A variable interest rate loan is a type of loan where the interest rate can change over time. It is a popular option for borrowers seeking flexibility in their loan terms and hoping to take advantage of potential interest rate decreases. With a variable interest rate loan, the interest you pay on your loan can fluctuate, usually tied to an underlying benchmark like the prime rate. This means that your monthly payments could go up or down, depending on the changes in the interest rate. In this blog article, we will dive deeper into what a variable interest rate loan entails and explore its pros and cons. So, let’s get started!
What is a Variable Interest Rate Loan?
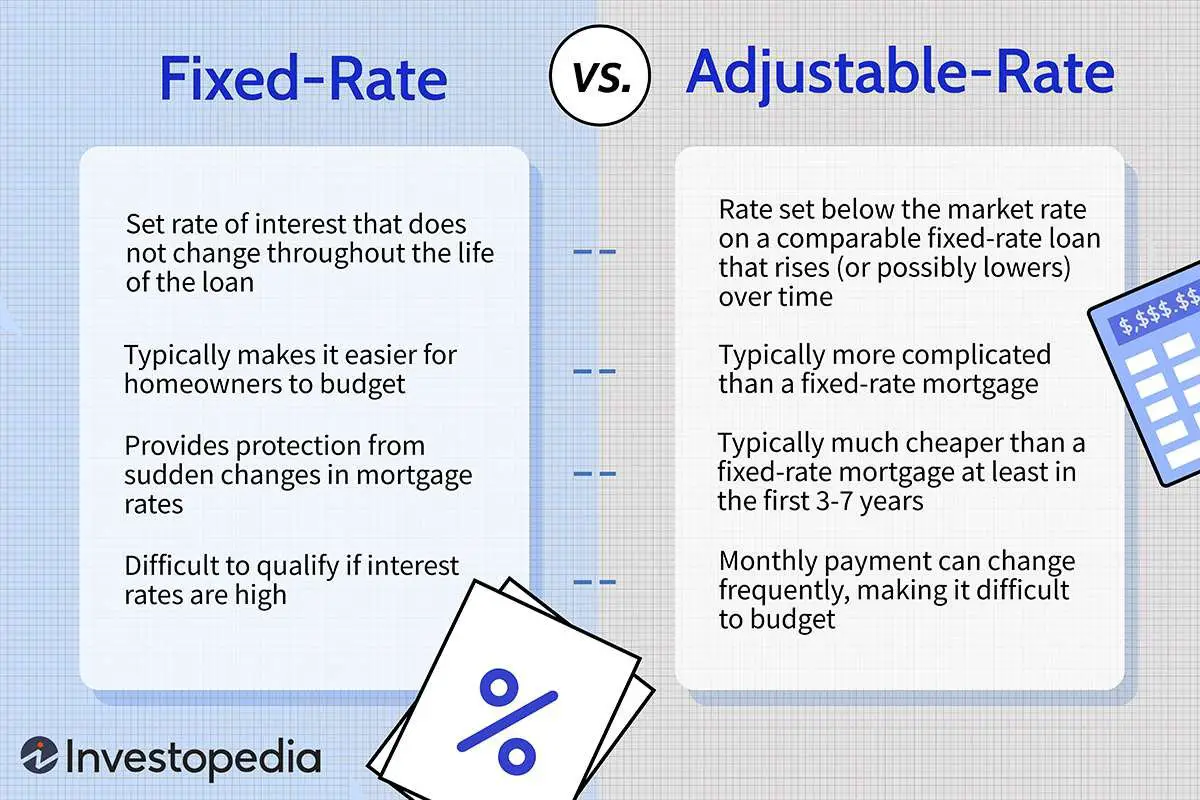
A variable interest rate loan, also known as an adjustable rate loan or floating rate loan, is a type of loan where the interest rate fluctuates over time. Unlike fixed interest rate loans, where the interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term, variable interest rate loans are subject to changes based on market conditions.
