Curious about social impact bonds? Wondering what they are and how they work? Look no further! In this article, we’ll unravel the intricacies of social impact bonds and shed light on what you need to know. Social impact bonds, or SIBs, are an innovative financial tool that aim to address social challenges. They bring together governments, investors, and service providers to tackle issues such as homelessness, education, and healthcare. So, let’s dive in and understand the fascinating world of social impact bonds. Get ready to explore their potential for driving positive change and making a difference in our society.
What to Know About Social Impact Bonds
Social impact bonds (SIBs) are innovative financial tools that aim to address social challenges and achieve positive outcomes. Also known as pay-for-success contracts, SIBs involve partnerships between public and private sectors to fund and implement social programs. This article will delve into the world of social impact bonds, explaining their key features, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding Social Impact Bonds
Social impact bonds are contractual agreements designed to fund social programs through private investment. These bonds are structured in a way that shifts the financial risk from the government to private investors. The underlying principle is that if the social program successfully achieves predetermined outcomes, the government repays the investors with a return on their initial investment. However, if the program does not achieve the desired outcomes, investors may lose their investment capital.
1. The Players Involved
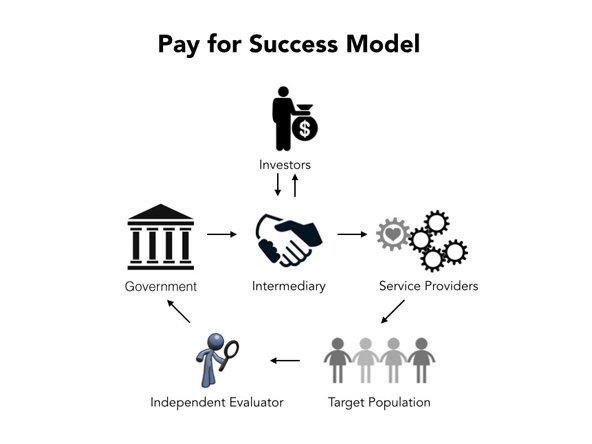
To fully grasp the concept of social impact bonds, it is essential to understand the key players involved:
- Government: The government initiates the social impact bond and identifies the social issue that needs to be addressed.
- Intermediary: The intermediary, typically a nonprofit organization, facilitates the collaboration between the government, service providers, and investors.
- Service Providers: These organizations deliver the social programs and interventions, helping to address the targeted social issue.
- Investors: Private investors provide the upfront capital needed to fund the social program. Their potential return is based on the program’s success in achieving outcomes.
- Evaluators: Independent evaluators assess the program’s performance and determine if the agreed-upon outcomes have been achieved.
2. How Social Impact Bonds Work
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how social impact bonds function:
- Identification of Social Issue: The government identifies a pressing social issue that requires intervention, such as reducing homelessness or improving educational outcomes.
- Outcome Metrics and Desired Results: The government, in collaboration with the intermediary, defines specific outcome metrics and sets ambitious but realistic targets.
- Investor Recruitment: The intermediary seeks private investors who are willing to provide the necessary funds to launch the social program.
- Contract Negotiation: Once the investors are identified, the government and the intermediary negotiate the terms of the contract, including the outcomes, payment terms, and duration.
- Program Implementation: Service providers deliver the social program, utilizing evidence-based interventions to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Evaluation: Independent evaluators assess the program’s performance, measuring the extent to which the predetermined outcomes have been achieved.
- Outcome Payments: If the program successfully achieves the agreed-upon outcomes, the government repays the investors with interest using a portion of the savings generated from the improved social outcomes.
- Government Savings: Successful social programs often result in cost savings for the government due to reduced expenses in areas such as healthcare, incarceration, or social services.
- Scaling or Termination: Depending on the program’s success, it can be scaled up to reach more beneficiaries or terminated if outcomes are not met.
The Benefits of Social Impact Bonds
Social impact bonds offer several advantages that make them an appealing financing mechanism for tackling social challenges:
1. Innovative Approach to Funding
- Social impact bonds provide an innovative way of funding social programs, attracting private investors who are motivated by financial returns as well as positive social impact.
- They leverage private sector expertise and resources, injecting additional capital into social programs that may otherwise face limited funding from traditional government sources.
2. Outcome-Focused Model
- By focusing on achieving specific outcomes, social impact bonds promote a results-oriented approach. This ensures that resources are allocated to programs that have a measurable impact on the lives of individuals and communities.
- The emphasis on outcomes encourages greater accountability and drives service providers to adopt evidence-based interventions that have been proven to deliver results.
3. Risk Sharing
- One of the key features of social impact bonds is the transfer of financial risk from the government to private investors. This incentivizes investors to support innovative and unproven social programs that may carry inherent risks.
- If the program fails to achieve the desired outcomes, the government avoids the financial burden, as investors bear the losses.
