Stagflation – a term that sends shivers down the spine of economists and policymakers alike. But what exactly is stagflation, and how can we prepare ourselves for it? Stagflation occurs when there is a detrimental combination of stagnant economic growth and rising inflation. It is a debilitating situation that can wreak havoc on both personal and national finances. In this article, we will delve into what stagflation entails, its potential consequences, and most importantly, how to navigate and safeguard our finances in the face of this economic challenge. So, let’s dive right into the world of stagflation and explore how to prepare for its potential impact.
What is Stagflation and How to Prepare
Understanding Stagflation
Stagflation is an economic phenomenon characterized by a combination of stagnant economic growth, high unemployment rates, and high inflation. It is a daunting scenario that can pose significant challenges for individuals, businesses, and governments. While traditional economic theory suggests that inflation and high employment rates are mutually exclusive, stagflation defies this notion by presenting a situation where both occur simultaneously.
Historically, stagflation has been a rare occurrence, with notable periods including the 1970s oil crisis and the global financial crisis of 2008. However, it is crucial to understand the concept and be prepared for potential stagflationary periods, as they can have far-reaching consequences on personal finances, investments, and overall economic stability.
Causes of Stagflation
Stagflation can arise due to various factors. Below are some common causes:
- Supply-side shocks: When there is a sudden disruption in the supply of essential goods or resources, such as a significant increase in the price of oil or raw materials, it can lead to rising production costs and inflation. This, coupled with a decrease in economic output, can result in stagflation.
- Monetary policy: In some cases, the actions of central banks and monetary authorities can inadvertently contribute to stagflation. For example, if a central bank excessively stimulates the economy through low interest rates or excessive money supply, it can lead to inflation. At the same time, if the underlying productive capacity of the economy remains stagnant, it can result in stagflation.
- Structural imbalances: When an economy faces long-term structural issues, such as high levels of national debt, rigid labor markets, or inefficient regulations, it can hinder economic growth while contributing to inflationary pressures.
The Impact of Stagflation
Stagflation can have significant repercussions across different aspects of the economy and personal finances. Understanding its potential impacts is crucial for effective preparation. Some key areas affected by stagflation include:
1. Employment and Income
During periods of stagflation, unemployment rates tend to rise as businesses struggle with reduced profitability and weak demand. This can lead to job losses, reduced income levels, and financial uncertainty for individuals and households.
2. Inflation and Purchasing Power
One of the defining characteristics of stagflation is high inflation. As prices rise, the purchasing power of consumers decreases. This means that individuals may find it more challenging to afford essential goods and services, leading to a decline in their standard of living.
3. Investments and Savings
Stagflation can have a detrimental impact on various investment instruments and savings accounts. Traditional investments like stocks and bonds may experience decreased returns, while inflation erodes the value of savings. It becomes crucial to explore alternative investment avenues and strategies to mitigate the effects of stagflation.
4. Business Operations and Profitability
For businesses, stagflation presents unique challenges. Decreased demand and increased production costs can lead to reduced profitability and financial strain. Managing costs, exploring new markets, or diversifying products and services become essential strategies to navigate through such periods.
5. Government Policies and Fiscal Measures
Governments play a crucial role in managing stagflation. They implement fiscal policies to stimulate economic growth while combating inflationary pressures. However, striking a balance is challenging, and poor policy decisions can exacerbate stagflation. Understanding government actions and their potential impact becomes vital for individuals and businesses alike.
Preparing for Stagflation
While it may not be possible to predict precisely when or if stagflation will occur, taking proactive measures to prepare for such scenarios can help minimize the impact. Here are some practical steps individuals and businesses can take:
1. Diversify Your Income Sources
Relying on a single source of income can be risky during stagflation. Explore opportunities to diversify your income by considering part-time jobs, freelancing, or starting a side business. This can provide a cushion against potential job losses or income reductions.
2. Build an Emergency Fund
Having an emergency fund is essential during uncertain times. Aim to save three to six months’ worth of living expenses in a liquid and easily accessible account. This can provide a financial safety net in case of unexpected job loss or income reduction.
3. Reduce Debt and Improve Financial Stability
Stagflation can increase the cost of borrowing, making it challenging to manage existing debts. Prioritize debt repayment to reduce financial obligations and improve overall stability. Additionally, consider refinancing high-interest debt to lower interest payments and free up cash flow.
