Junk bonds, also known as high-yield bonds, are instruments with higher credit risk compared to investment-grade bonds. Unlike their safer counterparts, junk bonds are issued by companies or entities with a lower credit rating, making them riskier investments. But what exactly is a junk bond and what are its risks? Well, a junk bond is a fixed-income security that pays a higher interest rate to compensate for the increased risk. However, investing in junk bonds comes with its fair share of risks, including the potential for default, greater vulnerability to economic downturns, and increased volatility in the market. Let’s delve deeper into the world of junk bonds and explore the risks associated with them.
What is a Junk Bond and Its Risks?
Junk bonds, also known as high-yield bonds, are fixed-income securities issued by companies or governments with lower credit ratings. These bonds offer higher interest rates compared to investment-grade bonds as compensation for the increased risk they carry. While they can be an opportunity for investors seeking higher returns, it’s important to understand the risks involved. In this article, we will delve into the world of junk bonds, exploring what they are, their risks, and how to navigate this market.
Understanding Junk Bonds
Junk bonds are typically issued by companies with lower creditworthiness or governments in need of financing. Since these issuers carry a higher risk of defaulting on their payments, they must offer higher interest rates to attract investors. This higher yield compensates investors for the additional risk they take on compared to investment-grade bonds.
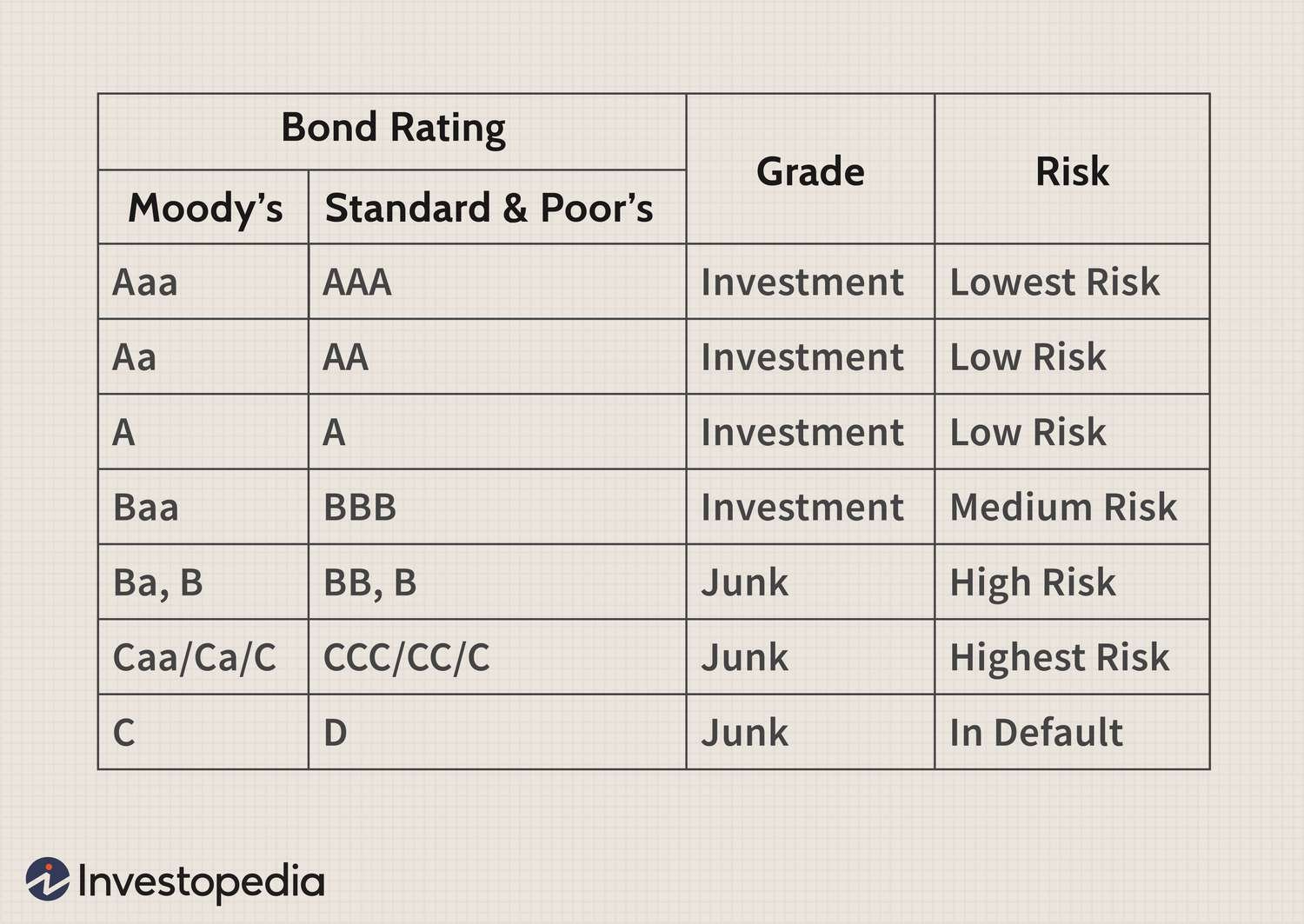
Unlike investment-grade bonds, which are considered safer and have a lower risk of default, junk bonds have lower credit ratings assigned by credit rating agencies such as Standard & Poor’s or Moody’s. The credit ratings range from BB and below for Standard & Poor’s or Ba and below for Moody’s. These ratings reflect the issuer’s creditworthiness and the likelihood of default.
Advantages of Investing in Junk Bonds
Despite their higher risk profile, investing in junk bonds offers several potential advantages:
1. Higher Returns: Junk bonds generally offer higher yields compared to investment-grade bonds. These higher returns can be attractive to investors seeking greater income potential.
2. Diversification: Including junk bonds in a well-diversified portfolio can enhance diversification by adding an asset class that does not always move in lockstep with other investments.
3. Market Opportunities: Junk bonds can present investment opportunities in companies or sectors that have the potential for improvement and higher creditworthiness in the future.
