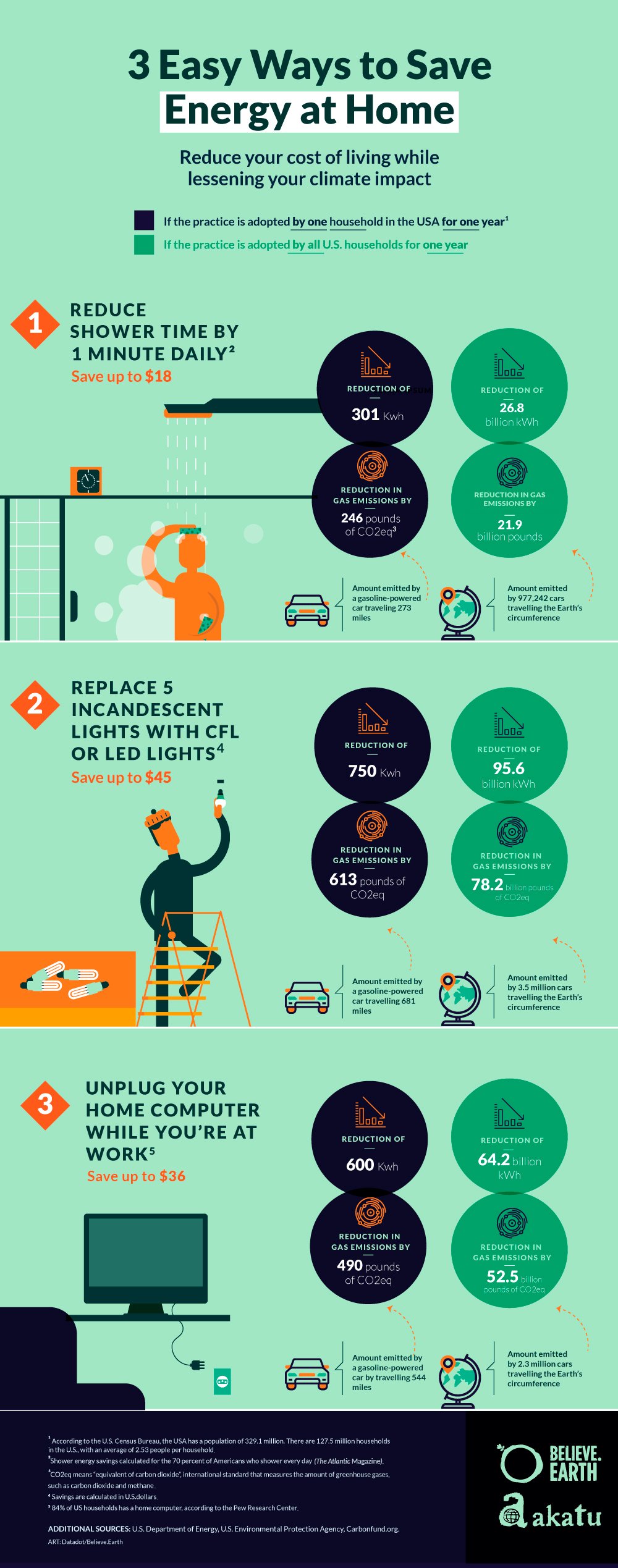
Financial leverage is a powerful tool in the world of finance, but it comes with its fair share of risks. So, what is financial leverage and its risks? Financial leverage refers to the use of borrowed money, like loans or debt, to increase the potential return on investment. In simpler terms, it means using other people’s money to amplify one’s own gains. However, while it can lead to higher profits, it also exposes individuals and organizations to greater financial vulnerabilities. In this article, we will delve into the concept of financial leverage, explore its benefits, and shed light on its potential risks. Let’s get started!
What is Financial Leverage and Its Risks?
Financial leverage is a strategy used by businesses and individuals to magnify potential returns on investment by using borrowed money, or debt, to finance their activities. It involves taking on debt to increase the amount of capital available to invest or expand operations. While financial leverage can be beneficial in certain situations, it also carries inherent risks that need to be carefully managed. In this article, we will explore the concept of financial leverage, its benefits, and the potential risks involved.
Understanding Financial Leverage
Financial leverage, also known as leverage or gearing, refers to the use of borrowed funds to amplify the potential return on investment. By leveraging their capital with borrowed money, individuals and businesses can increase their purchasing power and potentially achieve higher profits.
The concept of financial leverage can be illustrated through a simple example. Let’s say you want to buy a property worth $200,000, but you only have $50,000 in savings. Instead of using your savings, you decide to take a mortgage loan of $150,000 to finance the purchase. By doing so, you are leveraging your capital with the borrowed funds, allowing you to acquire an asset worth four times your initial investment.
The Benefits of Financial Leverage
Financial leverage offers several potential benefits for individuals and businesses:
1. Increased Return on Investment (ROI): By using borrowed money to invest or acquire assets, you have the potential to generate higher returns than if you had used only your own capital. This is because the leverage allows you to control a larger asset base with a smaller initial investment.
2. Capital efficiency: Leveraging allows individuals and businesses to spread their investment capital across multiple assets or projects, diversifying their risk and potentially maximizing returns.
3. Business growth: For businesses, financial leverage can be a way to fund expansion plans, acquire new assets, or invest in research and development. It can accelerate growth and help companies compete more effectively in the market.
4. Tax advantages: In some cases, the interest paid on borrowed funds used for investment purposes may be tax-deductible. This can help reduce the overall tax liability and increase the after-tax return on investment.
