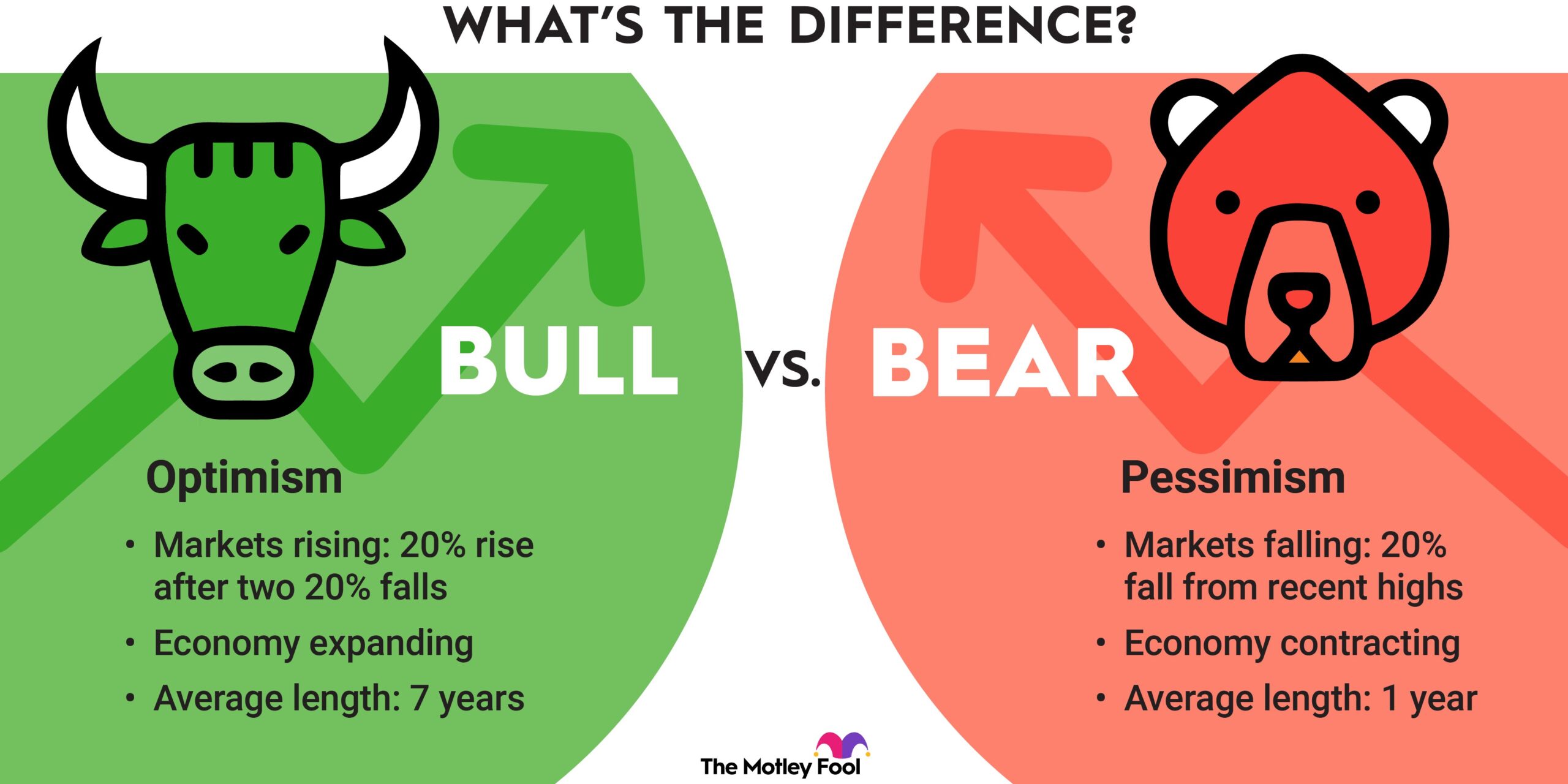
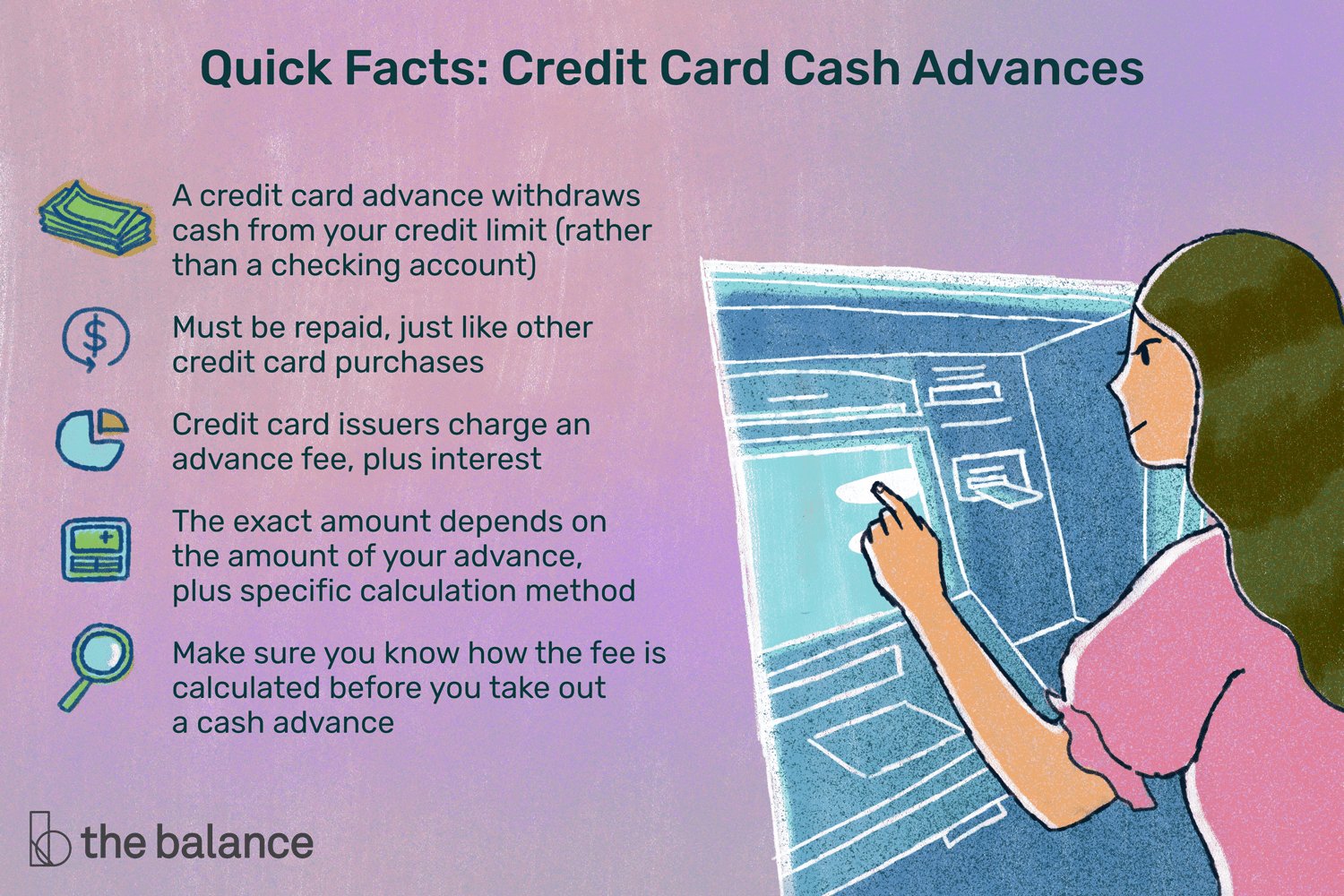
Financial derivatives can be complex and intimidating for those new to the world of finance. But fear not, understanding the basics of financial derivatives is easier than you might think. In this article, we will demystify this key aspect of the financial world, breaking it down into simple terms that anyone can grasp. So whether you’re a beginner looking to enhance your financial knowledge or a seasoned investor looking for a refresher, this article is for you. Let’s dive in and explore the fundamentals of financial derivatives together.
Understanding the Basics of Financial Derivatives
Financial derivatives play a crucial role in the world of finance. These investment instruments have become increasingly popular due to their ability to manage risk and provide opportunities for profit. In this article, we will delve into the basics of financial derivatives, exploring their definition, types, uses, and the risks associated with them.
What Are Financial Derivatives?
Financial derivatives are contracts that derive their value from an underlying asset or financial instrument. The value of a derivative is based on the price movements of the underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, or market indices. These contracts enable investors to speculate on price fluctuations, hedge against potential losses, or gain exposure to various assets without directly owning them.
Types of Financial Derivatives
There are several types of financial derivatives, each serving different purposes and catering to different investment strategies. Let’s explore some of the most common ones:
- 1. Futures Contracts: Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specified future date. They are commonly used in commodities trading and allow investors to speculate on the price movements of commodities like crude oil, gold, or wheat.
- 2. Options Contracts: Options contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific time frame. This flexibility makes options popular for hedging or speculating on stock or index price movements.
