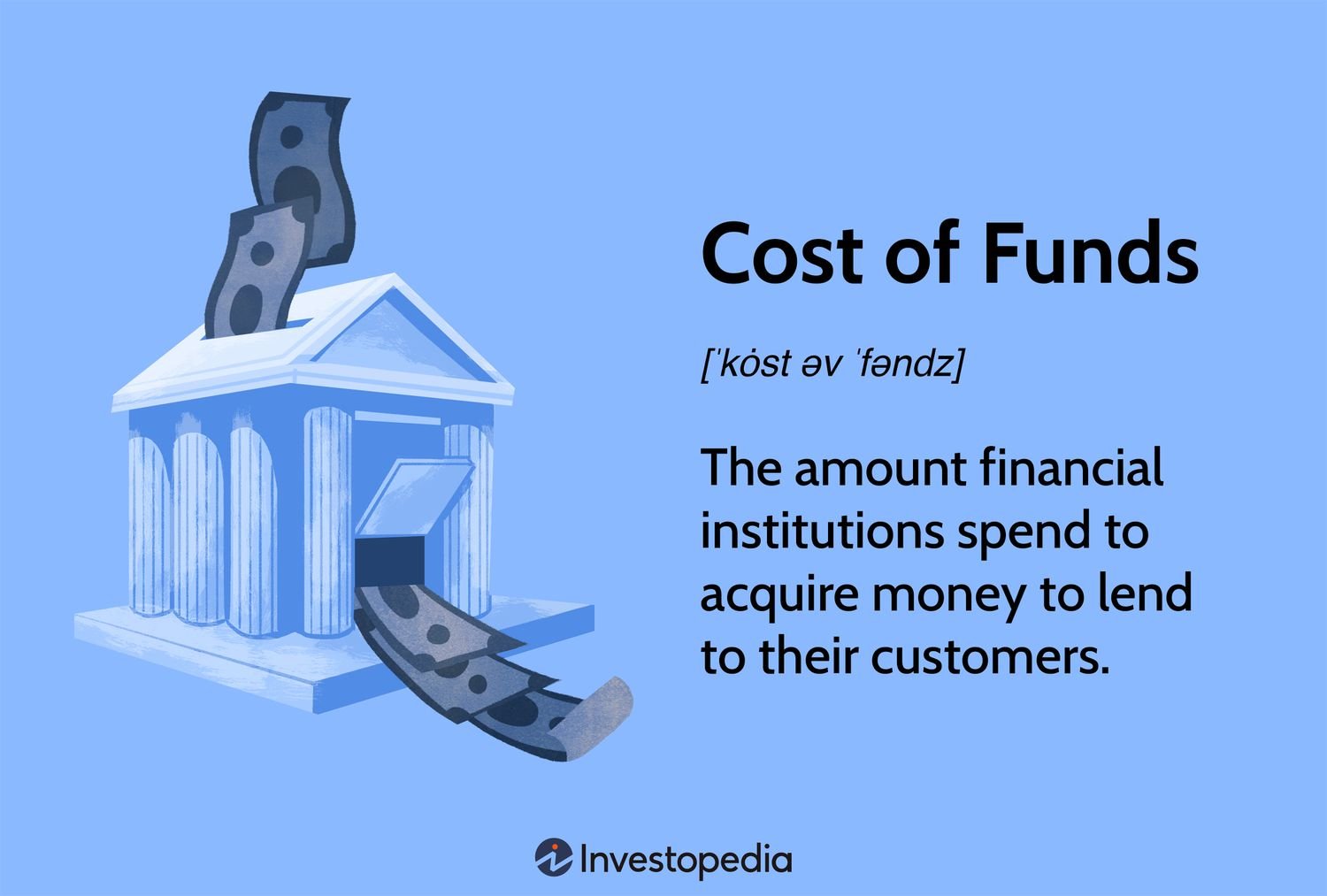
Are you curious about the factors that affect the cost of funds in lending? Understanding the cost of funds is crucial for anyone looking to borrow money or invest in loans. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this concept, shedding light on how it affects both lenders and borrowers alike. By grasping the cost of funds in lending, you will gain a deeper understanding of the financial landscape and be better equipped to make informed decisions. So, let’s dive right in and uncover the fascinating world of understanding the cost of funds in lending.
Understanding the Cost of Funds in Lending
In the world of finance, lending is a critical component that allows individuals and businesses to access capital for various purposes. When borrowers approach financial institutions for loans, they are often faced with different interest rates and fees. This variation is primarily influenced by the cost of funds for the lender. Understanding the cost of funds in lending is essential for borrowers to make informed decisions about their loan options. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the cost of funds in lending and shed light on its key components and implications.
What are Funds?
Before we dive into the concept of the cost of funds, let’s start by understanding what funds are. In the context of lending, funds refer to the money that financial institutions, such as banks and credit unions, have available to lend to borrowers. These funds can come from various sources, including customer deposits, equity capital, and borrowing from other financial institutions or the central bank.
Components of the Cost of Funds
The cost of funds is a comprehensive term that encompasses various factors that contribute to the overall expense for lenders. Let’s explore the key components of the cost of funds:
1. Interest Paid on Deposits
Financial institutions rely on customer deposits as a significant source of funds for lending. To attract deposits, these institutions offer interest rates to depositors. This interest paid on deposits is one of the primary costs incurred by lenders. The higher the interest rates offered on deposits, the greater the cost of funds for the lender.