The Risks of Financial Leverage
While financial leverage can offer significant benefits, it is important to be aware of the potential risks involved. Here are some of the key risks associated with financial leverage:
1. Increased Risk of Losses:
One of the primary risks of financial leverage is the potential for higher losses. When you borrow money to invest, you are not only amplifying the potential returns but also the potential losses. If the investment performs poorly, you may not only lose your initial capital but also have to repay the borrowed funds.
2. Interest and Debt Servicing:
Using borrowed funds means taking on additional interest expense and debt servicing obligations. If the return on investment is lower than the cost of borrowing, it can lead to a negative cash flow situation and financial strain.
3. Decreased Financial Flexibility:
When you have a significant amount of debt, it can restrict your financial flexibility. Debt obligations require regular repayments, which can limit your ability to respond to unexpected expenses or take advantage of new opportunities.
4. Financial Market Volatility:
Financial markets can be volatile, and leverage can amplify the impact of market fluctuations. If the value of your investments declines, it can lead to margin calls or increased collateral requirements, putting additional pressure on your financial position.
5. Credit Risk:
When you rely heavily on borrowed funds, you expose yourself to credit risk. If your financial situation deteriorates or you are unable to meet your debt obligations, it can negatively affect your credit rating and make it difficult to secure future financing.
6. Overleveraging:
Excessive financial leverage, or overleveraging, occurs when the debt burden becomes too high to manage. This can lead to a downward spiral, where the interest and debt servicing costs outweigh the potential returns, putting you in a precarious financial position.
Managing Financial Leverage:
To mitigate the risks associated with financial leverage, it is crucial to have a well-thought-out strategy and risk management plan in place. Here are some key considerations for managing financial leverage effectively:
1. Calculate and Assess Risk Tolerance:
Before taking on any debt, carefully evaluate your risk tolerance and financial capacity to handle potential losses. Consider factors such as your income stability, savings, and investment objectives to determine an appropriate level of leverage.
2. Diversify Investments:
Spreading your investments across different asset classes and sectors can help reduce the impact of any individual investment’s poor performance. Diversification can lower the overall risk profile of your investment portfolio.
3. Keep an Eye on Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
Monitoring your debt-to-equity ratio is essential to ensure you are not overleveraged. A high debt-to-equity ratio indicates a high level of borrowing relative to your own capital, increasing the risk exposure.
4. Regularly Review and Adjust Leverage:
Regularly assess your leverage position and adjust it based on changing market conditions, economic outlook, and your own financial circumstances. Flexibility is key to adapt to evolving situations.
5. Maintain Adequate Liquidity:
Having sufficient cash reserves or access to liquid assets is crucial to meet debt obligations and handle unexpected expenses. Maintain a buffer to withstand temporary setbacks or market downturns.
6. Seek Professional Advice:
Consider consulting with a financial advisor or accountant who specializes in leverage and risk management. They can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions.
Financial leverage can be a powerful tool to amplify potential returns and accelerate growth, but it also comes with inherent risks. Understanding these risks and implementing effective risk management strategies is vital to navigate the complexities of leveraging. By carefully assessing your risk tolerance, diversifying investments, monitoring leverage ratios, and maintaining adequate liquidity, you can harness the benefits of financial leverage while mitigating potential downsides. Remember, a balanced and informed approach is key to leveraging wisely.
Financial leverage explained
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is financial leverage?
Financial leverage refers to the use of borrowed funds or debt to acquire assets, make investments, or increase the potential return on investment. It involves utilizing debt to amplify potential gains and increase the overall profitability of an investment.
What are the risks associated with financial leverage?
Financial leverage comes with its own set of risks. Some common risks include:
What is leverage risk?
Leverage risk refers to the potential for increased losses due to the use of borrowed funds. When investments decline in value, the borrowed funds still need to be repaid, which can lead to significant losses and financial instability.
How does leverage impact investment returns?
Leverage can enhance investment returns when the underlying assets perform well. However, if the investments perform poorly, leverage can magnify losses, potentially resulting in greater financial losses than if no leverage were used.
What is interest rate risk in financial leverage?
Interest rate risk is the possibility that changes in interest rates can affect borrowing costs. If interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing will increase, potentially reducing the profitability of leveraged investments.
Is financial leverage suitable for all investors?
Financial leverage is not suitable for all investors. It involves higher risk and requires a good understanding of the market, investment strategies, and potential consequences. Investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer to avoid leverage.
What are the advantages of financial leverage?
Financial leverage can offer the potential for higher returns on investment. It allows investors to access more capital than they currently possess and increase their purchasing power. It can also help in diversifying investment portfolios and spreading risks.
How can one manage the risks associated with financial leverage?
To manage the risks associated with financial leverage, it is essential to have a well-diversified investment portfolio. Investors should also have a clear understanding of the risks involved, set appropriate limits on leverage, and regularly monitor their investments to minimize potential losses. Additionally, staying updated with market trends and seeking professional advice can be beneficial.
Final Thoughts
Financial leverage is a strategy employed by businesses and investors to amplify their potential returns by using borrowed funds. However, it also comes with its fair share of risks. One of the primary risks is that leverage magnifies losses as much as it amplifies gains. Moreover, high levels of debt can lead to financial distress, especially during economic downturns. Additionally, interest expenses can become burdensome, cutting into profitability. It is crucial for individuals and organizations to understand and carefully manage the risks associated with financial leverage to avoid unintended consequences and potential financial instability.