- 3. Swaps: Swaps involve the exchange of cash flows or liabilities between two parties. Common types of swaps include interest rate swaps, currency swaps, and commodity swaps. Swaps are often used to manage interest rate or currency risks.
- 4. Forward Contracts: Similar to futures contracts, forward contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future. However, unlike futures contracts, they are typically not traded on exchanges and can be customized to meet the specific needs of the parties involved.
Uses of Financial Derivatives
Financial derivatives serve various purposes in the world of finance. Let’s explore some of their common uses:
Hedging
One of the primary uses of financial derivatives is hedging. Hedging involves using derivatives to offset potential losses from adverse price movements in the underlying asset. By taking an opposite position in a derivative contract, investors can protect themselves from downside risks. For example, a commodity producer may use futures contracts to lock in a favorable price for their products, mitigating the impact of price fluctuations.
Speculation
Financial derivatives also provide opportunities for speculation. Speculators aim to profit from price movements in the underlying assets without necessarily owning them. They can take long (buy) or short (sell) positions in derivatives based on their market expectations. For instance, an investor expecting a rise in the price of a stock may choose to buy call options to benefit from potential upside movements.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage is another common use of financial derivatives. Arbitrageurs exploit price discrepancies between related financial instruments in different markets to make risk-free profits. By simultaneously buying and selling derivatives, they can capitalize on temporary price imbalances. However, arbitrage opportunities are often short-lived and require sophisticated trading strategies and systems.
Risks Associated with Financial Derivatives
While financial derivatives offer various benefits, it is crucial to understand the associated risks. Some of the key risks include:
Market Risk
Market risk refers to the potential losses arising from adverse price movements in the underlying asset. Derivatives amplify these risks since their value is derived from the underlying asset’s price. If the market moves against the anticipated direction, investors may face substantial losses.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk arises when it becomes difficult to enter or exit a derivative contract due to limited trading activity or a lack of counterparties. Illiquid markets can result in wider bid-ask spreads and may make it challenging to execute trades at desired prices. This can lead to higher transaction costs and potential difficulties in unwinding positions.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk refers to the risk of default by the other party involved in a derivative contract. If the counterparty fails to honor its obligations, investors could face significant financial losses. To mitigate this risk, investors often transact derivatives through clearinghouses, which act as intermediaries and guarantee the settlement of trades.
Complexity Risk
Financial derivatives can be complex instruments, often requiring a deep understanding of the underlying assets and the terms of the contracts. Lack of knowledge or misunderstanding can lead to poor investment decisions and substantial losses. It is crucial for investors to thoroughly educate themselves and seek professional advice before engaging in derivative trading.
Financial derivatives are powerful tools that allow investors to manage risk, speculate on price movements, and gain exposure to various assets. By understanding the basics of financial derivatives, investors can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of these instruments effectively. However, it is essential to recognize the risks involved and exercise caution when trading derivatives. With proper knowledge and risk management strategies, financial derivatives can be valuable additions to an investor’s toolkit.
Derivatives Explained in One Minute
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are financial derivatives?
Financial derivatives are financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset or a group of assets. These assets can include stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and market indices.
Why are financial derivatives used?
Financial derivatives are used for various purposes such as hedging against price fluctuations, speculating on market movements, managing risk exposure, and gaining leverage in trading.
What are the different types of financial derivatives?
There are several types of financial derivatives, including futures contracts, options contracts, swaps, and forward contracts.
How do futures contracts work?
Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. These contracts are standardized and traded on exchanges.
What are options contracts?
Options contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price before or on a specific date. It provides flexibility to the holder to decide whether to exercise the option.
What are swaps?
Swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange payments based on different financial variables, such as interest rates or currencies. They are commonly used for managing interest rate risk or currency exchange risk.
How do forward contracts work?
Forward contracts are customized agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified price on a future date. They are privately negotiated and are not traded on exchanges.
What are the risks associated with financial derivatives?
Financial derivatives involve certain risks, including market risk, counterparty risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk. It is important to understand these risks and implement appropriate risk management strategies.
How can one learn more about financial derivatives?
To gain a deeper understanding of financial derivatives, it is recommended to study relevant educational resources, enroll in courses, attend seminars, and consult with financial professionals experienced in derivatives trading.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the basics of financial derivatives is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complex world of financial markets. These instruments, such as options, futures, and swaps, allow investors and businesses to manage risk, speculate on price movements, and hedge against potential losses. By grasping the fundamentals, individuals can make informed investment decisions and protect their portfolios. Whether you’re an experienced investor or just starting out, a solid understanding of financial derivatives can provide valuable insights and opportunities in today’s dynamic financial landscape. So, dive into the basics and equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate this intricate realm successfully.