4. Explore Alternative Investments
During stagflation, traditional investments may underperform or be more volatile. Consider diversifying your investment portfolio with assets that have historically shown resilience during inflationary periods. These may include commodities, real estate investment trusts (REITs), or inflation-protected securities.
5. Stay Informed and Seek Professional Advice
Keep an eye on economic indicators and stay informed about market trends. This will help you make educated decisions regarding your finances and investments. Seek advice from financial professionals who specialize in navigating challenging economic conditions to ensure you are well-prepared.
6. Adapt Your Business Strategy
If you are a business owner, be prepared to adapt your business strategy to the changing economic landscape. This may involve exploring new markets, diversifying your product or service offerings, or implementing cost-saving measures to maintain profitability.
7. Monitor Government Policies and Regulations
Stay updated on government policies and fiscal measures that are being implemented to address stagflation. Understand how these policies may impact your personal finances or business operations, and adjust your strategies accordingly.
Stagflation presents unique challenges that can disrupt personal finances, investments, and overall economic stability. While it is impossible to predict when or if stagflation will occur, understanding its causes, impacts, and preparation strategies can help individuals and businesses navigate through such periods with resilience. By diversifying income sources, building emergency funds, reducing debt, exploring alternative investments, staying informed, seeking professional advice, and adapting business strategies, one can be better prepared to weather the storm of stagflation.
What is Stagflation And Should The US Prepare For It ???? | Stagflation Explained | Stagflation Risk
| Stagflation Explained | Stagflation Risk
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is stagflation and how does it affect the economy?
Stagflation refers to a situation where an economy experiences a combination of stagnant economic growth, high unemployment rates, and high inflation. It is a challenging economic condition as it contradicts the typical relationship between inflation and unemployment. Stagflation can harm businesses, decrease consumer purchasing power, and lead to decreased productivity.
How can individuals prepare for stagflation?
Individuals can take several steps to prepare for stagflation:
1. How can one protect their savings during stagflation?
During stagflation, the value of money can decrease due to inflation. To protect savings, individuals can consider investing in assets that act as a hedge against inflation, such as real estate, commodities, or precious metals.
2. What steps can individuals take to manage their expenses during stagflation?
During stagflation, it is important to prioritize expenses and cut back on non-essential items. Creating a budget, reducing discretionary spending, and finding ways to save on essential expenses can help individuals manage their finances effectively.
3. How can individuals diversify their income sources during stagflation?
Diversifying income sources can provide stability during stagflation. Generating additional income through part-time jobs, freelance work, or investing in income-generating assets can help individuals mitigate the impact of stagnant wages or job loss.
4. Are there any investment strategies that can be beneficial during stagflation?
During stagflation, investors can consider diversifying their portfolio by investing in assets that tend to perform well in such conditions. These may include commodities, inflation-protected securities, dividend-paying stocks, or real estate investment trusts (REITs).
5. How can businesses adapt to stagflation?
Businesses can take various steps to adapt to stagflation, such as adjusting pricing strategies to account for increased costs, reducing unnecessary expenses, improving productivity and efficiency, and exploring new markets or product lines that are less impacted by stagflation.
6. Is it advisable to take on debt during stagflation?
During stagflation, borrowing costs can increase, making it more challenging to service debt. It is generally advisable to minimize taking on new debt during such periods. However, each individual’s situation may vary, and careful evaluation of interest rates, repayment capabilities, and potential returns should be considered.
