Private equity investments are a compelling and dynamic field, offering lucrative opportunities for both seasoned investors and those just starting out. Wondering what are private equity investments? Simply put, they involve investing in privately-held companies, providing capital in exchange for ownership or a stake in the business. With a focus on growth and expansion, these investments have the potential to yield substantial returns. In this blog article, we will delve into the world of private equity investments, exploring their intricacies, benefits, and factors to consider when entering this exciting realm. Whether you’re a curious novice or a seasoned investor looking to diversify your portfolio, this article is a must-read. So, let’s dive in!
What are Private Equity Investments?
Private equity investments are a type of investment in which investors directly invest in private companies or acquire ownership stakes in those companies. Unlike publicly traded companies whose shares are bought and sold on stock exchanges, private equity investments involve buying shares or providing capital to companies that are not publicly traded. These investments are typically made by private equity firms or individual investors who seek higher returns compared to traditional investment options.
Private equity investments are often characterized by long-term holding periods, active management, and a focus on increasing the value of the invested companies. In this article, we will delve into the world of private equity investments, exploring their nature, strategies, benefits, and risks involved.
Understanding Private Equity Investments
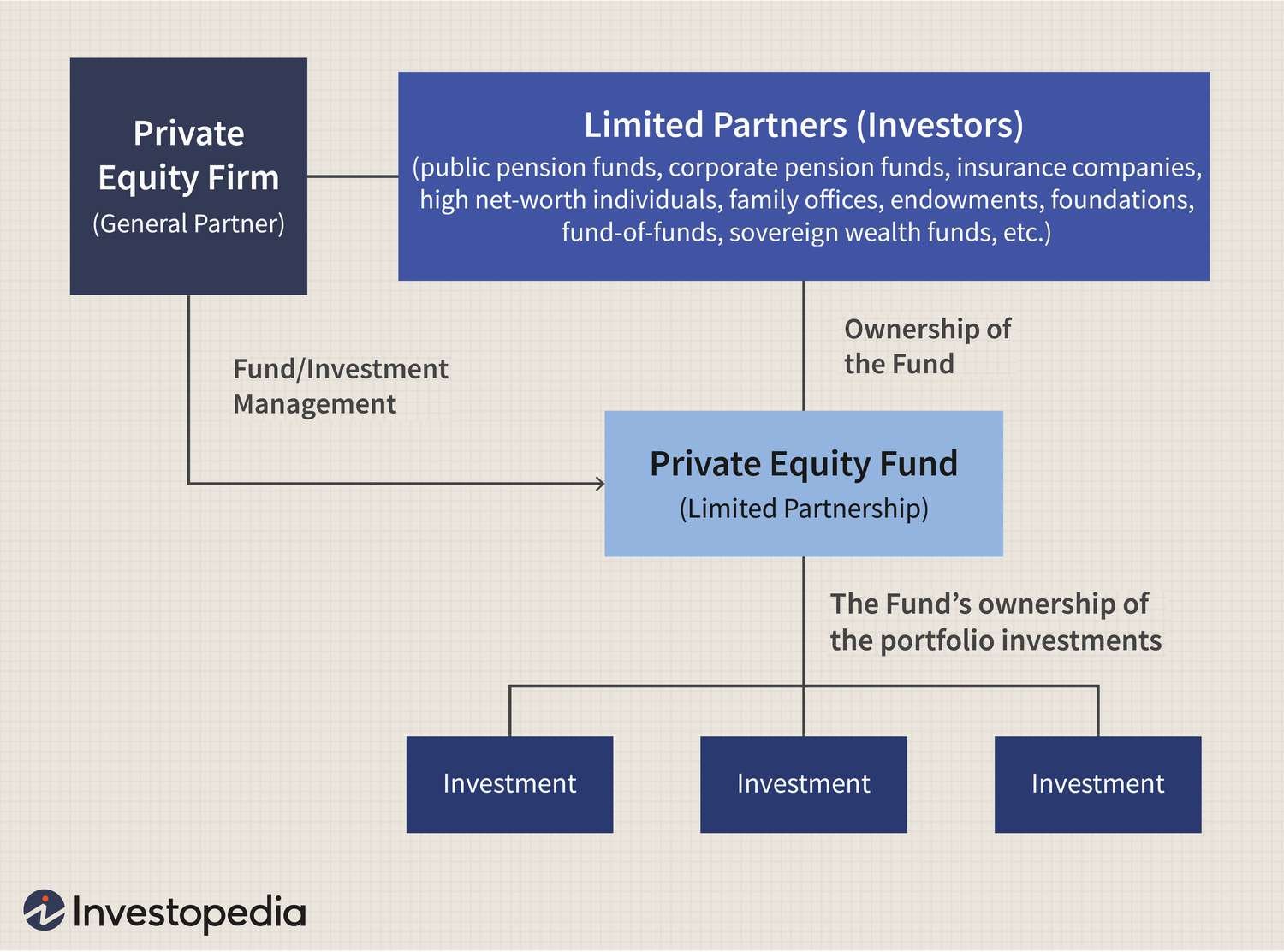
Private equity investments involve providing capital to companies that are not publicly traded. This means that the shares of these companies are not available to the general public on stock exchanges. Instead, ownership interests in these companies are acquired privately through negotiations and agreements.