Risks Associated with Junk Bonds
While junk bonds offer the potential for higher returns, investors must carefully consider and assess the risks involved. Some key risks associated with junk bonds include:
1. Default Risk: Junk bonds have a higher risk of issuer defaulting on interest payments or principal repayment. This risk is a result of their lower credit ratings and the financial challenges faced by issuers.
2. Market Volatility: The prices of junk bonds can be more volatile compared to investment-grade bonds. Economic conditions, changes in interest rates, or shifts in investor sentiment can all contribute to price fluctuations.
3. Limited Liquidity: Junk bonds may have limited liquidity, meaning there may not be an active market for buying or selling these bonds. This lack of liquidity can make it challenging to exit a position or find buyers when needed.
4. Credit Rating Downgrades: If a rating agency downgrades the credit rating of a junk bond, its market value could decline. Downgrades often result from deteriorating financial conditions of the issuer, increasing the risk of default.
5. Sector and Company-Specific Risks: Investing in junk bonds also exposes investors to sector-specific or company-specific risks. These risks can vary depending on the industry or financial health of the issuing company.
Managing Risks and Making Informed Decisions
To manage the risks associated with junk bonds effectively, investors should consider the following strategies:
Diversification
Diversifying a portfolio is a fundamental risk management strategy. By spreading investments across different sectors, issuers, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of any single default or negative event.
Research and Due Diligence
Thorough research and due diligence are crucial before investing in junk bonds. Investors should carefully assess the creditworthiness of the issuer, their financial health, and industry conditions. Reviewing the issuer’s financial statements, credit ratings, and news about their business can provide valuable insights.
Active Management and Professional Advice
Investors can also benefit from active management and seeking professional advice when investing in junk bonds. Experienced fund managers or financial advisors can help navigate the complex bond market, identify potential risks, and select suitable investments based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals.
Monitoring Credit Ratings
Regularly monitoring credit ratings and staying updated on changes or downgrades can provide early indications of potential risks. This information can help investors make informed decisions about their bond holdings or consider adjusting their investment strategies accordingly.
