Curious to know what fixed and variable costs in business entail? Look no further! In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of fixed and variable costs, exploring their significance and impact on the overall financial health of a business. Understanding these types of costs is crucial for entrepreneurs and managers alike, as it helps in making informed decisions and optimizing resource allocation. So, whether you’re starting a new venture or looking to elevate your existing one, mastering the concept of fixed and variable costs is essential. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey together!
What is Fixed and Variable Cost in Business?
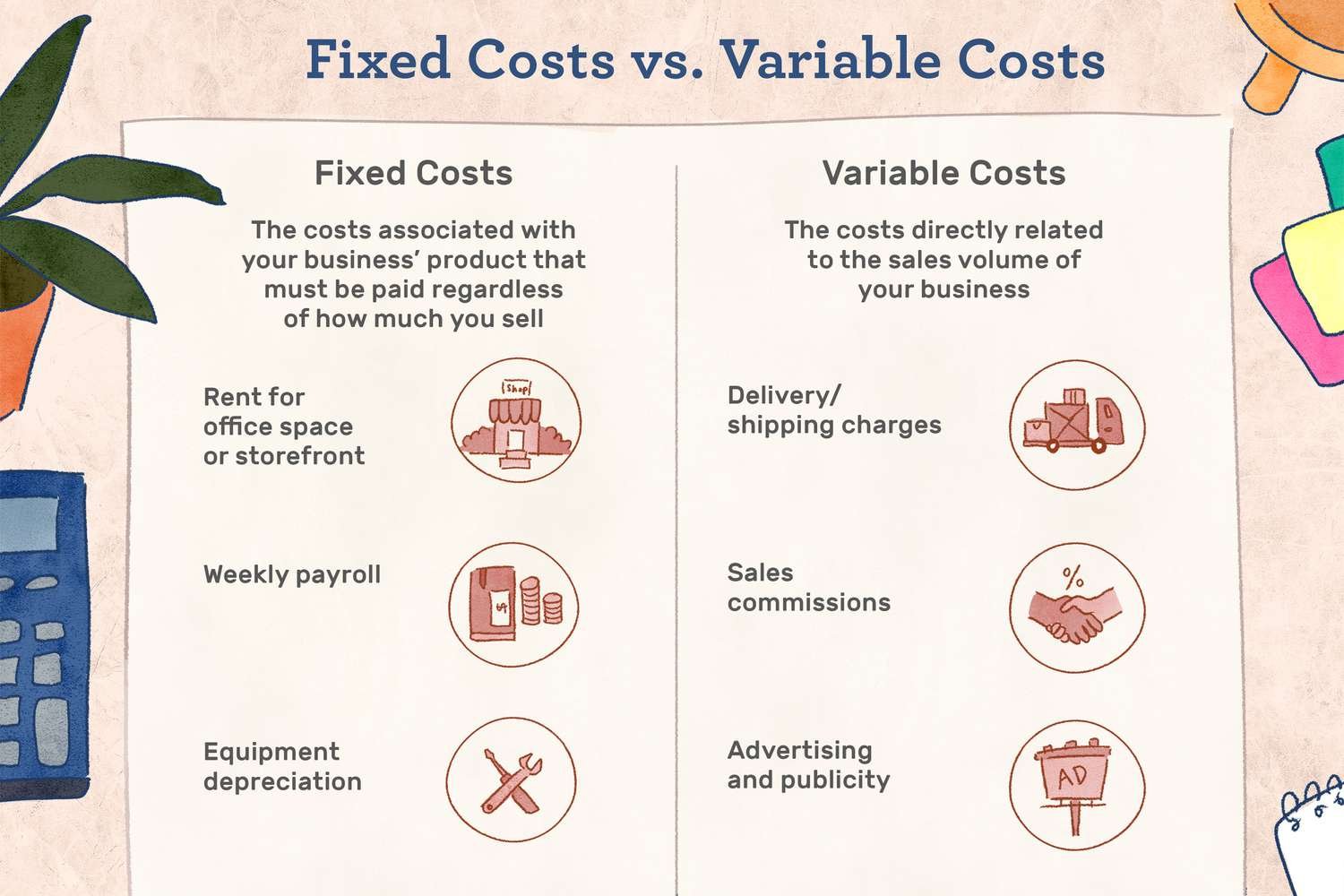
Running a successful business requires a deep understanding of the various costs involved in its operations. Two key categories of costs that every business owner must be familiar with are fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs refer to expenses that remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales, while variable costs fluctuate in direct proportion to the volume of production or sales. Recognizing and managing these costs effectively can significantly impact a company’s profitability and overall financial health. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of fixed and variable costs, explore their differences and similarities, and provide insights into how businesses can optimize their cost structures for maximum efficiency.
