Are you intrigued by the concept of compounding interest but unsure of how it actually works? Well, look no further! Understanding the principle of compounding interest is essential for anyone seeking to grow their wealth over time. In simple terms, compounding interest is when you earn interest not only on the initial amount of money you invest but also on the accumulated interest itself. It’s like a snowball effect, where your money grows exponentially over time. In this article, we will demystify the concept of compounding interest and show you how it can work to your advantage. So, let’s dive in and explore the power of compounding!
Understanding the Principle of Compounding Interest
When it comes to personal finance, one of the most crucial concepts to understand is the principle of compounding interest. Whether you are saving money, investing in stocks, or taking out a loan, compounding interest plays a significant role in determining your financial outcomes. In this article, we will delve into the details of compounding interest, how it works, and its implications on your financial decisions.
What is Compounding Interest?
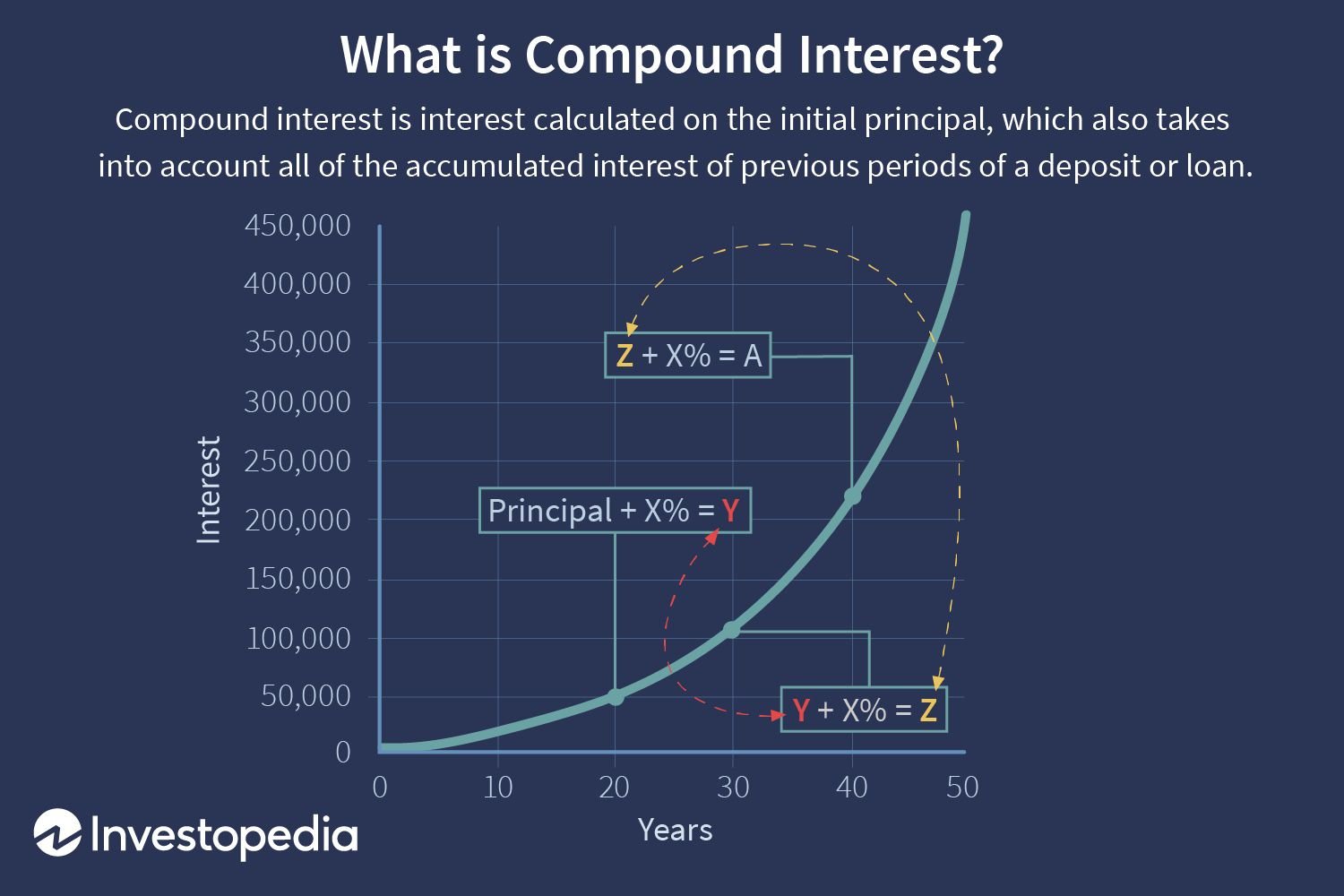
Compounding interest is the process of earning or paying interest on both the original principal amount and the accumulated interest from previous periods. In simpler terms, it means that you earn interest not only on your initial investment but also on the interest that has been added to it over time. This compounding effect has a snowball effect, allowing your money to grow exponentially.