How Does a Variable Interest Rate Loan Work?
When you take out a variable interest rate loan, the interest rate is initially set at a specified percentage above a benchmark rate, such as the prime rate or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). The benchmark rate serves as a baseline, and any changes in the benchmark rate will result in an adjustment to the interest rate of the loan.
Typically, the interest rate on a variable rate loan is adjusted periodically, often annually or monthly, based on the terms of the loan agreement. The adjustment is usually calculated by adding or subtracting a predetermined margin to the current benchmark rate. The margin is determined by the lender and is based on factors such as creditworthiness, loan term, and market conditions.
Advantages of Variable Interest Rate Loans
Variable interest rate loans offer several advantages that may be appealing to borrowers:
- Lower Initial Interest Rate: Variable rate loans often start with a lower interest rate compared to fixed rate loans, making them more affordable initially.
- Flexibility: The interest rate can go down if the benchmark rate decreases, potentially saving you money on interest payments.
- Short-Term Savings: If you plan to pay off the loan early or in a shorter time frame, a variable rate loan could save you money compared to a fixed rate loan.
Disadvantages of Variable Interest Rate Loans
While variable interest rate loans have their benefits, they also come with some potential drawbacks:
- Uncertainty: The interest rate can increase, leading to higher monthly payments and potentially making the loan less affordable.
- Financial Risk: If the interest rate rises significantly, you may face challenges in managing your monthly payments, especially if your income remains constant.
- Budgeting Challenges: The fluctuating interest rate makes it harder to predict future payments, which can make budgeting more difficult.
Factors Affecting Variable Interest Rates
Several factors influence the changes in variable interest rates. Understanding these factors can give you insights into the potential fluctuations in your loan’s interest rate:
Economic Conditions
The state of the economy, including factors such as inflation, unemployment rates, and economic growth, can impact variable interest rates. In times of economic expansion, interest rates tend to rise, while during periods of economic downturn, interest rates may decrease.
Central Bank Policy
The monetary policy decisions of central banks can influence interest rates. Central banks may increase interest rates to curb inflation or stimulate the economy by reducing interest rates.
Market Demand for Credit
The demand for credit in the market can impact variable interest rates. When demand is high, lenders may increase rates to capitalize on lending opportunities. Conversely, when demand is low, lenders may lower rates to attract borrowers.
Financial Market Conditions
Financial markets, such as the bond market, stock market, and foreign exchange market, can also influence interest rates. Changes in these markets, driven by factors like investor sentiment and global economic trends, can impact variable interest rates.
Benefits and Risks of Variable Interest Rate Loans
Benefits
- Potential for Lower Interest Payments: If interest rates decrease, borrowers can benefit from reduced monthly payments and overall interest costs.
- Flexibility: Variable rate loans offer flexibility, allowing borrowers to take advantage of lower rates without refinancing their loans.
- Opportunity for Savings: Over the long term, borrowers may save money if the average interest rate stays below the rate of fixed-rate loans.
Risks
- Uncertainty: The fluctuating nature of variable interest rates introduces uncertainty into monthly payments, making it harder to plan and budget.
- Higher Payments: If interest rates rise, borrowers may experience higher monthly payments, potentially stretching their budgets.
- Financial Stress: Significant interest rate increases can lead to financial stress, especially if borrowers are not prepared for the higher payments.
Choosing Between a Variable Interest Rate Loan and a Fixed Interest Rate Loan
When deciding between a variable interest rate loan and a fixed interest rate loan, it’s essential to consider your financial situation and your risk tolerance. Here are some factors to consider:
Financial Stability
If you have a stable income and can afford potential future rate increases, a variable interest rate loan may be a viable option. However, if your income is fixed or you prefer predictability in your budget, a fixed interest rate loan might be a better choice.
Market Conditions
Consider the current market conditions and any forecasts regarding interest rate movements. If rates are historically low, a variable interest rate loan might be more attractive. Conversely, if rates are already high or expected to rise significantly, a fixed interest rate loan could provide more stability.
