Are you curious about understanding trade deficits and their implications? Look no further! In this article, we delve into the intricacies of trade deficits and shed light on their implications for economies. From a basic definition to exploring the factors contributing to trade deficits, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding. Moreover, we will examine the potential consequences of trade deficits on a country’s economy and why they matter. So, fasten your seatbelt as we embark on this journey of unraveling the mysteries behind trade deficits and their implications.
Understanding Trade Deficits and Their Implications
Introduction
Trade deficits have been a topic of much discussion and debate in recent years. While some argue that trade deficits are detrimental to an economy, others believe they can be beneficial in certain circumstances. In this article, we will dive deep into understanding trade deficits and explore their implications on various aspects of an economy.
What is a Trade Deficit?
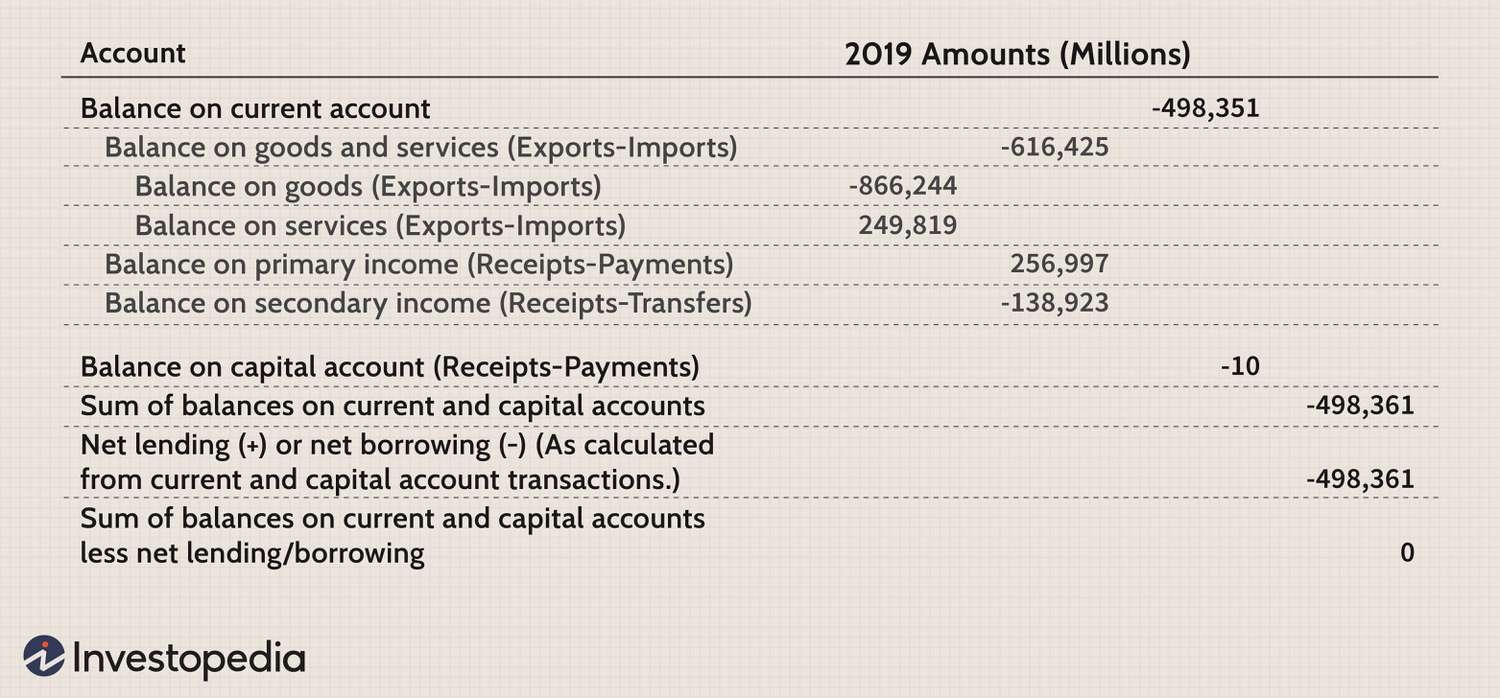
A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports. In other words, it represents a negative balance of trade. Trade deficits are measured by the difference between the value of a country’s imports and exports over a specific period, usually a year.
There are two types of trade deficits:
- Goods Trade Deficit: This occurs when a country imports more physical goods than it exports.
- Services Trade Deficit: This occurs when a country imports more services than it exports. Services include sectors like tourism, transportation, and financial services.
Causes of Trade Deficits
Several factors contribute to the emergence of trade deficits. It’s important to understand these causes to gain a comprehensive understanding of their implications. Some common causes include:
- Consumer Preferences: Trade deficits can occur when consumers in a particular country have a high demand for foreign goods or services.
- Competitiveness: If domestic industries are unable to produce goods or services that can compete with those produced abroad, it can lead to a trade deficit.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the cost of imports and exports, potentially leading to trade deficits.
- Government Policies: Policies that favor imports or hinder exports, such as tariffs or subsidies, can contribute to trade deficits.
Implications of Trade Deficits
Trade deficits have both positive and negative implications for an economy. Let’s explore them in detail.
Negative Implications
- Loss of Jobs: A persistent trade deficit can lead to job losses in domestic industries, especially those competing with cheaper imports.