Example of Compounding Interest
Let’s illustrate the power of compounding interest with an example. Imagine you have $1,000 in a savings account that earns an annual interest rate of 5%. At the end of the first year, you would earn $50 in interest, resulting in a total of $1,050. In the second year, you would earn 5% interest on the new balance of $1,050, which is $52.50, bringing your total to $1,102.50. As you can see, your interest is growing with each passing year, and this growth accelerates over time.
How Does Compounding Interest Work?
In essence, compounding interest takes advantage of the time value of money. It allows your money to work for you and generate returns over an extended period. The key factor that determines the growth of your investment is the compounding frequency, which can be daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually. The more frequently the interest is compounded, the faster your investment will grow.
There are two main types of interest: simple interest and compound interest. While simple interest only calculates interest based on the initial principal amount, compound interest factors in the accumulated interest. This crucial difference leads to significant variations in the growth of your money over time.
Simple Interest
Simple interest is a straightforward calculation that doesn’t take into account any accumulated interest. It is calculated using the following formula:
Simple Interest = Principal x Interest Rate x Time
For example, if you invest $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 3% for three years, the total interest earned would be $90 ($1,000 x 0.03 x 3).
Compound Interest
Compound interest, on the other hand, incorporates the accumulated interest into subsequent interest calculations. The formula to calculate compound interest is more complex:
Compound Interest = Principal x (1 + Interest Rate/Number of Compounding Periods)^(Number of Compounding Periods x Time)
Let’s use the same example as before, but this time with compound interest. If you invest $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 3% compounded annually for three years, the total amount at the end of the period would be $1,092.73. This means you would earn an additional $2.73 compared to simple interest.
The Power of Compounding Interest
The power of compounding interest lies in its ability to generate exponential growth over time. By reinvesting your earnings and allowing them to compound, your investment can grow significantly larger than if you were to receive simple interest or not reinvest your earnings.
Factors that Influence Compounding Growth
Several factors contribute to the growth of your investment through compounding interest:
- Principal Amount: The initial amount you invest or save plays a crucial role in determining the final value of your investment. The larger the principal, the more significant the compounding growth.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate directly affects the growth rate of your investment. A higher interest rate leads to faster compounding growth, while a lower interest rate slows down the growth.
- Time: The duration of your investment is a critical factor in harnessing the power of compounding interest. The longer your money compounds, the more time it has to grow and accumulate.
- Compounding Frequency: The frequency at which the interest is compounded affects the rate at which your investment grows. More frequent compounding periods lead to faster growth.
By understanding and carefully considering these factors, you can make informed financial decisions and take advantage of compounding interest to achieve your financial goals.
Applications of Compounding Interest
Compounding interest has various applications in personal finance, including savings, investments, and loans. Let’s explore each of these areas in detail:
Savings Accounts
When you deposit money into a savings account, the bank pays you interest on your balance. This interest is often compounded regularly, allowing your savings to grow over time. By consistently adding to your savings and reinvesting the interest, you can harness the power of compounding and watch your savings accumulate.
Investments
Compounding interest is also a fundamental principle in the world of investing. Whether you invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or other investment vehicles, the compounding effect can work in your favor. By reinvesting dividends or interest payments back into your investments, you can take advantage of compounding and potentially generate significant returns over the long term.
Loans
While compounding interest can work in your favor when saving or investing, it can also work against you when it comes to loans. When you borrow money, the accumulated interest is added to the principal, increasing the amount you owe. This means that the longer you take to repay a loan, the more interest will compound, resulting in a higher overall repayment amount.