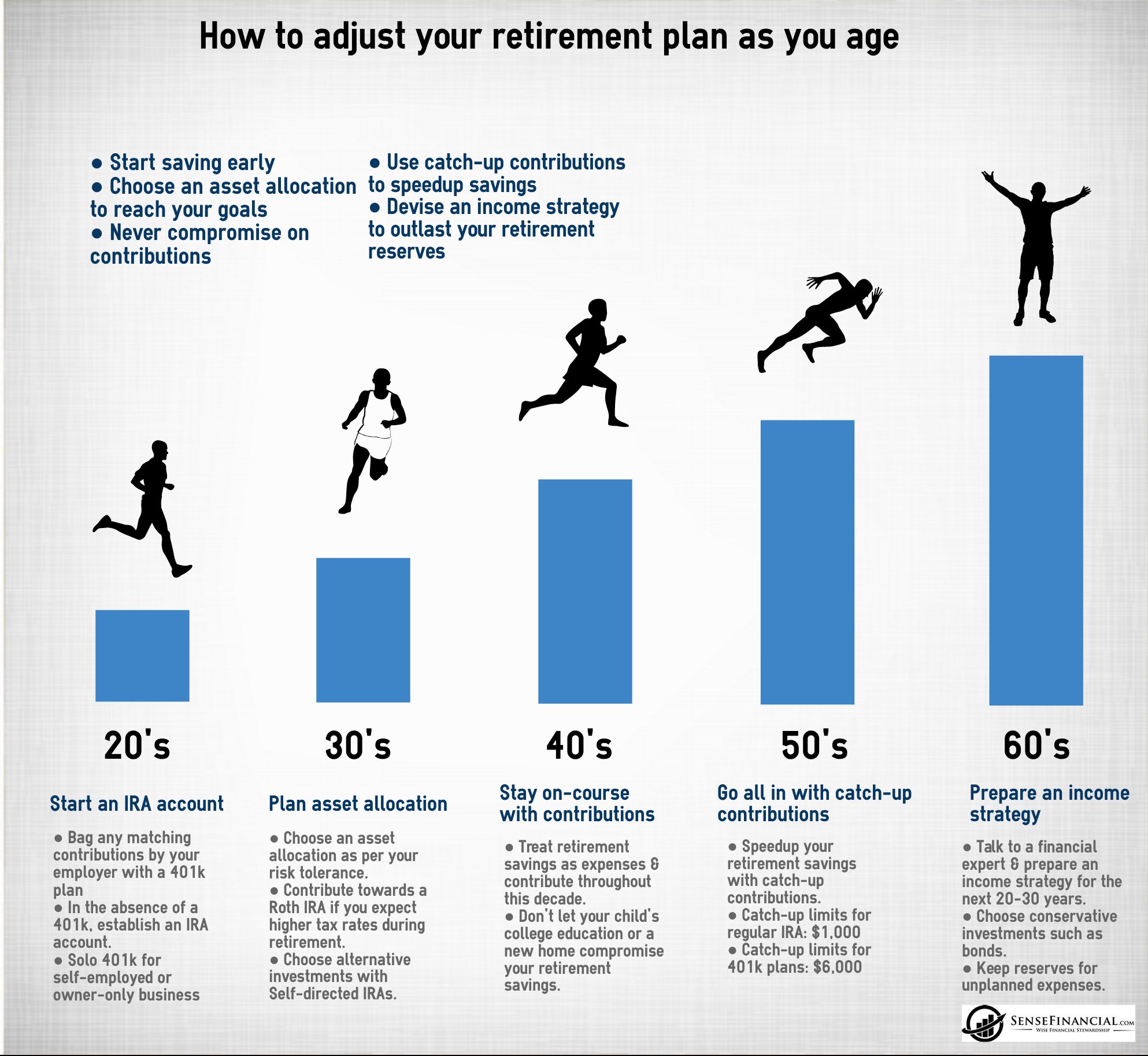
7. How can individuals protect their retirement savings during stagflation?
To protect retirement savings during stagflation, individuals can consider diversifying their investments by holding a mix of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and precious metals. Regularly reviewing and rebalancing portfolios can also help manage risk.
8. What role does government policy play in managing stagflation?
Government policies aimed at stabilizing the economy, such as fiscal stimulus measures, monetary policy adjustments, and employment initiatives, can play a significant role in managing stagflation. These policies aim to stimulate economic growth, control inflation, and reduce unemployment rates.
Final Thoughts
Stagflation, a rare economic phenomenon characterized by a combination of stagnant economic growth, high inflation, and high unemployment, poses unique challenges for individuals and businesses. To prepare for stagflation, it is crucial to diversify investments, hedge against inflation with assets like gold or real estate, reduce debt, and focus on developing essential skills that are in demand even during economic downturns. Additionally, maintaining a well-balanced budget, cultivating a strong emergency fund, and staying informed about economic trends will help individuals navigate the risks associated with stagflation and secure their financial well-being. Ultimately, understanding what stagflation is and taking proactive measures to prepare will be key in weathering its impact on the economy and personal finances.