2. Borrowing Costs
In addition to customer deposits, financial institutions may need to borrow funds from other sources to meet the demand for loans. Borrowing costs, such as interest rates on interbank loans or debt securities, are considered a key component of the cost of funds. Lenders incur expenses based on the interest rates and fees associated with these borrowing arrangements.
3. Operational Expenses
Financial institutions have various operational expenses, such as employee salaries, rent, utilities, and technology infrastructure, to maintain their lending operations. These expenses are also factored into the cost of funds. The higher the operational expenses, the higher the cost of funds for the lender.
4. Capital Costs
Maintaining a sufficient level of capital is essential for financial institutions to support their lending activities and absorb potential losses. The cost of maintaining this capital, known as capital costs, is another component of the overall cost of funds. Lenders need to generate returns on their capital investments, which influences the cost of funds they pass on to borrowers.
Implications for Borrowers
Understanding the cost of funds in lending is crucial for borrowers, as it directly impacts the interest rates and fees they encounter when seeking loans. Here are a few important implications to consider:
1. Interest Rates
The cost of funds plays a significant role in determining the interest rates that lenders offer to borrowers. Higher cost of funds generally results in higher interest rates, as lenders aim to cover their expenses and generate a profit. Borrowers should compare interest rates across different lenders to ensure they obtain the most favorable terms based on their financial situation.
2. Loan Fees
Apart from interest rates, lenders may also charge various fees, such as origination fees or processing fees, to cover their costs. These fees contribute to the overall cost of funds and can significantly impact the affordability of a loan for borrowers. It is essential to carefully review and understand the fee structure associated with a loan before committing to it.
3. Availability of Loans
The cost of funds influences the availability of loans in the market. When the cost of funds is high, lenders may become more cautious in extending loans, resulting in stricter lending criteria and reduced access to credit. Conversely, a lower cost of funds can lead to increased competition among lenders and a greater availability of loans.
4. Negotiation Power
Understanding the cost of funds empowers borrowers to negotiate better loan terms. Armed with knowledge about the factors that contribute to the cost of funds, borrowers can engage in discussions with lenders and potentially secure lower interest rates or reduced fees. Being well-informed about the cost of funds gives borrowers an advantage during loan negotiations.
The cost of funds in lending is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various elements, including interest paid on deposits, borrowing costs, operational expenses, and capital costs. This cost directly influences the interest rates and fees that borrowers encounter when seeking loans. By understanding the cost of funds, borrowers can make more informed decisions about their loan options, compare different lenders, and potentially negotiate better loan terms. Being aware of the implications of the cost of funds empowers borrowers to navigate the lending landscape more effectively and secure favorable financing for their needs.
Cost of Capital and Cost of Equity | Business Finance
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the Cost of Funds in Lending
What is the cost of funds in lending?
The cost of funds in lending refers to the expenses a financial institution incurs to obtain the money it lends to borrowers. It includes factors such as interest rates on deposits, borrowing costs, operational expenses, and profit margins.
How do banks determine the cost of funds for lending?
Banks typically determine the cost of funds by calculating the weighted average cost of their various sources of funding, including deposits, interbank borrowing, and long-term debt. This calculation takes into account the interest rates and fees associated with each funding source.
Why is it important for borrowers to understand the cost of funds?
Understanding the cost of funds helps borrowers make informed decisions about borrowing money. It allows them to evaluate the interest rates and fees associated with different lenders, compare loan offers, and assess the overall affordability of the loan.
What factors influence the cost of funds in lending?
Several factors influence the cost of funds in lending, including the current interest rate environment, the creditworthiness of the borrower, the duration of the loan, and the overall economic conditions. Additionally, market competition and the lender’s own operational costs can also impact the cost of funds.
Can the cost of funds vary between lenders?
Yes, the cost of funds can vary between lenders. Different financial institutions may have access to varying funding sources and may also have different operational costs. As a result, they may offer different interest rates and fees to borrowers, influencing the overall cost of funds.
How does the cost of funds affect the interest rates offered to borrowers?
The cost of funds directly affects the interest rates offered to borrowers. Lenders aim to cover their cost of funds while maintaining profitability, so they set interest rates based on the expenses they incur to obtain the funds. Higher costs of funds can result in higher interest rates for borrowers.
Are there any ways for borrowers to lower the cost of funds?
Borrowers can potentially lower the cost of funds by improving their creditworthiness. Maintaining a good credit score, having a stable income, and minimizing existing debts can make borrowers more attractive to lenders, potentially leading to lower interest rates and fees.
What are some additional costs besides interest rates that borrowers should consider?
Besides interest rates, borrowers should also consider other costs associated with borrowing, such as origination fees, prepayment penalties, and ongoing servicing fees. These additional costs can significantly impact the overall cost of the loan and should be carefully evaluated before making a borrowing decision.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the cost of funds in lending is crucial for both lenders and borrowers. By grasping this concept, lenders can determine the interest rates they need to charge in order to cover their costs and generate a profit. On the other hand, borrowers can make informed decisions when comparing loan options and understanding the total cost of borrowing. When considering the cost of funds, lenders take into account various factors such as the interest rates they incur from sources like deposits, bonds, or money market funds. Having a clear understanding of the cost of funds allows lenders to offer competitive rates to borrowers while still maintaining profitability. Additionally, understanding the cost of funds helps lenders assess risks and make appropriate lending decisions based on the financial market conditions. In conclusion, comprehending the cost of funds in lending is essential for lenders and borrowers alike, as it enables lenders to set competitive rates and borrowers to make informed borrowing decisions.