Loan Term
The length of your loan term can also influence your decision. If you have a short-term loan, the potential for interest rate increases may have less impact on your overall payments. For longer-term loans, the uncertainty of variable rates becomes more significant.
Tolerance for Risk
Assess your risk tolerance. If you are comfortable with potential fluctuations in your monthly payments and can adjust your budget accordingly, a variable interest rate loan might work for you. However, if the idea of uncertain payments causes stress, a fixed interest rate loan may be a better fit.
In summary, a variable interest rate loan is a type of loan where the interest rate fluctuates over time based on market conditions. While variable rate loans offer initial advantages such as lower interest rates, they also come with increased uncertainty and potential risks. When considering a variable interest rate loan, it’s crucial to carefully evaluate your financial situation, risk tolerance, and the current market conditions. Ultimately, choosing between a variable interest rate loan and a fixed interest rate loan depends on your individual circumstances and preferences.
How Do Variable Rate Mortgages Work? – Variable Rate Mortgages Explained (Adjustable Rate Mortgage)
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a variable interest rate loan?
A variable interest rate loan is a type of loan where the interest rate can change over time. Unlike a fixed interest rate loan, the interest rate on a variable rate loan is not set for the entire term of the loan and may fluctuate based on changes in market conditions or other factors.
How does a variable interest rate loan work?
In a variable interest rate loan, the interest rate is typically tied to a benchmark rate, such as the prime rate or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). The benchmark rate can change periodically, causing the interest rate on the loan to go up or down. This means that your monthly loan payments may also change during the term of the loan.
What are the advantages of a variable interest rate loan?
One advantage of a variable interest rate loan is the potential to benefit from lower interest rates. If the benchmark rate decreases, your loan’s interest rate and monthly payments may also decrease, allowing you to save money. Additionally, some variable rate loans may have lower initial interest rates compared to fixed rate loans.
What are the risks of a variable interest rate loan?
The main risk of a variable interest rate loan is the uncertainty of future interest rate changes. If the benchmark rate increases, your loan’s interest rate and monthly payments may also increase, potentially leading to higher costs. It is important to consider your financial situation and ability to handle potential payment increases before choosing a variable rate loan.
Can the interest rate on a variable rate loan go down?
Yes, the interest rate on a variable rate loan can go down. If the benchmark rate decreases, your loan’s interest rate and monthly payments may also decrease. However, it is important to note that there is no guarantee that the interest rate will go down, as it depends on market conditions and other factors.
How often can the interest rate change on a variable rate loan?
The frequency at which the interest rate can change on a variable rate loan depends on the terms of the loan agreement. It can vary from monthly to annually or even longer periods. It is important to review the loan agreement to understand how often the interest rate can change and the potential impact on your monthly payments.
Is there a limit on how much the interest rate can change?
Some variable rate loans have limits or caps on how much the interest rate can change during a specific time period. These limits are designed to protect borrowers from large and sudden interest rate increases. It is important to review the loan agreement to understand if there are any limits or caps on interest rate changes.
Can I switch from a variable rate loan to a fixed rate loan?
In some cases, it may be possible to switch from a variable rate loan to a fixed rate loan. This process is known as refinancing. Refinancing allows you to replace your current loan with a new loan that has a fixed interest rate. However, it is important to consider the costs and potential benefits of refinancing before making a decision.
Final Thoughts
A variable interest rate loan is a type of loan where the interest rate can change over time. This means that the amount of interest you pay on your loan may increase or decrease depending on the prevailing market conditions. It is important to carefully consider the risks and benefits associated with a variable interest rate loan before making a decision. Understanding how the interest rate is determined and being prepared for potential changes can help borrowers navigate the fluctuations in their loan payments. In conclusion, a variable interest rate loan offers flexibility but also carries a level of uncertainty as the interest rate can fluctuate.