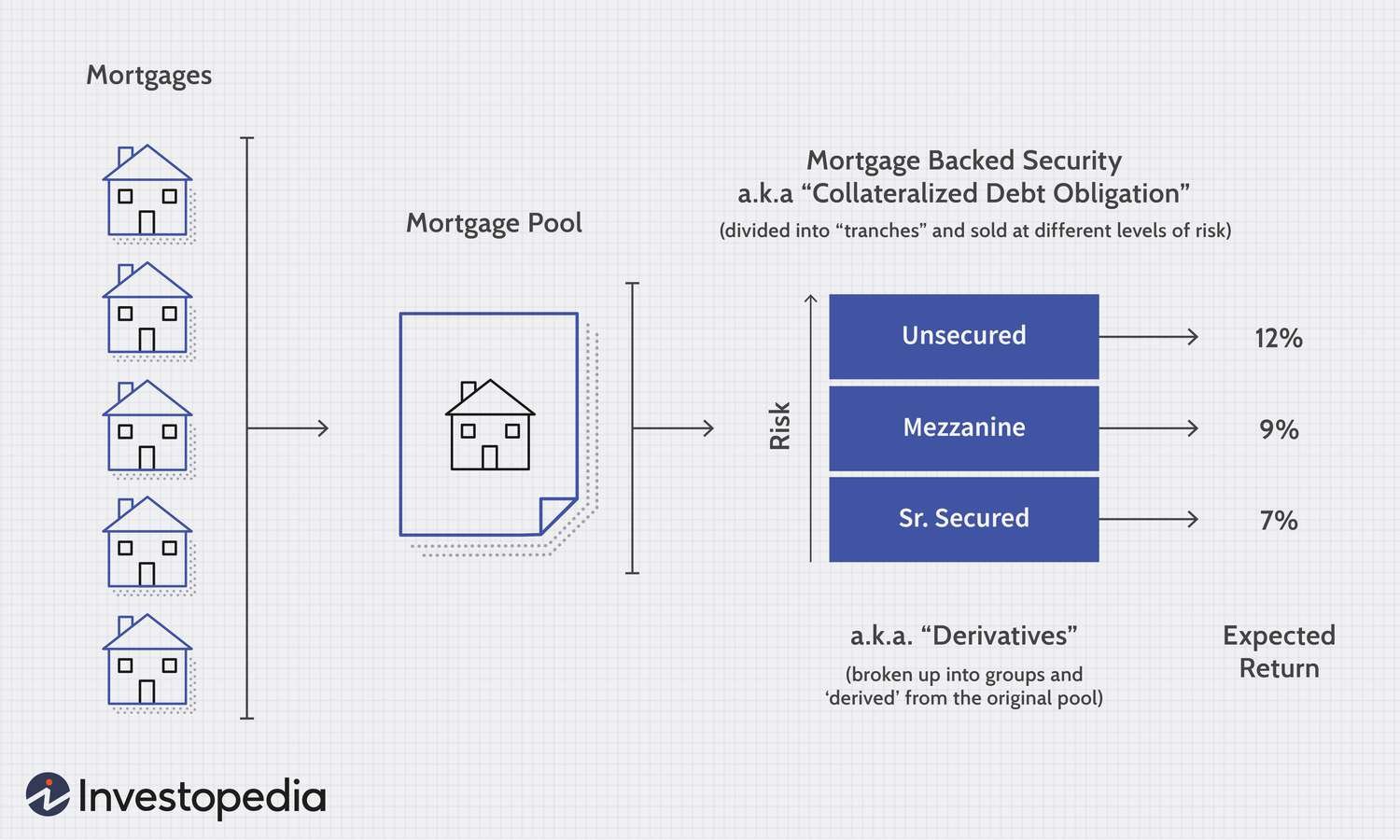
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are financial instruments that represent an ownership interest in a pool of mortgage loans. When individuals or families buy homes, they often finance their purchases by taking out mortgage loans from banks or other financial institutions. Mortgage lenders package these loans into pools and then sell securities backed by the cash flows from these underlying mortgages to investors.
The primary purpose of mortgage-backed securities is to provide liquidity to the mortgage market. By selling these securities, lenders can replenish their funds and continue to offer new mortgages to homebuyers. Investors, in turn, earn interest payments based on the principal and interest collected from the underlying mortgage loans.
How Do Mortgage-Backed Securities Work?
To understand how mortgage-backed securities work, let’s break down the process into a few key steps:
1. Origination: Homebuyers apply for a mortgage loan from banks or other financial institutions. The lenders evaluate their creditworthiness, income, and other factors to determine if they qualify for the loan.
2. Packaging: Lenders then package multiple mortgage loans into a pool. These loans may have different interest rates, maturity dates, and other characteristics.
3. Securitization: The pool of mortgage loans is transferred to a special purpose vehicle (SPV), which is typically a trust. The SPV issues mortgage-backed securities backed by the cash flow from the underlying loans.
4. Tranching: Mortgage-backed securities are divided into different tranches or classes, each with different levels of risk and return. Senior tranches have priority in receiving interest and principal payments, while junior tranches have higher risk but potentially higher returns.
5. Sale to Investors: The mortgage-backed securities are sold to investors, such as pension funds, insurance companies, mutual funds, and individual investors. Investors purchase these securities based on their investment objectives and risk appetite.
6. Cash Flows: As borrowers make monthly mortgage payments, the cash flows are passed through to the investors holding the mortgage-backed securities. These cash flows include both interest and principal payments.
