Stock buybacks are a common strategy used by companies to influence their stock prices and manage their capital structure. But what exactly are stock buybacks and how do they impact investors? Understanding stock buybacks and their impact is essential for anyone looking to navigate the intricacies of the stock market. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of stock buybacks, exploring their purpose, mechanics, and the potential implications for shareholders. So, let’s dive right in and shed light on the complex yet fascinating realm of understanding stock buybacks and their impact.
Understanding Stock Buybacks and Their Impact
Introduction to Stock Buybacks
Stock buybacks, also known as share repurchases, are a mechanism used by publicly traded companies to repurchase their own shares from the market. This process involves a company buying back its outstanding shares and removing them from circulation. Stock buybacks can be executed in various ways, such as open market purchases, tender offers, or privately negotiated transactions.
While stock buybacks are not a new concept, they have gained significant attention in recent years due to their increasing prevalence. According to data from S&P Dow Jones Indices, companies in the S&P 500 spent a record $806.4 billion on stock buybacks in 2018, surpassing the previous record of $589.1 billion set in 2007.
The Motivations Behind Stock Buybacks
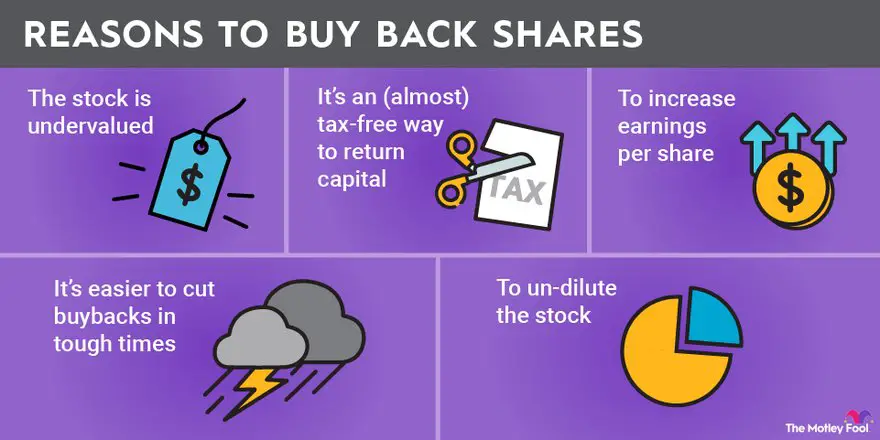
Companies resort to stock buybacks for several reasons, and understanding these motivations is crucial in comprehending their impact. Some common reasons behind stock buybacks include:
1. Capital Allocation: Companies may use excess cash to repurchase shares instead of investing in new projects, acquisitions, or research and development. This approach allows companies to allocate capital towards what they perceive as the best use for their shareholders.
2. Enhancing Shareholder Value: By reducing the number of outstanding shares, stock buybacks increase earnings per share (EPS) and potentially boost the company’s stock price. This action benefits existing shareholders by increasing their ownership percentage and potentially increasing their wealth.
3. Returning Cash to Shareholders: Stock buybacks provide a means for companies to return excess cash to shareholders. By repurchasing shares, companies can distribute cash to shareholders without paying dividends, which can have tax implications for investors.
4. Defending Against Hostile Takeovers: Stock buybacks can also serve as a defense mechanism against hostile takeovers. The reduction in the number of outstanding shares makes a company less attractive or prohibitively expensive for potential acquirers.
While these are some of the common motivations behind stock buybacks, it’s essential to note that not all buybacks benefit shareholders equally. The impact of buybacks on investor returns can vary depending on the circumstances and the company’s overall financial health.
The Impact of Stock Buybacks
The impact of stock buybacks can be analyzed from multiple perspectives, considering both positive and negative consequences.
Positive Impact
1. Increased Earnings Per Share (EPS): By reducing the number of outstanding shares, stock buybacks can boost a company’s EPS. This increase in EPS may lead to an increase in the company’s stock price if investors perceive the buyback as a signal of positive prospects.
2. Enhanced Shareholder Value: Shareholders can benefit from stock buybacks in several ways. The reduction in outstanding shares increases the ownership stake of existing shareholders, potentially leading to higher returns. Additionally, as the stock price may increase due to buyback activity, shareholders can experience capital appreciation.
3. Efficient Capital Allocation: Stock buybacks provide companies with a flexible mechanism for capital allocation. By repurchasing shares, companies can invest excess cash when they believe their stock is undervalued, potentially generating higher returns for shareholders in the long run.
Negative Impact
1. Capital Misallocation: Critics argue that some companies use stock buybacks to artificially inflate their stock prices without investing in long-term growth opportunities. This practice may divert capital away from investments in research and development or new projects, potentially hindering innovation and future growth.
