Are you curious about mutual fund expenses and their impact? Look no further! In this article, we will delve into the world of mutual fund expense ratios and how they can affect your investments. Understanding these ratios is crucial for investors who want to make informed decisions about their portfolios. So, what exactly is a mutual fund expense ratio and what impact does it have? Let’s explore the answers together.
What is a Mutual Fund Expense Ratio and Its Impact
An Introduction to Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are a popular investment vehicle that allow individuals to pool their money together to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. These funds are managed by professional portfolio managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors. One important factor to consider when investing in mutual funds is the expense ratio.
Understanding the Mutual Fund Expense Ratio
The mutual fund expense ratio is a measure of the costs associated with managing and operating a mutual fund. It represents the percentage of a fund’s assets that are used to cover various expenses, including administrative fees, management fees, marketing expenses, and other operational costs. This ratio is calculated annually and is expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average net assets.
Components of the Expense Ratio
To fully understand the impact of the expense ratio, it’s important to break down its components:
- Management Fees: These fees compensate the fund manager for their expertise and time spent managing the portfolio. They are typically the largest component of the expense ratio.
- Administrative Fees: These fees cover the administrative costs associated with running the mutual fund, such as record-keeping, custodial services, and shareholder services.
- 12b-1 Fees: These fees are named after the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rule that allows mutual funds to use a portion of their assets to pay for distribution and marketing expenses. They are often used to compensate intermediaries, such as financial advisors or brokers.
- Other Expenses: This category includes various operational costs incurred by the mutual fund, such as legal fees, accounting expenses, and other professional services.
The Impact of the Expense Ratio
The expense ratio can have a significant impact on the overall returns of a mutual fund. Here’s how it affects investors:
Reduced Investment Returns
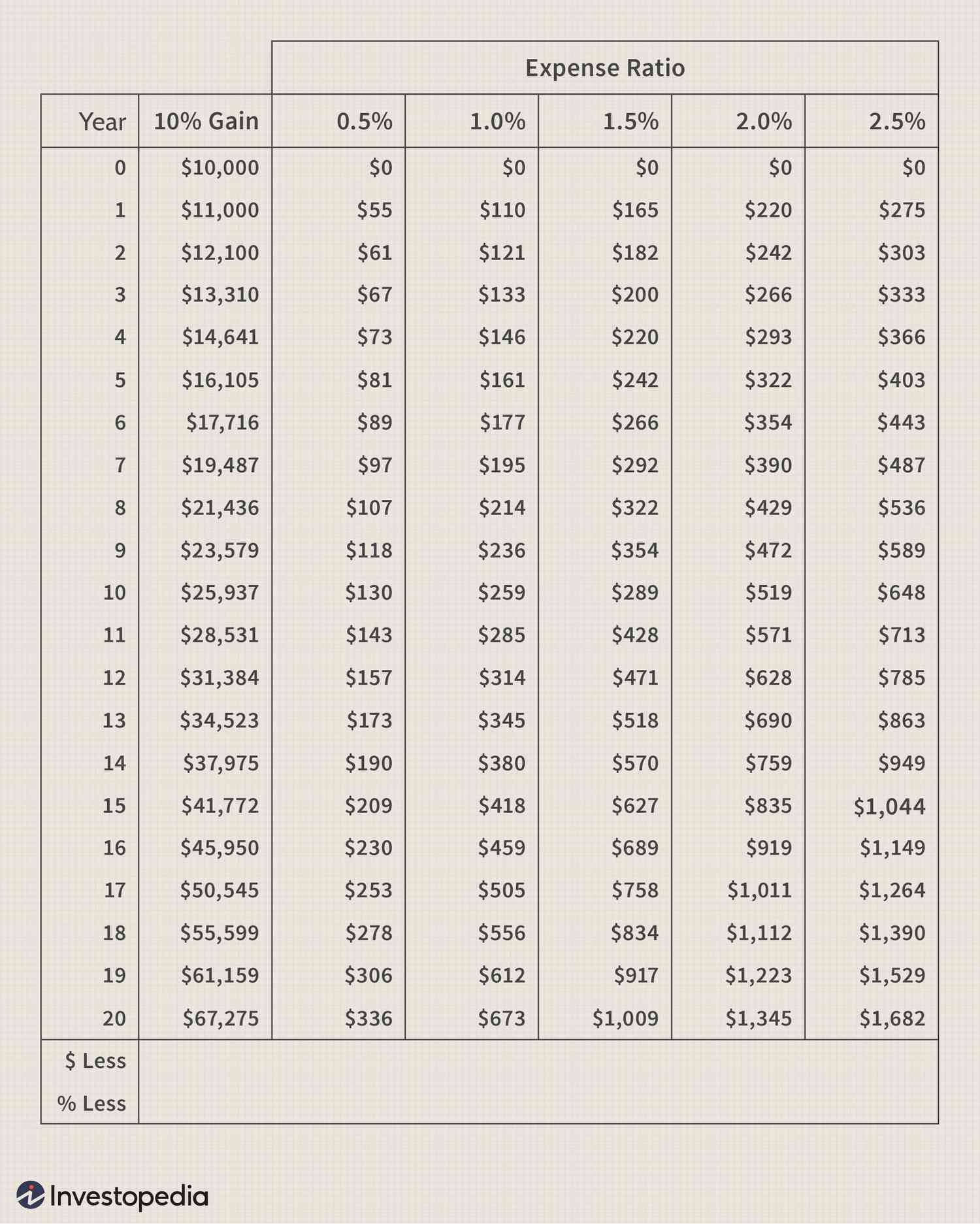
The expense ratio is deducted from the fund’s assets, resulting in reduced investment returns for investors. For example, if a mutual fund has an expense ratio of 1% and the fund’s annual return is 8%, investors will effectively receive a net return of 7% after deducting the expense ratio. Over time, these seemingly small reductions can have a substantial impact on the overall growth of an investment.
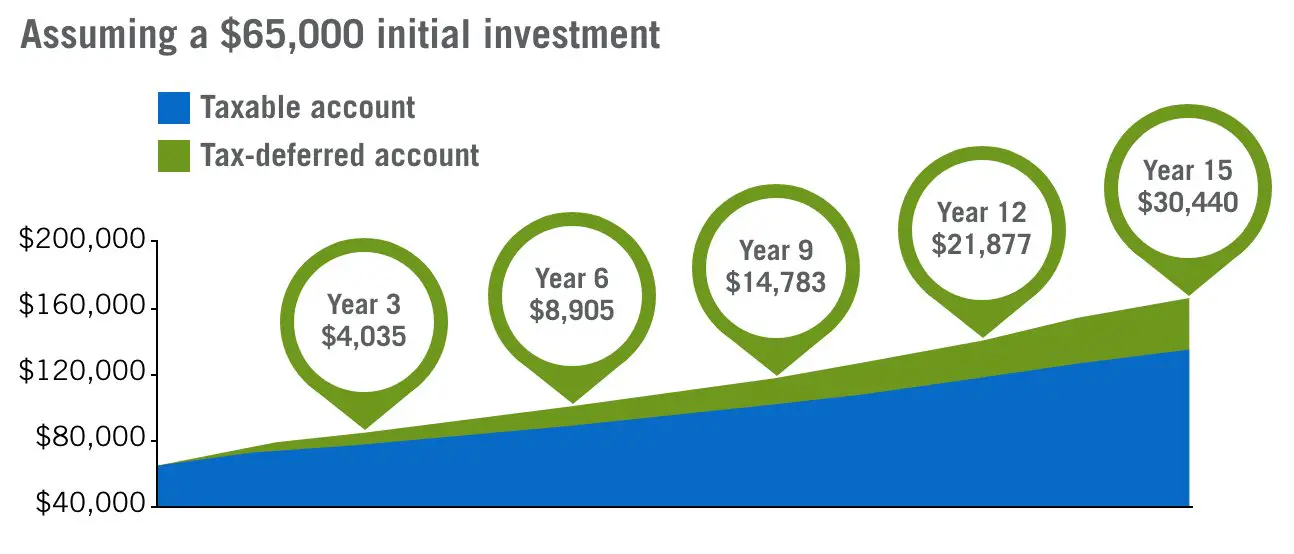
Long-Term Impact on Wealth Accumulation
When considering the impact of the expense ratio, it’s important to remember the power of compounding returns. Even a seemingly small difference in expense ratios can result in significant differences in wealth accumulation over a long-term investment horizon. Funds with lower expense ratios allow investors to keep more of their returns, compounding their wealth over time.
Choosing a Low-Expense Ratio Fund
Selecting mutual funds with low expense ratios is a crucial step towards maximizing investment returns. Here are some benefits of choosing funds with lower expense ratios:
- Higher Net Returns: Low-cost funds leave more money in the pockets of investors, resulting in higher net returns over the long term.