The Basics: Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are the expenses that businesses incur regardless of their level of production or sales activity. These costs remain constant over a given time frame, regardless of the volume of output or revenue generated. Some common examples of fixed costs include:
1. Rent and Lease Payments: The cost of renting or leasing a physical space for business operations.
2. Mortgage Payments: If the business owns a property, mortgage payments fall under fixed costs.
3. Salaries and Wages: The base salaries of permanent employees, regardless of their productivity levels.
4. Insurance Premiums: Regular payments made to cover insurance policies.
5. Depreciation: The systematic allocation of an asset’s cost over its expected useful life.
6. Property Taxes: Taxes levied on the value of business property owned.
7. Utilities: Fixed monthly expenses for services like electricity, water, and internet.
8. Office Supplies: Expenses for necessary office supplies that have consistent costs.
It is essential to note that fixed costs are not affected by changes in production or sales volume. Whether a business produces one unit or a thousand units, these costs remain the same. Fixed costs lay the foundation for a business’s operations, providing stability and essential resources.
Understanding Variable Costs
Unlike fixed costs, variable costs are directly related to the quantity of goods or services produced or sold. These expenses fluctuate as the production or sales volume changes. Variable costs typically include:
1. Cost of Raw Materials: The expenses incurred in acquiring the raw materials necessary for production.
2. Direct Labor: Wages and benefits paid to employees directly involved in production or service delivery.
3. Utilities (Usage-based): Costs that vary depending on the level of consumption, such as electricity or gas needed for manufacturing.
4. Shipping and Freight: Variable costs associated with transporting goods to customers or distributing finished products.
5. Commissions: Payments made to sales representatives or brokers based on a percentage of sales.
6. Packaging Materials: Costs related to materials used for packaging products.
7. Direct Operating Expenses: Variable expenses incurred in the direct operation of manufacturing machinery or equipment.
8. Direct Sales Costs: Marketing and advertising expenses that directly contribute to sales.
Variable costs are directly influenced by changes in production or sales volume. As the volume increases, variable costs rise accordingly, and vice versa. This dynamic nature makes it crucial for businesses to carefully manage and analyze their variable costs to maintain profitability.
The Relationship Between Fixed and Variable Costs
While fixed and variable costs differ significantly, they are both essential components of a business’s cost structure. Understanding the relationship between these two types of costs can help business owners make informed decisions. Some key points to consider include:
1. Total Cost: The total cost of production or operations is the sum of fixed costs and variable costs. By understanding these components, businesses can determine the financial impact of changes in production or sales volume.
2. Cost per Unit: Calculating the cost per unit is crucial for pricing decisions. It requires dividing the total cost by the number of units produced. Fixed costs are spread out over more units as production increases, reducing the cost per unit. Conversely, variable costs per unit remain constant.
3. Break-even Point: The break-even point occurs when total revenue equals total costs. It is the point at which a business starts generating profit. By analyzing fixed and variable costs, businesses can determine the level of sales or production required to break even.
4. Profitability: Understanding the relationship between fixed and variable costs allows businesses to analyze profitability at different levels of production or sales. By identifying the point at which revenue exceeds the sum of fixed and variable costs, businesses can optimize their operations for maximum profitability.