2. Misleading Financial Metrics: By reducing the number of outstanding shares, stock buybacks can make financial metrics, such as EPS, appear more favorable than they actually are. This potential distortion may mislead investors and lead to a skewed perception of a company’s financial health.
3. Unequal Distribution of Benefits: Shareholders who sell their shares during a buyback can benefit immediately, while long-term shareholders who hold onto their shares might experience a dilution of ownership. This disparity in benefits can create a divide between short-term and long-term investors.
4. Reduced Capital for Growth: When companies allocate a significant portion of their available capital towards stock buybacks, it can limit their ability to invest in organic growth, acquisitions, or research and development. This restriction may impact a company’s long-term competitiveness and potential for innovation.
Regulatory Considerations
Stock buybacks are subject to regulations and legal restrictions imposed by regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. These regulations aim to ensure fair and transparent practices and prevent market manipulation. Companies must comply with rules regarding disclosure, timing, and the maximum amount of shares that can be repurchased.
Additionally, buybacks can attract scrutiny from policymakers and the public due to concerns about their impact on income inequality, executive compensation, and broader economic implications. Debates about the fairness and potential consequences of buybacks continue to shape discussions around corporate governance and regulations.
Stock buybacks are a complex and often controversial topic in the world of finance. Understanding the motivations behind buybacks and their potential impact is essential for investors and stakeholders alike. While buybacks can enhance shareholder value and provide efficient capital allocation, they can also lead to capital misallocation and unequal distribution of benefits. As regulations and public sentiment surrounding buybacks evolve, it remains crucial for companies to carefully consider the implications before engaging in such activities.
References:
1. Boudreaux, R., & Karolyi, A. G. (2020). Do Buybacks Really Reduce Long-Term Investment? Harvard Business Review. [Link](https://hbr.org/2020/01/do-buybacks-really-reduce-long-term-investment)
2. Securities and Exchange Commission. (2021). Stock Buybacks: A Guide for Investors. [Link](https://www.sec.gov/oiea/investor-alerts-and-bulletins/ib_buybacks)
3. Investopedia. (2021). Stock Buyback. [Link](https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/buyback.asp)
The Debate Over Stock Buybacks, Explained | WSJ
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a stock buyback?
A stock buyback, also known as a share repurchase, is when a company purchases its own shares from the market. This reduces the number of outstanding shares and increases the ownership stake of the remaining shareholders.
Why do companies engage in stock buybacks?
Companies engage in stock buybacks for various reasons. Some common motives include increasing shareholder value, boosting earnings per share, utilizing excess cash reserves, and signaling confidence in the company’s future prospects.
How are stock buybacks financed?
Stock buybacks can be financed through several methods. Companies may use their cash reserves, issue debt, or utilize existing credit lines to fund the repurchase of shares.
What is the impact of stock buybacks on stock prices?
Stock buybacks can potentially have a positive impact on stock prices. By reducing the number of shares in circulation, the earnings per share (EPS) may increase, which can attract more investors and potentially lead to a rise in stock prices.
Do stock buybacks affect dividends?
Yes, stock buybacks can affect dividends. When a company repurchases its shares, the remaining shareholders may receive a larger slice of the company’s profits. This can potentially result in an increase in dividends per share.
Are stock buybacks always beneficial for investors?
While stock buybacks can be advantageous for investors in certain situations, their benefits may vary. Investors should consider factors such as the company’s financial health, growth prospects, and the price at which the buybacks are executed before determining the impact on their investment.
Can stock buybacks be a sign of financial trouble?
In some cases, stock buybacks can be a sign of financial trouble. If a company repurchases its shares at a price higher than their intrinsic value or if the buybacks are funded through excessive debt, it may indicate financial difficulties and poor management decision-making.
How do stock buybacks impact the economy?
Stock buybacks can influence the overall economy in various ways. By reducing the number of outstanding shares, they can contribute to increased earnings per share and potentially stimulate investor confidence. However, critics argue that excessive stock buybacks can divert resources from productive investments, limiting long-term economic growth.
Can stock buybacks be reversed?
Yes, stock buybacks can be reversed. If a company wishes to increase its outstanding shares again, it can issue new shares through a secondary offering or other equity issuance methods. Reversing stock buybacks allows the company to raise capital or adjust its ownership structure as needed.
Final Thoughts
Stock buybacks are an important mechanism utilized by companies to repurchase their own shares from the market. These buybacks can have a significant impact on various aspects of a company and its stakeholders. Understanding stock buybacks and their impact is crucial for investors and individuals interested in the stock market. By repurchasing shares, companies can improve their financial ratios, increase earnings per share, and signal confidence in their future prospects to investors. Additionally, buybacks can provide liquidity to shareholders looking to sell their shares. Overall, comprehending stock buybacks and their impact is essential for navigating the complexities of the stock market and making informed investment decisions.