- Cost Efficiency: Funds with lower expense ratios reflect a more cost-efficient approach to investing. This indicates that the fund management is focused on minimizing expenses and maximizing the value for investors.
- Increased Diversification: Investing in low-cost funds allows investors to diversify their portfolios without incurring excessive expenses. This helps spread investment risk across various asset classes and reduces the dependence on any single investment.
- Lower Portfolio Turnover: Funds with lower expense ratios tend to have lower portfolio turnover, which can result in reduced transaction costs and potential tax savings for investors.
Factors Influencing Expense Ratios
Expense ratios can vary significantly across different mutual funds. Here are some factors that influence expense ratios:
Size of the Fund
Larger mutual funds tend to have lower expense ratios due to economies of scale. As the assets under management increase, the fixed costs associated with running the fund are spread across a larger investor base, resulting in lower expense ratios.
Asset Class
The expense ratios for different asset classes can vary. For example, equity funds may have higher expense ratios than bond funds due to the higher costs associated with analyzing and trading stocks.
Investment Style
Different investment styles, such as actively managed funds and index funds, have different expense ratios. Actively managed funds typically have higher expense ratios due to the costs associated with research and active trading, while index funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index and tend to have lower expense ratios.
Share Class
Mutual funds often offer different share classes, each with its own expense ratio. Share classes typically vary based on the initial investment amount, ongoing fees, and minimum holding period. Institutional share classes, typically available to larger investors, often have lower expense ratios compared to retail share classes.
Understanding the mutual fund expense ratio and its impact is crucial for investors looking to maximize their investment returns. By choosing funds with lower expense ratios, investors can potentially increase their net returns and grow their wealth over time. It’s important to carefully analyze and compare expense ratios when selecting mutual funds to ensure a cost-efficient and well-diversified investment portfolio.
How Does Expense Ratio 'Get Charged?'
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a mutual fund expense ratio?
A mutual fund expense ratio is the percentage of a mutual fund’s total assets that is used to cover expenses like management fees, administrative costs, and other operating expenses. It is an ongoing charge that investors pay for investing in a mutual fund.
How does the mutual fund expense ratio impact my investment?
The mutual fund expense ratio directly affects the returns you can expect from your investment. A higher expense ratio means more of your investment returns are used to cover the fund’s expenses, resulting in lower net returns for you as an investor.
Why is it important to consider the mutual fund expense ratio?
Considering the mutual fund expense ratio is crucial because it directly affects your investment returns. Lower expense ratios mean higher net returns for investors. Over time, even seemingly small differences in expense ratios can significantly impact your overall investment growth.
How can I find the mutual fund expense ratio?
You can find the mutual fund expense ratio in the fund’s prospectus, which is a legal document that provides details about the fund’s objectives, strategies, and fees. It is important to review the expense ratio before investing in a mutual fund.
Are all mutual funds’ expense ratios the same?
No, different mutual funds can have different expense ratios. Expense ratios can vary based on factors such as the size of the fund, the investment strategy, and the fund manager’s expertise. It is important to compare expense ratios when choosing between mutual funds.
What is considered a high expense ratio?
While the definition of a high expense ratio may vary, generally, expense ratios above 1% are considered relatively high. It is important to assess the expense ratio in the context of the fund’s performance and comparable alternatives in the market.
Can a high expense ratio impact the long-term performance of a mutual fund?
Yes, a high expense ratio can impact a mutual fund’s long-term performance. Higher expenses reduce the overall return potential of the fund, making it more challenging for the fund to outperform its benchmark or peers over time.
Are there any alternatives to mutual funds with lower expense ratios?
Yes, there are alternatives to mutual funds with lower expense ratios, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds. These investment vehicles often have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed mutual funds, making them attractive options for cost-conscious investors.
Final Thoughts
A mutual fund expense ratio is the percentage of a fund’s assets that are used to cover operating expenses. It includes management fees, administrative costs, and other expenses incurred by the fund. This ratio is an important factor to consider when investing in mutual funds as it directly impacts your returns. The higher the expense ratio, the lower your potential returns may be. It is crucial to pay attention to this ratio and choose funds with lower expense ratios to maximize your investment gains. Understanding and monitoring the mutual fund expense ratio is key to making informed investment decisions.