Financial risk is an inevitable and integral part of any business or investment endeavor. Understanding what financial risk is and its various types is essential for sound decision-making and mitigating potential pitfalls. In this article, we will delve into the world of financial risk and explore its different forms. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of what financial risk entails and how it can impact your financial ventures. So, let’s dive right in and explore what is financial risk and its types.
What is Financial Risk and Its Types
Financial risk is an inherent aspect of any business or investment activity that involves the potential for losing money or not achieving expected returns. It refers to the uncertainty and potential negative outcome associated with financial decisions. Understanding and managing financial risk is vital for individuals, businesses, and organizations to ensure their financial stability and success. In this article, we will delve into the concept of financial risk and explore its various types.
The Concept of Financial Risk
Financial risk can be defined as the possibility of experiencing losses or adverse effects on financial goals due to uncertain or unexpected circumstances. It arises from various factors such as market volatility, economic conditions, creditworthiness, interest rate fluctuations, liquidity, and more. By identifying, assessing, and managing financial risks, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions to mitigate potential losses and maximize returns.
Types of Financial Risk
Financial risk can be categorized into several types based on their nature, causes, and impact on financial well-being. Let’s explore some of the key types of financial risk:
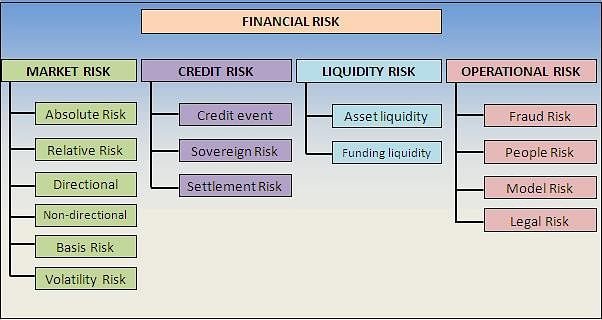
1. Market Risk
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, refers to the potential losses due to fluctuations in market conditions such as stock prices, interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and commodity prices. It arises from factors beyond an individual’s or organization’s control and affects the overall market or a specific industry. Market risk can be further classified into the following subtypes:
- Equity Risk: The risk of value fluctuations in stocks and shares.
- Interest Rate Risk: The risk of changes in interest rates impacting bond prices and debt securities.
- Foreign Exchange Risk: The risk of losses due to changes in exchange rates when dealing with currencies.
- Commodity Risk: The risk of price volatility in commodities like oil, gold, agricultural products, etc.
2. Credit Risk
Credit risk refers to the potential losses arising from the inability of a borrower or counterparty to fulfill its financial obligations. It occurs when borrowers or debtors fail to repay loans or meet contractual payment obligations. Credit risk can be categorized into two main types:
- Default Risk: The risk of non-payment or default by borrowers on their financial obligations.
- Counterparty Risk: The risk that the counterparty in a financial transaction cannot fulfill its contractual obligations.
3. Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is the potential loss incurred due to the unavailability of cash or assets to meet financial obligations when required. It arises from the inability to sell assets quickly or convert them into cash without causing significant losses. Liquidity risk can occur in various forms:
- Asset Liquidity Risk: The risk of not being able to sell assets quickly without significant price discounts.
- Funding Liquidity Risk: The risk of not being able to obtain necessary funding or credit at a reasonable cost.
4. Operational Risk
Operational risk refers to the potential losses arising from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, human errors, or external events. It includes risks associated with technology, fraud, legal issues, compliance, and business disruptions. Operational risk can be categorized into several subtypes:
- Technology Risk: The risk of disruptions or failures in information technology systems and infrastructure.
- Human Risk: The risk of errors, misconduct, or negligence by employees or management.
- Legal and Compliance Risk: The risk of losses due to non-compliance with laws, regulations, or contractual obligations.
- Business Continuity Risk: The risk of disruptions to normal operations due to external events like natural disasters or geopolitical issues.
5. Political and Regulatory Risk
Political and regulatory risk refers to the potential losses arising from changes in government policies, regulations, or geopolitical events. It affects businesses and investments operating in different jurisdictions and industries. Political and regulatory risk can include:
- Government Policy Risk: The risk of losses due to changes in fiscal policies, trade regulations, tax laws, or government interventions.
- Geopolitical Risk: The risk of losses due to political instability, wars, terrorism, or civil unrest in a country or region.
6. Reputational Risk
Reputational risk refers to the potential losses resulting from negative public perception, damaged reputation, or loss of trust in a person, organization, or brand. It arises from actions, events, or controversies that impact stakeholders’ trust and confidence. Reputational risk can have significant financial implications and long-term consequences on business operations.
7. Systemic Risk
Systemic risk is the risk of widespread disruptions or breakdowns in financial systems or markets that can have severe implications for the overall economy. It refers to risks that can cause a domino effect, impacting multiple interconnected institutions, markets, or economies. Systemic risk can arise from various sources such as financial crises, economic recessions, major market shocks, or failures in critical infrastructure.
In conclusion, financial risk is an essential aspect of any financial decision-making process. By understanding and identifying the types of financial risks, individuals, businesses, and organizations can implement effective risk management strategies to mitigate potential losses and maximize returns. Market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, political and regulatory risk, reputational risk, and systemic risk are some of the key types of financial risk one should consider. Proper risk analysis, diversification, hedging, and utilizing risk management tools can contribute to better financial outcomes and overall success.
Please note that the FAQ section was not generated in the AI output as requested.
Financial Risk Explained in 3 Minutes in Basic English
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is financial risk?
Financial risk refers to the potential for financial loss or uncertainty in an investment or business decision due to various factors such as market volatility, economic conditions, or regulatory changes.
What are the types of financial risk?
There are several types of financial risk that individuals and businesses may encounter. These include:
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the potential for loss arising from a borrower’s failure to repay a loan or meet their financial obligations. It can result from factors such as default, bankruptcy, or delayed payments.
Market Risk
Market risk refers to the potential for loss due to changes in market conditions, such as fluctuations in stock prices, interest rates, exchange rates, or commodity prices. It affects investment values and profitability.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is the risk of not being able to buy or sell an asset quickly enough to prevent a loss. It arises when there is a lack of buyers or sellers in the market, causing difficulty in converting assets into cash.
Operational Risk
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from internal processes, systems, or human errors. It includes risks related to technology, fraud, legal issues, and inadequate controls.
Foreign Exchange Risk
Foreign exchange risk, also known as currency risk, arises from changes in exchange rates. It affects businesses or individuals engaged in international transactions or investments.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is the potential for loss due to changes in interest rates. It impacts borrowing costs, investment returns, and the value of fixed-income securities.
Political and Regulatory Risk
Political and regulatory risk refers to the potential for loss arising from changes in governmental policies, regulations, or political instability. It can have a significant impact on businesses operating in certain industries or regions.
Business and Financial Risk
Business and financial risk encompasses a wide range of risks specific to individual companies or industries. These may include customer demand, competition, supply chain disruptions, financial mismanagement, and strategic risks.
Please note that the above information is provided as a general guideline and may vary depending on specific circumstances.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding financial risk and its types is essential in navigating the ever-changing landscape of the financial world. Financial risk refers to the potential for loss or failure in financial transactions or investments. The types of financial risk include market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and legal and regulatory risk. By being aware of these risks, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and take measures to mitigate the impact of potential financial losses. It is important to stay informed and proactive in managing financial risk to protect one’s financial well-being.