- Industry Decline: Trade deficits can weaken domestic industries as they face increased competition from foreign producers.
- Current Account Balance: Trade deficits contribute to a negative current account balance, which can make a country more dependent on foreign borrowing.
- Domestic Debt: To finance trade deficits, countries may accumulate debt, which can lead to economic instability in the long run.
- Reduced GDP Growth: Trade deficits can impact a country’s GDP growth rate, especially if the deficit is significant and sustained over time.
- Impact on Exchange Rates: If a country has a persistent trade deficit, it can put downward pressure on its currency exchange rates.
Positive Implications
While trade deficits are generally viewed negatively, they can also have positive implications for an economy. Some of the positive aspects include:
- Access to Goods and Services: Trade deficits allow countries to access a wider range of goods and services that may not be available domestically or at a competitive price.
- Consumer Benefits: Importing cheaper goods can benefit consumers by providing them with affordable options and improving their standard of living.
- Foreign Investments: Trade deficits can attract foreign investments as countries look to capitalize on the growing demand for their goods and services.
- Innovation and Competition: Increased competition from imports can drive domestic industries to innovate and become more competitive in the global market.
- Enhancing Productivity: Foreign competition can push domestic industries to improve their productivity and efficiency to remain competitive.
Addressing Trade Deficits
To address trade deficits, countries can employ various strategies. It’s vital to understand these strategies to analyze their potential impact.
Export Promotion
- Government Support: Governments can provide financial assistance, subsidies, or tax incentives to domestic industries to boost their competitiveness in export markets.
- Trade Agreements: Entering into trade agreements or reducing trade barriers can enhance export opportunities for domestic producers.
- Export Financing: Governments can offer export financing and insurance to domestic businesses to facilitate export activities.
Import Control
- Tariffs and Quotas: Imposing tariffs or quotas on imports can reduce competition from foreign goods and protect domestic industries.
- Import Substitution: Encouraging the production of goods domestically instead of relying on imports can help reduce trade deficits.
- Quality Standards: Implementing stringent quality standards can reduce reliance on low-quality imports and encourage domestic consumption.
Exchange Rate Policies
- Currency Depreciation: A depreciated domestic currency can make exports cheaper and imports more expensive, thus reducing trade deficits.
- Monetary Policies: Central banks can implement monetary policies that influence the exchange rate, thereby impacting trade deficits.
Economic Diversification
- Investing in New Industries: Governments can promote investments in emerging industries to reduce dependence on certain imports.
- Encouraging Innovation: Supporting research and development efforts can foster innovation and create new export opportunities.
Understanding trade deficits and their implications is crucial to comprehend the complex dynamics of international trade. While trade deficits can have negative consequences, they can also bring positive outcomes for an economy. It’s essential for policymakers to carefully analyze the causes and potential impact of trade deficits to develop appropriate strategies for sustainable economic growth. By striking a balance between imports and exports, countries can harness the benefits of international trade while minimizing the adverse effects of trade deficits.
Understanding Trade Deficits
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a trade deficit?
A trade deficit occurs when a country’s imports exceed its exports, resulting in a negative balance of trade. It means that a country is buying more goods and services from foreign nations than it is selling to them.
What are the causes of a trade deficit?
Several factors can contribute to a trade deficit, including a country’s domestic consumption patterns, exchange rates, tariffs and trade barriers, and differences in the cost of labor and production between countries.
What are the implications of a trade deficit?
A trade deficit can have both positive and negative implications. On the negative side, it may lead to job losses in industries facing international competition and can weaken a country’s domestic manufacturing sector. However, a trade deficit can also indicate strong domestic demand and the ability to import goods and services not readily available domestically.
How does a trade deficit affect the economy?
A trade deficit can impact the economy in various ways. It can put downward pressure on a country’s currency, increase its foreign indebtedness, and potentially lead to inflation. However, it can also provide consumers with access to a wider variety of goods and services at potentially lower prices.
Why do some countries have persistent trade deficits?
Persistent trade deficits can be attributed to several factors, such as structural issues in the economy, including a lack of competitiveness in certain industries, insufficient domestic savings, and imbalances in global trade relationships.
Are all trade deficits bad?
No, not all trade deficits are necessarily bad. While a large and persistent trade deficit can have negative consequences, a temporary or moderate trade deficit can be a normal part of economic growth and development.
How can a country reduce its trade deficit?
A country can reduce its trade deficit through various strategies, such as promoting exports, implementing import substitution policies, negotiating trade agreements, addressing domestic structural issues, and focusing on improving competitiveness in key industries.
Can trade deficits be eliminated entirely?
Eliminating trade deficits entirely can be challenging as they are influenced by various global factors. However, countries can aim to reduce their trade deficits by implementing appropriate policies and fostering a conducive economic environment. Achieving a balanced trade position may be more realistic than complete elimination.
Final Thoughts
Understanding trade deficits and their implications is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports. This imbalance can have various consequences, including increased national debt, currency devaluation, and loss of domestic industries. It hinders economic growth and job creation while potentially impacting the exchange rate and overall competitiveness. Therefore, comprehending the causes and effects of trade deficits is essential for making informed policy decisions and implementing measures to address them. By fostering a balanced approach to international trade, countries can strive towards sustainable economic development and maintain a competitive edge in the global marketplace while avoiding the adverse effects of trade deficits.