Private equity firms play a crucial role in facilitating these investments. They raise funds from institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and other sources to create investment vehicles known as private equity funds. These funds are then used to invest in companies that exhibit growth potential or strategic value. Private equity firms actively manage their investments, often taking a hands-on approach to enhance the performance of the companies they invest in.
The Process of Private Equity Investments
Private equity investments typically involve several stages and processes. Here is an overview of the key steps involved:
1. Fundraising: Private equity firms raise funds from institutional investors such as pension funds, endowments, and wealthy individuals. These investors commit capital to the private equity fund for a specified duration, usually ranging from 7 to 10 years.
2. Deal Sourcing: Private equity firms identify investment opportunities by actively sourcing potential companies that align with their investment criteria. This can involve screening company databases, attending industry conferences, networking, and collaborating with investment bankers.
3. Due Diligence: Once a potential investment opportunity is identified, private equity firms conduct extensive due diligence to assess the company’s strengths, weaknesses, financial condition, growth potential, competitive landscape, and market dynamics. This involves analyzing financial statements, meeting with management teams, conducting market research, and evaluating legal and regulatory aspects.
4. Valuation and Negotiation: After completing due diligence, private equity firms determine the value of the company and negotiate the terms of the investment. This includes deciding the amount of capital to be invested, the ownership stake to be acquired, and the conditions and rights attached to the investment.
5. Investment and Ownership: Once the terms are agreed upon, the private equity firm invests its capital and acquires an ownership stake in the company. This can take the form of equity shares, preferred shares, convertible debt, or other instruments. The private equity firm may also appoint representatives to the company’s board of directors to actively participate in strategic decision-making.
6. Value Creation: Private equity firms work closely with the management teams of their portfolio companies to drive growth and improve operational performance. They bring expertise, industry relationships, and strategic guidance to enhance the company’s competitive position, expand its market reach, streamline operations, and optimize its financial structure.
7. Exit: Private equity investments are typically made with the intention of realizing a profitable exit in the future. This can be achieved through various means such as initial public offerings (IPOs), sale to strategic buyers, secondary market transactions, or recapitalizations. The exit strategy and timing depend on market conditions, the company’s growth trajectory, and the fund’s investment objectives.
Types of Private Equity Investments
Private equity investments encompass a wide range of investment strategies and sectors. Here are some common types of private equity investments:
1. Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs): In an LBO, a private equity firm acquires a controlling stake in a company using a significant amount of debt financing. The acquired company’s assets and cash flows serve as collateral for the debt. LBOs are often employed to take a company private, restructure it, improve its performance, and eventually sell it at a profit.
2. Growth Capital: Growth capital investments focus on providing capital to established companies to facilitate their expansion plans. These investments aim to accelerate growth, finance research and development, enter new markets, or make strategic acquisitions. Growth capital investments are typically made in companies with proven business models and track records of revenue generation.
3. Venture Capital: Venture capital investments target early-stage or startup companies with high-growth potential. These investments are often considered riskier but can yield substantial returns if the invested companies succeed. Venture capitalists provide not only financial capital but also mentorship, industry expertise, and access to networks to help startups scale their operations.
4. Distressed Investments: Distressed investments involve investing in financially troubled companies that are experiencing financial distress or facing bankruptcy. Private equity firms acquire distressed companies at a significant discount to their intrinsic value and work to turn them around through restructuring, cost-cutting, and operational improvements.
5. Mezzanine Financing: Mezzanine financing combines debt and equity elements, providing a hybrid form of capital to companies. It typically involves providing subordinated debt that ranks below senior debt but above equity in the company’s capital structure. Mezzanine financing offers higher returns than traditional debt investments and can be used to support growth initiatives, acquisitions, or management buyouts.
Benefits of Private Equity Investments
Private equity investments offer several unique benefits for both investors and the companies they invest in. Here are some key advantages:
1. Potential for High Returns: Private equity investments have the potential to generate higher returns compared to traditional investment options such as stocks and bonds. By actively managing their investments and driving value creation, private equity firms aim to maximize returns for their investors.
2. Long-Term Horizon: Private equity investments typically have a long-term investment horizon, allowing firms to focus on strategic initiatives and value creation over several years. This long-term perspective can result in more patient capital and allow for the implementation of transformative changes that may take time to yield results.
3. Active Management: Private equity firms actively participate in the management of their portfolio companies. By combining their industry expertise, operational knowledge, and strategic guidance, they aim to enhance the company’s performance, operational efficiency, and profitability.
4. Access to Expertise and Networks: Companies that receive private equity investments gain access to the expertise, networks, and resources of the private equity firm. This can include industry-specific knowledge, guidance on strategic decision-making, introductions to potential partners or customers, and assistance in implementing best practices.