Strategies to Optimize Fixed and Variable Costs
Optimizing fixed and variable costs is crucial for businesses seeking to improve profitability and achieve long-term success. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Fixed Costs:
– Negotiate Leases and Contracts: Periodically review and renegotiate lease agreements to ensure competitive rates. Similarly, explore opportunities to reduce costs in services such as insurance and utilities.
– Consider Remote Work: Embrace remote work options to reduce the need for extensive office space, thereby lowering rent and utility expenses.
– Implement Energy-Efficient Measures: Invest in energy-efficient equipment and practices to reduce utility bills.
– Outsource: Consider outsourcing non-core functions to reduce the burden of fixed costs such as salaries and benefits.
2. Variable Costs:
– Optimize Production: Continuously assess production processes to identify areas for improvement, reduce wastage, and enhance efficiency.
– Supplier Negotiations: Regularly evaluate supplier contracts to ensure competitive pricing and explore bulk purchasing options.
– Streamline Inventory Management: Implement inventory management systems to avoid overstocking and minimize storage costs.
– Monitor Sales and Marketing ROI: Track the effectiveness of different marketing efforts to focus on strategies that generate the highest return on investment (ROI).
– Pricing Strategies: Analyze the relationship between price, volume, and profitability to determine the optimal pricing strategy for the business.
By proactively managing fixed and variable costs, businesses can improve their financial health, increase their competitive edge, and make informed decisions about pricing, production, and growth.
In conclusion, fixed and variable costs are fundamental concepts in business finance. Fixed costs remain constant over time, regardless of production or sales volume, while variable costs fluctuate based on the level of activity. Understanding the relationship between these costs is crucial for effective financial management, pricing decisions, and overall business profitability. By implementing strategies to optimize both fixed and variable costs, businesses can achieve financial stability, improve their competitive position, and enhance their long-term success.
Business Costs (Fixed Costs and Variable Costs) Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between fixed and variable costs in business?
Fixed costs refer to expenses that do not change regardless of the level of production or sales, such as rent, salaries, or insurance. Variable costs, on the other hand, are directly related to the level of production or sales and fluctuate accordingly, such as raw materials or utilities.
How do fixed costs affect a business?
Fixed costs represent the minimum expenses that a business needs to cover even if there is no production or sales. They contribute to the break-even point, which is the sales volume required to cover all costs. If fixed costs are high, the business will need to generate higher revenue to reach the break-even point.
What are examples of fixed costs in a business?
Some examples of fixed costs in a business include rent or lease payments, monthly salaries or wages, insurance premiums, property taxes, and loan payments.
What are the advantages of having fixed costs in a business?
Having fixed costs provides stability and predictability to a business. It allows for accurate budgeting and financial planning, as these costs remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales.
How are variable costs calculated in a business?
Variable costs are calculated by determining the cost per unit of the variable resource or input. This cost is then multiplied by the actual quantity of the variable resource used in the production process to derive the total variable cost.
Give examples of variable costs in a business.
Examples of variable costs in a business include the cost of raw materials, direct labor wages, sales commissions, shipping costs, and packaging expenses.
How do changes in sales volume impact fixed and variable costs?
Changes in sales volume affect both fixed and variable costs differently. Fixed costs remain the same, regardless of changes in sales volume. However, variable costs increase or decrease in proportion to the level of sales, as they are directly tied to production or sales activities.
What is the importance of understanding fixed and variable costs in business?
Understanding fixed and variable costs helps business owners make informed decisions regarding pricing, production levels, and overall cost management. It allows for better financial analysis and helps in determining the profitability of products or services.
Final Thoughts
In business, fixed costs and variable costs play crucial roles in determining the overall cost structure and profitability of a company. Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales, such as rent, salaries, and insurance. On the other hand, variable costs fluctuate with the level of activity, such as raw materials and direct labor. Understanding the distinction between fixed and variable costs is essential for effective financial planning, decision-making, and cost control. By analyzing and managing these costs, businesses can optimize their operations and improve their bottom line. So, what is fixed and variable cost in business? It is the key to successful financial management and sustainable growth.