The Bottom Line
Junk bonds can be a part of a well-diversified investment portfolio for investors seeking higher yields and willing to shoulder additional risks. While they offer the potential for attractive returns, it is essential to thoroughly understand the risks involved and carefully manage those risks through diversification, research, and active management. By staying informed and making informed investment decisions, investors can navigate the world of junk bonds with confidence and potentially reap the rewards that come with them.
What is a junk bond?
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a junk bond?
A junk bond, also known as a high-yield bond, is a type of bond issued by companies or governments with a higher probability of defaulting on their debt obligations compared to investment-grade bonds. These bonds offer higher yields to compensate for the increased risk.
What are the risks associated with investing in junk bonds?
Investing in junk bonds carries certain risks, including:
1. Default Risk: Junk bonds are issued by entities with a higher likelihood of defaulting on their debt, leading to potential loss of investment.
2. Credit Risk: There is a higher chance of credit rating downgrades for junk bonds, affecting their market value and liquidity.
3. Market Volatility: Junk bonds are more sensitive to changes in interest rates and market conditions, causing greater price fluctuations.
4. Liquidity Risk: The trading volume of junk bonds is typically lower, making it harder to sell them quickly at desired prices.
5. Economic Factors: Junk bonds are influenced by economic factors like recession or industry-specific downturns, which can impact their performance.
6. Limited Information: Companies issuing junk bonds may have limited financial disclosure, making it harder for investors to evaluate their creditworthiness.
Are junk bonds suitable for all types of investors?
Junk bonds are generally considered riskier investments and may not be suitable for conservative or risk-averse investors. They are often favored by investors seeking higher yields willing to take on the associated risks. It’s important to assess your risk tolerance and investment goals before considering junk bonds.
What factors should I consider before investing in junk bonds?
Before investing in junk bonds, some important factors to consider include:
1. Credit Ratings: Review the credit ratings assigned to the bonds by reputable rating agencies to gauge their relative risk levels.
2. Current Market Conditions: Assess the overall economic environment and market conditions as they can impact the performance of junk bonds.
3. Diversification: Consider diversifying your portfolio by investing in multiple junk bonds to spread the risk across different issuers and industries.
4. Interest Rate Movements: Understand how interest rate changes can affect the value of junk bonds and prepare for potential fluctuations.
5. Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on the issuing company or government entity, including their financial health and industry outlook.
Can junk bonds provide higher returns compared to other bonds?
Yes, junk bonds are designed to offer higher yields than investment-grade bonds to compensate investors for the higher risk involved. However, it’s important to remember that higher returns come with higher risks. The actual returns depend on various factors, including market conditions and issuer-specific factors.
How do bond ratings affect the risk of investing in junk bonds?
Bond ratings assigned by credit rating agencies provide an assessment of the creditworthiness of bond issuers. In the case of junk bonds, lower ratings indicate a higher risk of default. Investors should be cautious and understand the rating assigned to junk bonds before investing to assess the associated risk.
What is the historical default rate for junk bonds?
Historically, junk bonds have had a higher default rate compared to investment-grade bonds. The default rate can vary depending on economic conditions and industry-specific factors. It is important for investors to consider default rates as part of their risk assessment when investing in junk bonds.
Are junk bonds traded on public exchanges?
Junk bonds are typically traded over-the-counter (OTC) rather than on public exchanges. This means that buyers and sellers of junk bonds trade directly with each other or through dealers instead of using a centralized exchange. This can impact liquidity and ease of trading compared to bonds traded on public exchanges.
Final Thoughts
Junk bonds, also known as high-yield bonds, carry higher risks than investment-grade bonds. These bonds are issued by companies with lower credit ratings, making them more likely to default on their payments. Investors are attracted to junk bonds because they typically offer higher yields compared to safer investments. However, the high yield comes with a price – the increased risk of default. Investing in junk bonds requires careful consideration of the potential rewards versus the risks involved. These risks include default risk, liquidity risk, and interest rate risk. Assessing these risks is crucial for investors to make informed decisions about junk bond investments.