7. Prepayment Risk: One important consideration with mortgage-backed securities is prepayment risk. Borrowers may choose to refinance their mortgages or pay them off early, which affects the cash flow to MBS investors. This risk is typically accounted for by calculating the average life of the mortgage pool.
Risks and Benefits of Mortgage-Backed Securities
Like any investment, mortgage-backed securities come with their own set of risks and benefits. It is important to understand these factors before deciding to invest in MBS. Here are some key points to consider:
Risks:
1. Prepayment Risk: As mentioned earlier, prepayment risk is a significant concern for MBS investors. When borrowers refinance or pay off their mortgages early, it reduces the expected cash flow to investors. This risk can be managed by analyzing the average life of the mortgage pool and evaluating the potential impact of prepayments.
2. Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can also affect the performance of mortgage-backed securities. When interest rates rise, borrowers are less likely to refinance, resulting in a longer average life for the mortgage pool. Conversely, when interest rates drop, borrowers may refinance at lower rates, leading to shorter average lives and potentially lower returns for MBS investors.
3. Credit Risk: Mortgage-backed securities can also be exposed to credit risk. If a large number of borrowers default on their mortgage payments, it can impact the cash flows to investors. Evaluating the credit quality of the underlying mortgage loans and the structure of the MBS can help mitigate this risk.
Benefits:
1. Diversification: Mortgage-backed securities provide investors with an opportunity to diversify their portfolios. By investing in MBS, investors gain exposure to the housing market, which may perform differently from other asset classes.
2. Income Potential: MBS can offer attractive yields compared to other fixed-income investments. Investors receive regular interest payments based on the cash flows from the underlying mortgage loans.
3. Liquidity: Mortgage-backed securities are traded in the secondary market, providing liquidity to investors who may want to buy or sell their investments without waiting for the underlying mortgage loans to mature.
Understanding mortgage-backed securities is essential for investors looking to navigate the complexities of the financial markets. These securities play a vital role in providing liquidity to the mortgage market while offering attractive investment opportunities. By comprehending the risks and benefits associated with mortgage-backed securities, investors can make informed decisions and potentially enhance their investment portfolios.
FAQs
-
What is the difference between mortgage-backed securities and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs)?
While both mortgage-backed securities and collateralized debt obligations involve pools of underlying assets, there are some key differences. Mortgage-backed securities are backed by mortgage loans, whereas CDOs can be backed by various types of debt, including mortgages, corporate loans, and credit card receivables. -
Are mortgage-backed securities safe investments?
Mortgage-backed securities can carry various risks, including prepayment risk, interest rate risk, and credit risk. However, thorough analysis and due diligence can help investors manage these risks. -
Who are the typical investors in mortgage-backed securities?
Mortgage-backed securities are attractive to a range of investors, including pension funds, insurance companies, mutual funds, and individual investors who seek income-generating assets and portfolio diversification.
Mortgage-backed securities I | Finance & Capital Markets | Khan Academy
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are mortgage-backed securities?
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are financial instruments that represent a share of ownership in a pool of mortgage loans. These loans are typically made to homebuyers, and the cash flows from the mortgage payments are then distributed to the holders of the MBS.
How do mortgage-backed securities work?
Mortgage-backed securities work by pooling together a large number of mortgage loans and creating a tradable security. When homeowners make their mortgage payments, the cash flows are used to pay interest and principal to the MBS holders.
What is the purpose of mortgage-backed securities?
The purpose of mortgage-backed securities is to provide a way for investors to participate in the mortgage market and earn a return on their investment. They also help to increase liquidity in the mortgage market by making it easier for lenders to sell their loans.
What are the risks associated with mortgage-backed securities?
Some of the risks associated with mortgage-backed securities include prepayment risk, interest rate risk, and credit risk. Prepayment risk refers to the possibility that borrowers may pay off their mortgages early, which can affect the cash flows to the MBS holders. Interest rate risk arises from changes in interest rates, which can impact the value of the MBS. Credit risk is the risk of default by the borrowers underlying the mortgage loans.
Who can invest in mortgage-backed securities?
Mortgage-backed securities are typically available to a wide range of investors, including individuals, institutional investors, and financial institutions. They can be purchased through brokerage firms or other financial intermediaries.
What are the advantages of investing in mortgage-backed securities?
Investing in mortgage-backed securities offers several advantages, such as regular income payments, diversification of investment portfolios, and the potential for attractive yields. MBS also provide a way to invest in the housing market without directly owning properties.
Are mortgage-backed securities guaranteed by the government?
Not all mortgage-backed securities are guaranteed by the government. Some MBS are issued by government-sponsored enterprises like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which have implicit government backing. However, others are issued by private entities and do not have government guarantees.
How can I assess the quality of mortgage-backed securities?
Assessing the quality of mortgage-backed securities involves evaluating factors such as the creditworthiness of the borrowers, the type of mortgages underlying the MBS, and the overall economic environment. Credit ratings assigned by rating agencies can also provide an indication of the quality of the MBS.
Please note that these responses serve as general guidance and should not be considered as financial or investment advice. It is recommended to consult with a professional financial advisor for specific questions related to mortgage-backed securities.
Final Thoughts
Understanding mortgage-backed securities is crucial for investors and individuals wanting to navigate the complex world of finance. These investment vehicles, which are backed by pools of mortgage loans, offer opportunities for diversification and income generation. By dissecting the structure and risks associated with these securities, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment goals and risk tolerance. Additionally, understanding the role of mortgage-backed securities in the global financial system can help to comprehend the potential impact of economic factors on these investments. Overall, grasping the nuances of mortgage-backed securities is essential for anyone seeking to engage in the world of finance.