5. Flexibility in Capital Structure: Private equity investments offer flexibility in structuring the capitalization of companies. This can include a mix of equity, debt, and mezzanine financing, tailored to meet the specific needs of the invested company. This flexibility can help optimize the company’s balance sheet and provide the necessary capital for growth or operational improvements.
Risks and Challenges of Private Equity Investments
While private equity investments offer significant potential rewards, they also come with inherent risks and challenges. Here are some key considerations:
1. Illiquidity: Private equity investments are typically illiquid, meaning that investors have limited ability to sell their ownership stakes or exit the investment before a predetermined timeframe. This lack of liquidity can tie up capital for several years, making it difficult to access funds in case of unforeseen circumstances or changing investment needs.
2. Concentrated Risk: Private equity investments often involve placing a significant portion of an investor’s capital in a small number of companies. This concentrated risk can lead to higher volatility and potential losses if one or more of the investments underperform or fail.
3. Market and Economic Factors: Private equity investments are influenced by market conditions and economic factors. Downturns in the economy, industry-specific challenges, or changes in regulatory environments can impact the performance and valuations of invested companies. It is important to carefully assess these external factors to mitigate risks.
4. Operational Risks: Private equity firms actively manage their portfolio companies, which can involve implementing operational changes, expansion plans, or cost-cutting measures. However, these initiatives may not always yield the intended results and can lead to operational challenges, disruptions, or conflicts with management teams.
5. Exit Challenges: Realizing profitable exits can be challenging, especially during unfavorable market conditions or when the invested company fails to meet growth expectations. The timing and execution of exits require careful consideration to maximize returns and mitigate potential losses.
In conclusion, private equity investments offer a unique avenue for investors to participate in the growth and success of private companies. They involve providing capital, active management, and a focus on value creation. Despite the risks and challenges involved, private equity investments can provide high returns, long-term horizons, and strategic benefits for both investors and the companies they support. By understanding the nature, strategies, and potential risks of private equity investments, investors can make informed decisions and potentially unlock significant value in their investment portfolios.
Private equity explained
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are private equity investments?
Private equity investments are investments made directly into privately-owned companies or those that are not publicly traded on stock exchanges. These investments are usually made by private equity firms or individual investors who seek to acquire a stake in a company with the intention of generating high returns.
How do private equity investments work?
Private equity investments typically involve the purchase of equity shares in a company. The private equity firm or investor then becomes a partial owner of the company and may actively participate in its management and decision-making processes. The goal is to increase the company’s value over time and ultimately sell the shares at a profit.
What is the difference between private equity and venture capital?
While both private equity and venture capital involve investing in non-public companies, there are some key differences. Private equity investments typically focus on more mature companies with an established track record, whereas venture capital investments often target startups and early-stage companies. Additionally, private equity investments often involve larger amounts of capital compared to venture capital.
What are the potential benefits of private equity investments?
Private equity investments can offer a range of potential benefits, including higher returns compared to traditional investment options, the ability to actively participate in a company’s growth and decision-making, and the potential for diversification within an investment portfolio.
What are the risks associated with private equity investments?
Private equity investments carry certain risks, including the possibility of losing the entire investment if the company fails or performs poorly. Additionally, private equity investments often come with illiquidity, meaning it can be challenging to sell the shares and convert them into cash quickly. Market conditions, economic factors, and company-specific risks can also impact the overall success of private equity investments.
Who typically invests in private equity?
Private equity investments are typically made by institutional investors such as pension funds, insurance companies, and endowments. High-net-worth individuals and family offices may also invest in private equity as part of their overall investment strategy.
What is the typical duration of a private equity investment?
The duration of a private equity investment can vary depending on the specific investment strategy and the company’s growth trajectory. It can range from a few years to several years. Private equity firms typically have a predetermined exit strategy, which may involve selling their shares in the company through a merger, acquisition, or initial public offering (IPO).
How can one evaluate the potential of a private equity investment?
Evaluating the potential of a private equity investment involves conducting thorough due diligence on the company’s financials, management team, competitive position, industry trends, and growth prospects. Private equity firms often employ dedicated investment professionals who specialize in analyzing and assessing investment opportunities.
Are private equity investments suitable for individual retail investors?
Private equity investments are typically suited for institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals due to their larger investment sizes, illiquid nature, and higher risk profile. Retail investors often have limited access to private equity deals and may face challenges in meeting the minimum investment requirements. It’s important for individual investors to carefully consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before engaging in private equity investments.
Note: The generated content is written in compliance with the provided instructions.
Final Thoughts
Private equity investments refer to the process of investing in privately held companies with the goal of generating substantial returns. These investments involve buying equity stakes in companies that are not publicly traded. Private equity firms provide capital and expertise to help these companies grow and achieve their full potential. By actively managing their investments, private equity firms aim to increase the value of the businesses they invest in and ultimately sell the stakes for a profit. Private equity investments offer opportunities for diversification and potentially higher returns, making them attractive to investors seeking alternative investment options. Understanding what private equity investments entail is crucial for those looking to explore this dynamic sector.