4. Cost Savings for Government
- Successful social programs funded through social impact bonds can generate cost savings for the government.
- For example, a program that effectively reduces recidivism rates among ex-offenders can lead to significant savings in incarceration costs.
- These savings can be reinvested in other social programs or used to repay investors, creating a sustainable cycle of funding.
The Limitations of Social Impact Bonds
While social impact bonds offer an innovative approach to financing social programs, they are not without limitations. It is important to consider these factors when evaluating the suitability of a social impact bond:
1. Complexity and High Transaction Costs
- The process of designing, implementing, and evaluating social impact bonds can be complex and time-consuming.
- There are significant transaction costs associated with the development of contracts, negotiations between stakeholders, and the ongoing monitoring and evaluation of programs.
2. Limited Applicability
- Social impact bonds may not be suitable for all social issues or programs.
- Programs that are difficult to measure in terms of outcomes or have a long payback period may not attract sufficient investor interest.
3. Potential for Gaming the System
- There is a risk that service providers may prioritize activities that maximize the likelihood of achieving outcomes, even if they do not necessarily address the root causes of the social issue.
- Measuring outcomes can be subjective, and there is a possibility of manipulating data to present a more favorable picture of program performance.
4. Limited Evidence Base
- As social impact bonds are a relatively new financing mechanism, there is limited robust evidence regarding their long-term impact and effectiveness.
- Further research and evaluation are necessary to determine the success of social impact bonds in achieving sustainable social outcomes.
Social impact bonds have emerged as a promising tool for addressing complex social issues while leveraging the resources and expertise of both the public and private sectors. By aligning financial incentives with positive social outcomes, social impact bonds offer a new approach to funding social programs. While they have their limitations, social impact bonds have the potential to drive innovation, accountability, and improved outcomes in the social sector. It is crucial to continue monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of social impact bonds to ensure their long-term success in creating positive social change.
Social Impact Bonds Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are social impact bonds?
Social impact bonds, also known as pay-for-success contracts, are financial agreements that involve private investors funding social programs. The investors are repaid by the government or other funding organizations if the program achieves predefined social outcomes.
How do social impact bonds work?
Social impact bonds typically follow a four-step process. First, private investors provide upfront capital to a service provider to implement a social program. Second, independent evaluators measure the outcomes of the program. Third, if the program achieves the desired outcomes, the government repays the investors, often with a return. Lastly, the government and society benefit from improved social outcomes.
What are the benefits of social impact bonds?
Social impact bonds offer several advantages. They allow governments and organizations to access additional funding from private investors to implement social programs. They also incentivize outcomes and performance-based contracting, ensuring that funding is directed towards initiatives that effectively address social challenges.
What are the potential risks associated with social impact bonds?
While social impact bonds have the potential to yield positive results, they also come with risks. One risk is the complexity of designing and implementing the contracts. Additionally, if the outcomes are not achieved, the investors may not receive repayment, leading to financial losses. Furthermore, the focus on specific outcomes may result in neglecting other important aspects of the social issue being addressed.
What types of social programs can be funded through social impact bonds?
Social impact bonds can be used to fund a wide range of social programs. These can include initiatives aimed at reducing homelessness, improving educational outcomes, reducing recidivism rates, and addressing issues related to mental health, substance abuse, and workforce development.
How are the outcomes of social impact bond programs measured?
To ensure accountability and effectiveness, independent evaluators measure the outcomes of social impact bond programs. These evaluators collect and analyze data related to the defined social outcomes to determine if the program has achieved the desired impact. The evaluation process typically involves a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods.
Are social impact bonds widely used?
While social impact bonds have gained attention in recent years, they are still relatively new and not yet widely used. The implementation of social impact bonds varies across different countries and regions. However, their potential for addressing social challenges has attracted interest and ongoing experimentation in various sectors.
Who can invest in social impact bonds?
Social impact bonds provide an opportunity for private investors to align their investment goals with social impact objectives. These investors can include individuals, philanthropic organizations, impact investment funds, and institutional investors such as pension funds and insurance companies. The eligibility criteria for investing in social impact bonds may vary depending on the specific bond and jurisdiction.
Final Thoughts
Social impact bonds (SIBs) are an innovative financial tool that aims to address social issues while generating returns for investors. These bonds are outcome-based, meaning that investors receive a financial return if certain predefined social outcomes are achieved. SIBs have gained traction globally as a means to finance and scale social interventions. They involve collaboration between governments, investors, and service providers, incentivizing efficient and effective delivery of social programs. By aligning the interests of different stakeholders, SIBs have the potential to drive positive social change. As social impact investing continues to gain momentum, understanding how SIBs work and their potential benefits is crucial for those interested in creating meaningful impact. So, what to know about social impact bonds?