Understanding the implications of compounding interest on loans can help you make smarter borrowing decisions and pay off your debts more efficiently.
The Effects of Compounding Frequency
We mentioned earlier that the compounding frequency significantly influences the growth of your investment. Let’s take a closer look at how different compounding frequencies can impact your financial outcomes. To illustrate this, we will use the same initial investment of $1,000 and an annual interest rate of 5%, but with different compounding periods.
- Annual Compounding: If the interest is compounded annually, at the end of five years, your investment would grow to $1,276.28.
- Semi-Annual Compounding: With semi-annual compounding, the interest is compounded twice a year. After five years, your investment would grow to $1,283.68.
- Quarterly Compounding: When compounding occurs quarterly, at the end of five years, your investment would be approximately $1,288.95.
- Monthly Compounding: Monthly compounding leads to an investment value of $1,293.36 after five years.
- Daily Compounding: If your investment compounds daily, after five years, it would be valued at around $1,294.58.
As you can see from the example above, more frequent compounding periods result in slightly higher investment values. While the differences may seem small initially, they can become significant over longer timeframes or with larger investments.
Tax Implications and Compounding Interest
It is important to consider the tax implications when it comes to compounding interest. In most cases, the interest earned on investments or savings accounts is taxable. The tax rate applicable to the interest will depend on your income tax bracket and the regulations in your country.
When investing, it is worth exploring tax-efficient investment vehicles, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) or tax-free savings accounts (TFSAs), which can help minimize the impact of taxes on your compounding growth.
The principle of compounding interest is a powerful concept that can greatly impact your financial well-being. By understanding how compounding works and considering the various factors that influence its growth, you can make informed financial decisions to maximize your wealth over time. Whether you are saving, investing, or taking out a loan, compounding interest should be a fundamental consideration in your financial strategy. So, start harnessing the power of compounding interest today and watch your wealth grow tomorrow.
Compound Interest Explained in One Minute
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is compounding interest?
Compounding interest is the concept of earning interest on both the initial principal amount and the accumulated interest. It allows your money to grow exponentially over time.
How does compounding interest work?
When you invest or save money, the interest you earn is added to your initial investment, forming a larger base for future interest calculations. As a result, you earn interest on the new total amount, leading to accelerated growth.
What is the difference between simple interest and compounding interest?
Simple interest is calculated only on the initial principal amount, while compounding interest takes into account the accumulated interest as well. With compounding interest, your earnings can snowball over time, leading to greater returns.
How often is interest compounded?
The frequency of compounding depends on the investment or savings account. It can be compounded annually, semi-annually, quarterly, monthly, or even daily. The more frequent the compounding, the faster your money will grow.
What factors affect the growth of compound interest?
The growth of compound interest is influenced by three main factors: the interest rate, the time period of investment, and the frequency of compounding. Higher interest rates, longer investment durations, and more frequent compounding lead to greater growth.
Can you provide an example to understand compounding interest better?
Certainly! Let’s say you invest $1,000 in an account with a 5% annual interest rate, compounded annually. After the first year, you would earn $50 in interest, resulting in a total balance of $1,050. In the second year, you would earn interest on $1,050, not just the initial $1,000. This compounding effect continues over time, leading to exponential growth.
Is compounding interest beneficial for long-term investments?
Yes, compounding interest is highly beneficial for long-term investments. The longer you stay invested, the more time your money has to compound and grow. Over several years, compounding can significantly enhance your returns.
What should I consider when choosing an investment account with compounding interest?
When selecting an investment account, consider factors such as the interest rate, compounding frequency, fees, and terms and conditions. It’s essential to assess which account offers the best combination of these factors to maximize your earnings.
Is compounding interest guaranteed?
While compounding interest can generate substantial returns, it is important to note that investment returns are subject to market fluctuations. Therefore, compounding interest is not guaranteed, and it’s crucial to consider the associated risks before investing.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the principle of compounding interest is crucial for financial success. It allows you to grow your money exponentially over time. By reinvesting any interest earned, you can take advantage of the power of compounding. Whether it’s through investing in the stock market or opening a high-interest savings account, compounding interest is a powerful tool for wealth accumulation. By understanding how compounding works, you can make informed financial decisions and maximize your returns. So, take the time to understand the principle of compounding interest and start harnessing its potential today.